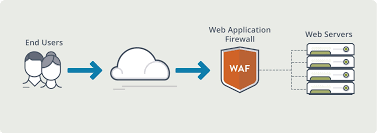
1. What is meany by WAF?
A firewall that monitors, filters, and stops HTTP traffic going to and from a website or web application is known as a WAF web application firewall. Network-based, host-based, or cloud-based WAFs are all possible. It is frequently used in front of one or more websites or apps and delivered using a reverse proxy. The WAF inspects each packet and employs a rule base to evaluate Layer 7 web application logic and filter out potentially dangerous traffic that might assist web attacks. It can run as a network appliance, server plugin, or cloud service.
Web application firewalls are a prominent security measure used by organizations to protect web systems against zero-day exploits, malware infections, impersonation, and other known and unknown vulnerabilities and threats.
A WAF in security can identify and prevent some of the most critical web application security problems through customized inspections, which standard network firewalls and other intrusion detection systems (IDSes) and intrusion prevention systems (IPSes) may not be able to perform. WAFs are particularly beneficial to businesses that offer products or services through the internet, such as e-commerce shopping, online banking, and other transactions between consumers or business partners.
2. How it works?
Software, appliances, or services can all be part of a WAF SaaS. It examines HTTP requests and adopts a set of guidelines to determine what parts of the interaction are legitimate and which are malicious.
GET and POST requests are the major components of HTTP dialogues that a WAF examines. POST requests are used to submit data to a server to modify its state, whereas GET requests are used to get data from the server. A WAF can analyses and filter the content of these HTTP requests using one of three methods:
1. Whitelisting
2. Blacklisting
3. Hybrid Security
Whitelisting
By default, the WAF rejects all requests and only accepts those that are known to be trustworthy. An inventory of known-safe IP addresses is provided. Whitelisting uses fewer resources than blacklisting. The disadvantage of whitelisting is that it may inadvertently block legitimate traffic. It can be effective and cast a wide net, however it also has the potential to be inaccurate.
Blacklisting
Blacklisting utilizes predefined signatures to restrict malicious online traffic and help to protect risk factors of websites or web applications. It is a collection of rules that may be used to detect malicious packets. Blacklisting is ideal for public websites and web apps since they receive a lot of traffic from unknown IP addresses that aren’t recognized as malicious or benign. Blacklisting has a drawback that it uses more resources and requires more data to filter packets based on specific criteria as opposed to just using trusted IP addresses by default.
Hybrid Security
A security model that combines blacklisting and whitelisting features is known as a hybrid security model.
A WAF in networking analyses HTTP interactions and lowers or, ideally, removes malicious activity or communications before it reaches a server for processing, regardless of the security framework it uses. Most WAFs require that their rules be updated often in order to address emerging vulnerabilities. However, some WAFs can now update automatically as a result of the latest advances in machine learning.
3. Why is WAF important in Cyber Security?
WAFs have become crucial for a growing number of organizations that provide products or services online, such as mobile app developers, social media providers, and digital banking. A WAF may help you in protecting sensitive data, such as client details and credit card information, and preventing data theft.
Most organizations keep much of their sensitive data in a backend database that can be accessed via web apps. Mobile applications and IoT devices are rapidly being used by organizations to facilitate business interactions, with many online transactions taking place at the application layer. Attackers frequently target web applications in order to get access to this data.
Using a WAF may help you in meeting compliance standards such as PCI DSS (the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), which applies to any organization that handles cardholder data and mandates the implementation of a firewall. As a result, a WAF is an integral component of every organization’s security model.
WAF is important, however, it is advised that it be combined with additional security measures like intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and traditional firewalls to establish a defense-in-depth security model.
4. Types of Web Application Firewalls
The three most observed types of web application firewalls are as follows:
Network-based WAF
Network based WAF is often hardware-based and deployed locally to reduce latency. However, this is the most expensive form of WAF and requires physical equipment storage and maintenance.
Host-based WAF
Host-based WAF can be completely integrated into an application’s software. This approach is less expensive and more configurable than network-based WAFs, though it requires major local server resources, is complicated to build, and can be costly to maintain. The machine that runs a host-based WAF frequently must be hardened and customized, which takes time and money.
To administer these WAFs, extra personnel may be needed, such as developers, system analysts, and DevOps or DevSecOps.
Cloud-based WAF
Cloud-based WAF is an economical, easy-to-implement solution that requires no upfront investment, with customers paying a monthly or annual security-as-a-service subscription. A cloud-based WAF may be regularly updated at no additional costs and with no user effort. However, because you rely on a third party to operate your WAF, it is critical that cloud-based WAFs provide appropriate customization choices to fit your organization’s business standards. CEH course will help you get the ultimate CEH v12 course with great mentors.
5. WAF Features and Capabilities in Cyber Security?
Web Application Firewalls are generally designed to have the following features and capabilities:
Application Profiling
Application involves looking into the structure of an application, including the most prevalent queries, URLs, values, and data types allowed. This enables the WAF to identify and reject potentially malicious requests.
Analysis of Traffic Patterns Using Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence systems enable traffic pattern behavioural analysis, employing behavioural baselines for various forms of traffic to discover abnormalities that suggest an attack. This enables you to detect attacks that do not follow well-known malicious patterns.
Monitoring and Logging
The majority of WAFs include comprehensive monitoring and logging features, which are essential in determining the nature of possible security assaults. Like AWS CloudWatch Alarms, AWS CloudTrail logs, and AWS WAF web access control list traffic tracking, Amazon Web Services provides a variety of monitoring and reporting options for its WAF resources.
Attack Signature Repositories
Attack signatures are patterns of malicious communication, such as request types, unusual server answers, and known malicious IP addresses. Earlier WAFs relied heavily on attack pattern databases, which were less efficient against fresh or undiscovered attacks.
Improved Compliance
One of the most popular drives for organizations to adopt security services such as the Web Application Firewall (WAF) is to comply with industry or government security regulations. A WAF is required by Section 6.6 of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) to secure apps that process credit card data.
If an organization is unable to directly secure application code, WAFs have been implemented. This might happen with legacy applications whether the source code is unavailable or knowledge of how the application operates has left the organization.
A WAF is an application security solution that can offer the necessary protection as the secure software development life cycle (SDLC) cannot resolve such an issue.
CDNs, or Content Delivery Networks
If you utilize a content delivery network (CDN) service for a domain name that is vulnerable to online attacks, it is advisable that you also use a Web Application Firewall (WAF) service to secure your web services.
The performance of the website is improved when combined with a Content Delivery Network (CDN), without compromising security. The website loads quicker because less computing resources are needed to process user requests because content is cached and served from the nearby data centre rather than the web server every time.
Correlational engines
These examine incoming traffic and triage it using known threat signatures, application profiling, AI analysis, and custom rules to determine if it should be banned.
Customization
Customization means the security rules that apply to application traffic can be defined by operators. This enables organizations to adapt WAF behaviour to their own requirements while avoiding the blockage of legitimate traffic.