Endpoint Management And Security : Key To Handling And Securing Future IT Operations
Endpoint management and security is not one of the top areas of discussion regarding IT security, and this doesn’t come as a surprise.
For the better part of the last decade, most enterprise endpoints were safely barricaded within the enterprise network that, in turn, was secured with firewalls, routers, and proxy servers.
When the global labor force began working from home, endpoint management and security started to matter.
We witnessed IT admins grappling with securing and updating enterprise endpoints to transition to a remote work environment.
Organizations of all sizes soon determined they needed to shift from how IT management and security were previously perceived.
They realized that security should ideally be enforced from the most minor units in their networks—the endpoints.
Owing to the work culture adopted during the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations have started following a hybrid working style in many parts of the world.
The labor force also seems to reflect the same sentiments as revealed in the USA Today-Harris Poll survey that found that 40% of Americans preferred to work from home full-time, compared with 35% who sought a home-office hybrid.
These numbers portray a trend and preference for flexible and hybrid work environments.
Having become comfortable with the rhythm of remote work, the labor force now expects the same flexibility and the ability to work from anywhere, on any device, at any time, and will in the future to come.
Cisco conducted a global survey across 21 markets in America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Japan, and China, surveying over 3,000 IT decision-makers from small businesses to large enterprises.
The survey results in point to similar trends irrespective of the size of the organization.
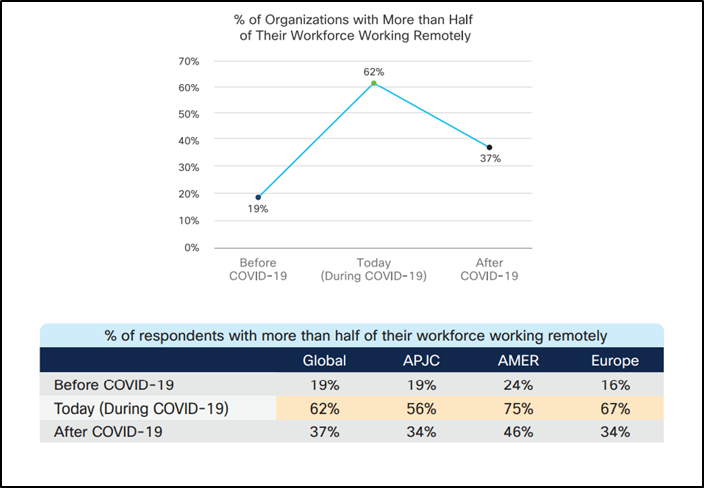
Managing devices and enforcing cybersecurity in a hybrid work environment comes with its share of reassessment of existing cybersecurity measures and revamping the security posture to include all user devices.
Analyzing the challenges faced in the transition to remote work and how quickly they can be overcome will shed light on aspects to consider while designing a robust security system to efficiently handle a hybrid work environment.
This looks like the trend the world is marching towards.
Endpoint Management Solutions Challenges 2023
- Significant increase in the number of cyber threats
- Increasing difficulty in onboarding bring your device (BYOD)/personal devices.
- Increase in patching complexities
- Irregular work hours
- The steep increase in help desk tickets
- Increased installation of remote collaborative tools
- Focusing on endpoint management and security for enhancing protection in hybrid work environments
- Coping with insider attacks
- E-mail and browser security
- Security education and culture among the employees
Significant increase in the number of cyber threats:
With users accessing the organization’s resources remotely or in the cloud, threat actors quickly exploited the security gaps induced by this sudden transition. A near-immediate result was the jump in cyber threats and security alerts in most regions worldwide.

Increasing difficulty in onboarding bring your device (BYOD)/personal devices:
ManageEngine polled IT and infosec professionals to study the impact of COVID-19 on IT work.
The results revealed that about 15% of the organizations had an acute shortage of corporate laptops prompting them to allow their labor force to use personal devices for work.
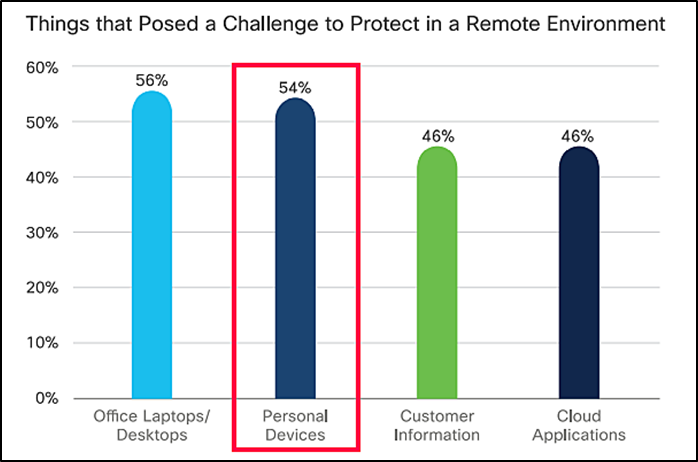
Cisco also confirms this finding by stating that 54% of the organizations found protecting personal devices the biggest challenge for their IT security team.
Increase in patching complexities:
With remote work, we saw organizations that hadn’t adopted a cloud-based patch management system struggling to achieve their periodic patching goals. Most now require devices to connect to VPN for patch scans and deployment.
According to ManageEngine’s polls, 73% of the organizations polled required users to connect to their corporate VPN for vulnerability and patch scans, but since most corporate VPNs were not equipped to handle an influx of devices at once, there were significant bandwidth-related bottlenecks to patching that resulted in a drop in regular patching and update deployment.
Irregular work hours:
During the initial days of remote work, the labor pool was challenged with sticking to a traditional 9-5 workday.
This directly impacted the patch schedules as IT admins now had to allow end users to skip patch deployment tasks to prevent disruptions in their productivity.
ManageEngine’s polls show that 48% of organizations had to grant their end users the flexibility to postpone patch deployment tasks and subsequent reboots.
The steep increase in help desk tickets:
With the pandemic, IT admins started receiving average 25 help desk tickets per day, an average of a 43% increase in tickets since adopting remote work.
IT admins now spend 2.5 hours each workday sorting through and resolving issues.
Increased installation of remote collaborative tools:
To maintain business continuity and create a seamless work environment, companies worldwide embraced remote collaborative tools, like virtual meeting applications, cloud-based file storage and transfer applications, and chat applications.
IT admins, in turn, prompted a 46% increase in remote troubleshooting applications acquired to resolve IT issues efficiently.
Focusing on endpoint management and security for enhancing protection in hybrid work environments
Remote work challenges were steadily overcome by adopting countermeasures and employing tools that ensured continued protection to corporate devices no matter where they were. Companies started prioritizing cybersecurity measures more, leading to the focus shift to endpoint protection.

Selecting the right tools and policies to enable a hybrid work environment:
As the first steps to staying afloat, organizations adopted increased VPN capacity, moved to web-based or cloud solutions, implemented multi-factor authentication methods, and started focusing on endpoint protection tools.
These changes are slowly becoming long-term and they are a good place to start prepping for hybrid operations.

Responding to zero-day vulnerabilities:
Among the patching bottlenecks faced by companies during remote work, we saw many IT admins resort to temporarily blocking or blacklisting the applications, software versions, or files susceptible to the zero-day vulnerabilities on endpoints running them before patches were available.
This ensures that your device security strategies to combat zero-day vulnerabilities can be adopted as a full-time approach.

Using domain name system (DNS) and network access control (NAC):
Since most attacks target endpoint users, ensure you have a DNS as the first security line. Block suspicious domains that seem malicious.
You can also configure compliance policies under NAC and restrict or block access to internet and intranet resources if the machines don’t comply with your policies.
Boosting productivity in a hybrid environment:
With no managers around to physically oversee employees working from home, it is tough to stop minds from wandering to the gaming consoles and video streaming apps, resulting in a decline in productivity.
This can be solved largely by simply blacklisting social media and gaming applications on the end-users corporate devices.
According to the ManageEngine survey, almost 42% of companies used this method to address productivity problems and help block the spread of malware through non-business critical applications.
Coping with insider attacks:
Insider attacks are challenging to detect and prevent with antivirus protection, patching, or perimeter security.
These attacks can take down an organization from within, from corporate data theft to malware injection.
Organizations can help prevent such attacks by creating a zero-trust environment with privilege management, initially giving the workforce standard privileges and curbing access to sensitive data.
Higher-level access can be extended on an as-needed basis.
A zero-trust environment often has device control policies that detect and prevent access to new peripheral devices connected to the network and trace the files shared to and from corporate devices.
38% of the organizations, according to ManageEngine’s survey, adopted a device control policy during remote work and are planning to retain it even when they head back to offices.
E-mail and browser security:
With e-mail ranking #1 in the list of attack vectors, Email security is extremely important to have a security solution that prevents phishing attacks, ransomware, and business e-mail compromises.
It is also important to stop the end user from accessing malicious websites, and downloading add-ons and extensions that might cause harm to the network.
In accordance with this, 70% of organizations have adopted endpoint-level browser security controls to restrict access to malicious web content without proxy servers or DNS filtering.
Security education and culture among the employees:
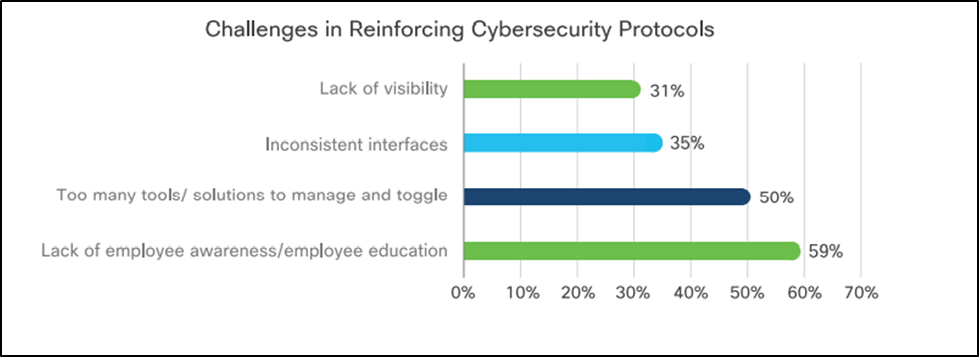
A network is only as strong as its least educated and aware user.
When asked what system administrators found a challenge when enforcing cybersecurity protocols, lack of user awareness and education received the maximum votes in the Cisco survey.
Organizations should have regular security and privacy assessment sessions and tests to update their workforce on the security norms they comply with or desire to comply with.
Endpoint management and security: Two sides of the same coin
We have covered in detail the challenges that organizations faced while moving to remote work, and how they focused on and prioritized certain aspects of security to get over these challenges and develop sustainable systems that could handle future hybrid work requirements.
We didn’t cover the number of solutions to establish an ideal endpoint management and security environment.
ManageEngine conducted polls during a recent live seminar, asking attendees how many solutions they thought needed to ensure endpoint management and security in their enterprise environments.
The majority voted for three to five solutions with around 20% saying they used separate solutions for endpoint management and security activities.
There has been a significant gap between endpoint management and security solutions for a long time.
This gap weighs heavily on an organization’s IT budget, with many shelling out ridiculous amounts of money on specialized solutions that provide limited capabilities.
Another factor to consider while investing in multiple solutions is the management overhead.
IT admins need to check if the solutions are compatible with each other carefully and if their schedules overlap.
For example, installing software and deploying patches simultaneously can consume a lot of bandwidth.
The scheduling and compatibility evaluation process is highly time-consuming and might require the organization’s IT setup to be modified to accommodate many applications. This can be both a costly and tedious process.
Any good solution will make your work easier, not more clunky and unwieldy.
IT vendors understand system admins’ frustrations to select a good option for their network, and are now working towards integrating endpoint management and security needs into a single solution.
Below are some of the requirements that a good endpoint management and security solution must meet:
- Simple and unified console: The IT admin should be able to manage and secure multiple devices from a single console.
- Automates work: It should let you automate your IT operations from deploying software and updates, asset management, and OS deployment to troubleshoot your devices.
- Manage heterogeneous roaming devices and devices on LAN, WAN, and closed networks: One solution should be able to manage devices of various flavors spread across various mediums.
- Comprehensive vulnerability scanning and remediation: It should scan your networks regularly for vulnerabilities and deploy patches to fix these vulnerabilities if detected.
- Remediate system misconfigurations: It should identify system misconfigurations, such as default settings and poor passwords, and remediate them.
- Automates OS and third-party patch management: It should make your patching routine seamless and hassle-free.
- Enforce device control: It should prevent unauthorized peripheral devices from connecting to the network.
- Establish application control and least privilege policy: The solution should be able to blacklist/whitelist applications according to enterprise requirements and enforce privilege management on an application level.
- Ensure browser security: It should be able to filter malicious websites and prevent corrupt add-ons and extensions from being downloaded.
- BitLocker management and drive encryption: The solution should prevent data loss in case of theft, and BitLocker encryption needs to be enabled in all endpoints along with drive encryption.
ManageEngine Endpoint Central with its Endpoint Security features aims to bridge the gap between endpoint management and security.
Endpoint Central packs features needed for the complete management of heterogeneous endpoints along with its security by extending vulnerability management, device control, application control, browser security, and BitLocker management.





