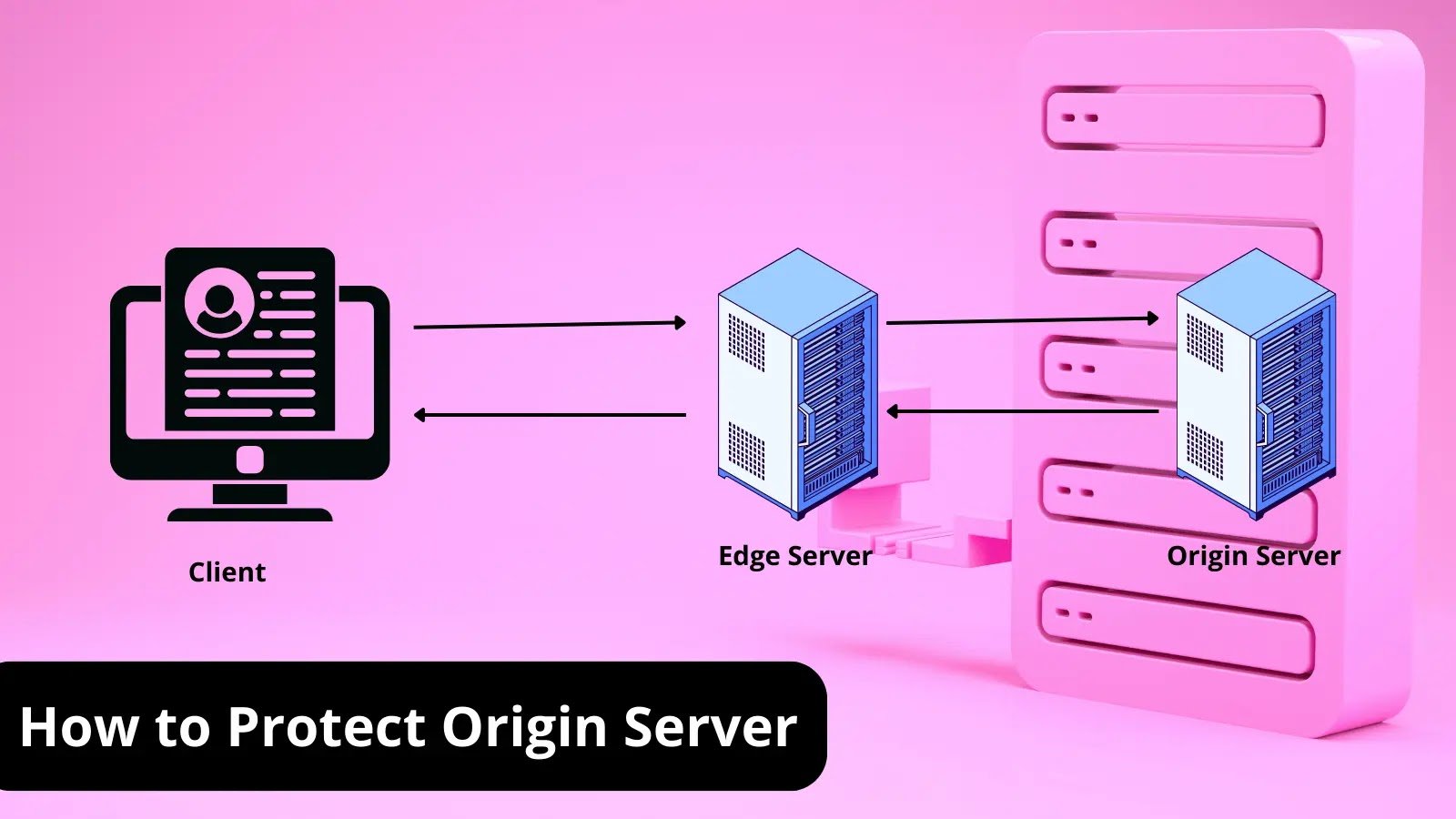
Protecting Backups with PAM
Protecting backups with Privileged Access Management (PAM) involves securing and controlling access to privileged accounts and actions that can impact backup systems and repositories. PAM solutions provide centralized management and monitoring of privileged access, ensuring that only authorized individuals can perform critical backup-related tasks.
Here are some steps to protect backups with Privileged Access Management:
- Identify privileged accounts: Identify the privileged accounts associated with backup systems and repositories. These may include administrator accounts, backup operators, or any other accounts with elevated access rights.
- Implement least privilege principle: Apply the principle of least privilege by granting privileged access only to individuals who require it for their specific roles and responsibilities. Avoid granting unnecessary or excessive privileges.
- Deploy PAM solution: Select and deploy a PAM solution that aligns with your backup infrastructure and requirements. PAM solutions typically provide features like centralized authentication, session monitoring, privilege elevation, and granular access control.
- Define access policies: Define access policies within the PAM solution to control and manage privileged access to backup systems. These policies should specify who can access backup resources, what actions they can perform, and under what circumstances.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Enforce the use of multi-factor authentication for privileged accounts accessing backup systems. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional authentication factors, such as a token, biometrics, or smart cards.
- Implement just-in-time access: Implement just-in-time (JIT) access, which provides temporary and time-limited access to privileged accounts. JIT access reduces the attack surface by minimizing the time privileged accounts are active and accessible.
- Monitor and record privileged sessions: Enable session monitoring and recording capabilities provided by the PAM solution. This allows you to track privileged activities, detect any suspicious behavior, and generate audit logs for compliance purposes.
- Automate password management: Use the password management capabilities of the PAM solution to automate password rotation, ensure strong password policies, and eliminate shared or default passwords for privileged accounts.
- Regularly review access rights: Conduct regular reviews of privileged access rights to ensure they are still required and appropriate. Remove unnecessary privileges and promptly revoke access for individuals who no longer require it.
- Train and educate users: Provide training and education to users with privileged access on security best practices, the importance of safeguarding backup systems, and the risks associated with mishandling privileged access.
Remember that PAM is just one component of a comprehensive backup security strategy. It should be complemented with other security measures such as encryption of backups, secure network communication, and physical security of backup media. Regular vulnerability assessments and security updates should also be performed to protect against emerging threats.