The cloud has become an integral part of our lives, revolutionizing the way we store and access data. But with this convenience comes a whole new set of security challenges. As cybercriminals become more sophisticated, traditional perimeter-based security measures are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive information. That’s where Zero Trust comes in. Imagine a world where every user and device is treated as a potential threat until proven otherwise. In this article, we will explore why Zero Trust is crucial for cloud security and how it can help organizations stay one step ahead of cyber attackers.
Why Zero Trust is important for Cloud Security?
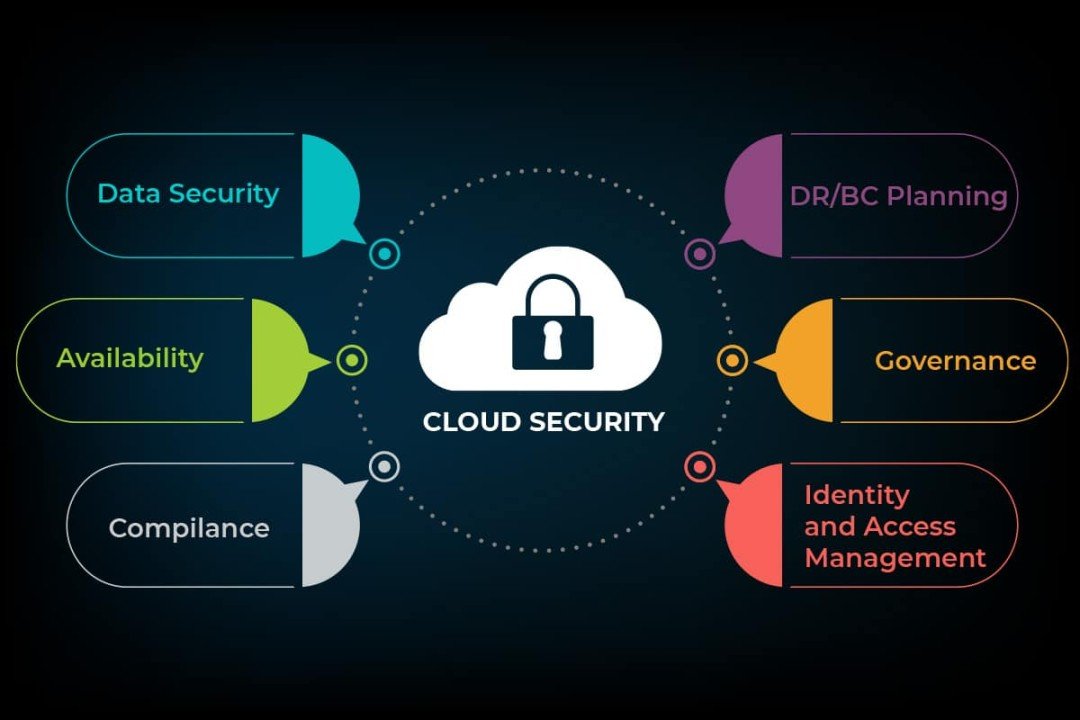
Zero Trust is important for cloud security because it provides a proactive and effective approach to securing data and systems in the cloud, particularly in an era where traditional network perimeters are becoming increasingly porous and obsolete. Here are several reasons why Zero Trust is crucial for cloud security:
- Evolving Network Boundaries: In traditional network security models, security was primarily perimeter-based, assuming that everything inside the corporate network was trusted. However, with the adoption of cloud computing and remote work, network boundaries have become increasingly fluid and dynamic. Zero Trust recognizes this shift and treats all resources and connections as potentially untrusted.
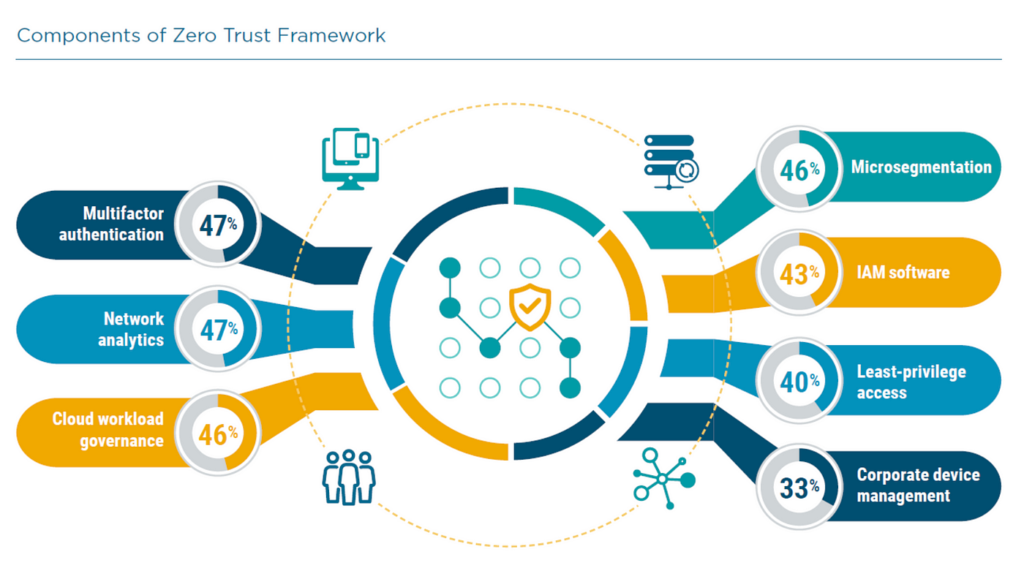
- Principle of Least Privilege: Zero Trust is built on the principle of least privilege, which means that users and systems are granted the minimum level of access they need to perform their tasks. This limits the potential damage that can occur in case of a security breach.
- Micro-Segmentation: Zero Trust often involves micro-segmentation, which divides the network into smaller, isolated segments, making it more difficult for attackers to move laterally within the network if they manage to breach one segment.
- Identity-Centric Security: Zero Trust emphasizes identity as the new perimeter. It places a strong focus on verifying the identity of users and devices before granting access to resources. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and identity and access management (IAM) solutions are integral components of Zero Trust security.
- Continuous Monitoring: Zero Trust involves continuous monitoring of network traffic, user behavior, and system activity. This enables early detection of anomalies and potential security threats.
- Cloud-Centric Approach: Cloud services and infrastructure have unique security challenges, and Zero Trust aligns well with the cloud-centric approach. It can enforce security policies consistently across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Zero Trust reduces the attack surface by implementing strict access controls and monitoring, minimizing the potential pathways for attackers to exploit.
- Enhanced Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS) require organizations to have strong security controls in place. Zero Trust helps in achieving and maintaining compliance by enhancing security.
- User-Centric and Mobile Workforce: With the rise of remote and mobile workforces, users may access corporate resources from various locations and devices. Zero Trust ensures that access is secure and context-aware, regardless of the user’s location.
- Threat Detection and Response: Zero Trust emphasizes real-time threat detection and rapid incident response. It enables security teams to quickly identify and mitigate security incidents.
Conclusion:
Zero Trust is vital for cloud security because it adapts to the changing landscape of modern IT environments. It acknowledges the reality of persistent threats, the dynamic nature of cloud computing, and the need for a more granular, identity-focused approach to security. By implementing Zero Trust principles and technologies, organizations can significantly enhance their cloud security posture and reduce the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.