Network Switches and Wireless Solutions
In today’s digital landscape, network switches and wireless solutions play a crucial role in ensuring optimal network connectivity. These devices are integral to both local area networks (LAN) and larger business networks.
Types of Network Switches
There are various types of network switches available, including managed switches, unmanaged switches, and smart switches. Managed switches offer advanced features for network management and security, while unmanaged switches provide basic connectivity without complex configuration.
Wireless Solutions
Alongside switches, wired and wireless access points are essential for establishing a robust wireless network. These network devices allow for seamless connectivity and data transmission across various devices in a network.
Power Over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology enables network cables to deliver both data and power to devices such as IP cameras and wireless access points, simplifying installation and reducing the need for additional power sources.
Switch Features and Capabilities
Modern network switches often feature Ethernet ports that support Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching, allowing for efficient routing of data packets based on MAC addresses and IP addresses. Core switches, stackable switches, and modular switches provide scalability and flexibility for network infrastructure.
Network Security and Management
Effective network security is paramount in any network infrastructure. Network administrators can manage traffic flow and prevent congestion through proper configuration of switch ports and data packet filtering.
Conclusion
Investing in the right network switches and wireless solutions is essential for optimizing your network and ensuring seamless communication across devices. Whether deploying a simple home network or a complex data center, understanding the difference between a switch and a router, as well as the various types of switches available, is critical for successful implementation.
Network Switch: Router and Wireless Networking Solutions
In the fast-evolving landscape of digital connectivity, understanding the fundamental components of networking infrastructure is vital for businesses aiming to enhance their operational efficiency. Network switches, routers, and wireless networking are critical elements that form the backbone of modern communication systems, enabling devices in a network to connect seamlessly. As companies strive to maintain robust, secure, and high-performing networks, the nuances of how switches can forward data become increasingly pertinent. This article delves into the intricacies of network switches, offering insight into their types, functionalities, and the distinctions between switches and routers.
Understanding Network Switches
Network switches are pivotal devices that facilitate communication within a local area network (LAN) by connecting various network segments, thereby enabling seamless data exchange. These devices operate at different layers of the OSI model, primarily at Layer 2 and Layer 3, to manage data packets efficiently and ensure optimal network performance through effective switch work. Network switches come in various forms, including managed and unmanaged switches, each offering distinct capabilities to suit diverse network management needs. As businesses grow, the demand for reliable and scalable network solutions becomes imperative to support increased traffic and ensure uninterrupted connectivity.
What is a Network Switch?
A network switch is a hardware device that connects multiple devices within a LAN, directing data packets to their intended destinations by utilizing MAC addresses. Unlike routers, which operate at the network layer (Layer 3) handling IP addresses, network switches primarily function at the data link layer (Layer 2). This distinction allows switches to efficiently manage traffic within a LAN, enhancing data transfer speeds and reducing congestion. By providing dedicated switch ports for each connected device, network switches ensure that data collisions are minimized, thereby optimizing network performance and reliability.
Types of Network Switches
Network switches are available in various configurations to cater to different network requirements. Common types include stackable switches, core switches, and leaf switches.
| Type of Switch | Description |
|---|---|
| Unmanaged Switches | Offer plug-and-play simplicity for basic connectivity. |
| Managed Switches | Provide advanced features such as network management, VLAN support, and enhanced security protocols. |
| Smart Switches | Offer a balance between ease of use and management capabilities. |
| Stackable and Modular Switches | Enable scalability and flexibility for larger, more complex networks. |
Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches further enhance network utility by supplying power to devices like wireless access points through ethernet cables, simplifying infrastructure deployment.
Difference Between a Switch and a Router
The difference between a switch and a router lies in their operational layers and functions within a network. While a network switch connects devices within a single network, facilitating intra-network communication, a router connects multiple networks, directing data between them. Routers operate at the network layer, managing IP addresses and routing data packets across different networks, including the Internet, while also connecting to edge switches for enhanced performance. In contrast, switches are confined to handling data within a single LAN. This fundamental distinction underscores the complementary roles of switches and routers in ensuring comprehensive network connectivity and functionality, particularly in environments utilizing both core and leaf switches.
Ethernet Switch vs Wireless Networking
What is an Ethernet Switch?
An Ethernet switch serves as a cornerstone in the architecture of a local area network, efficiently directing data packets based on source and destination to their rightful destinations. By leveraging MAC addresses, Ethernet switches manage data flow within a LAN, thereby optimizing network performance and minimizing the risk of data collisions. These switches operate predominantly at the data link layer, ensuring seamless and reliable connectivity across various network segments. With the ability to connect numerous devices through dedicated Ethernet ports, Ethernet switches are an indispensable component in both small business networks and expansive data center environments, facilitating robust and secure communication pathways.
How Wireless Networks Work
Wireless networks function by transmitting data over radio frequencies, allowing devices to connect to the network without the need for physical cables. Central to this technology are wireless access points, which act as hubs for devices to communicate wirelessly within a network. Utilizing protocols such as Wi-Fi 6 and the emerging Wi-Fi 7, wireless networks provide high-speed connectivity, even in environments densely populated with devices. Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology can also be employed to power wireless access points, simplifying installation and reducing the need for additional power sources. This flexibility is vital for businesses seeking to enhance mobility and scalability.
Comparison of Ethernet and Wireless Networks
When comparing Ethernet and wireless networks, each offers distinct advantages tailored to specific operational needs. Ethernet networks provide reliable and high-speed connectivity through direct, wired connections, ideal for environments requiring stable performance, such as data centers. Conversely, wireless networks offer unparalleled flexibility and mobility, enabling seamless connectivity for devices in dynamic and spread-out workspaces, while also complementing the functionality of core switches. However, wireless networks may face challenges related to network security and signal interference. The choice between Ethernet and wireless solutions often hinges on the specific needs for network security, speed, and the physical layout of the business environment, with some enterprises opting for a hybrid approach to balance reliability and convenience.
Advanced Switching Solutions
Introduction to 10G Switching
In the realm of cutting-edge networking, 10G switching represents a significant leap forward in data transfer capabilities, enabling businesses to handle increasingly demanding workloads with ease. This advanced technology supports high-speed network connections, facilitating enhanced performance and reliability across network segments. By utilizing 10G Ethernet switches, enterprises can achieve superior data throughput, minimizing latency and maximizing productivity. With the rise of data-intensive applications and the need for real-time processing in sectors such as finance and media, the deployment of 10G switches ensures that businesses remain competitive in a fast-paced digital environment.
Wi-Fi 6 and 7 Technologies Explained
The advent of Wi-Fi 6 and the upcoming Wi-Fi 7 technologies mark a transformative era in wireless networking, promising faster speeds, greater efficiency, and improved connectivity for an ever-expanding array of devices. Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, enhances network capacity and performance in dense environments, utilizing advanced techniques like MU-MIMO and OFDMA to optimize data packet transmission. Looking ahead, Wi-Fi 7 aims to further elevate these capabilities, offering even higher throughput and reduced latency. These innovations empower businesses to support more simultaneous users and devices, ensuring seamless and robust wireless access in diverse operational settings.
Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switches
Understanding the distinction between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches is crucial for effective network management. Layer 2 switches operate at the data link layer, focusing on media access control (MAC) address-based forwarding, which is ideal for efficient intra-network communication within a LAN. In contrast, Layer 3 switches incorporate routing capabilities, functioning at the network layer by handling IP addresses to facilitate communication between different networks. This dual functionality allows Layer 3 switches to serve as a bridge between switching and routing, offering enhanced flexibility and scalability for complex network architectures that require both high-speed local connectivity and broader network integration.
Wi-Fi Performance and Management
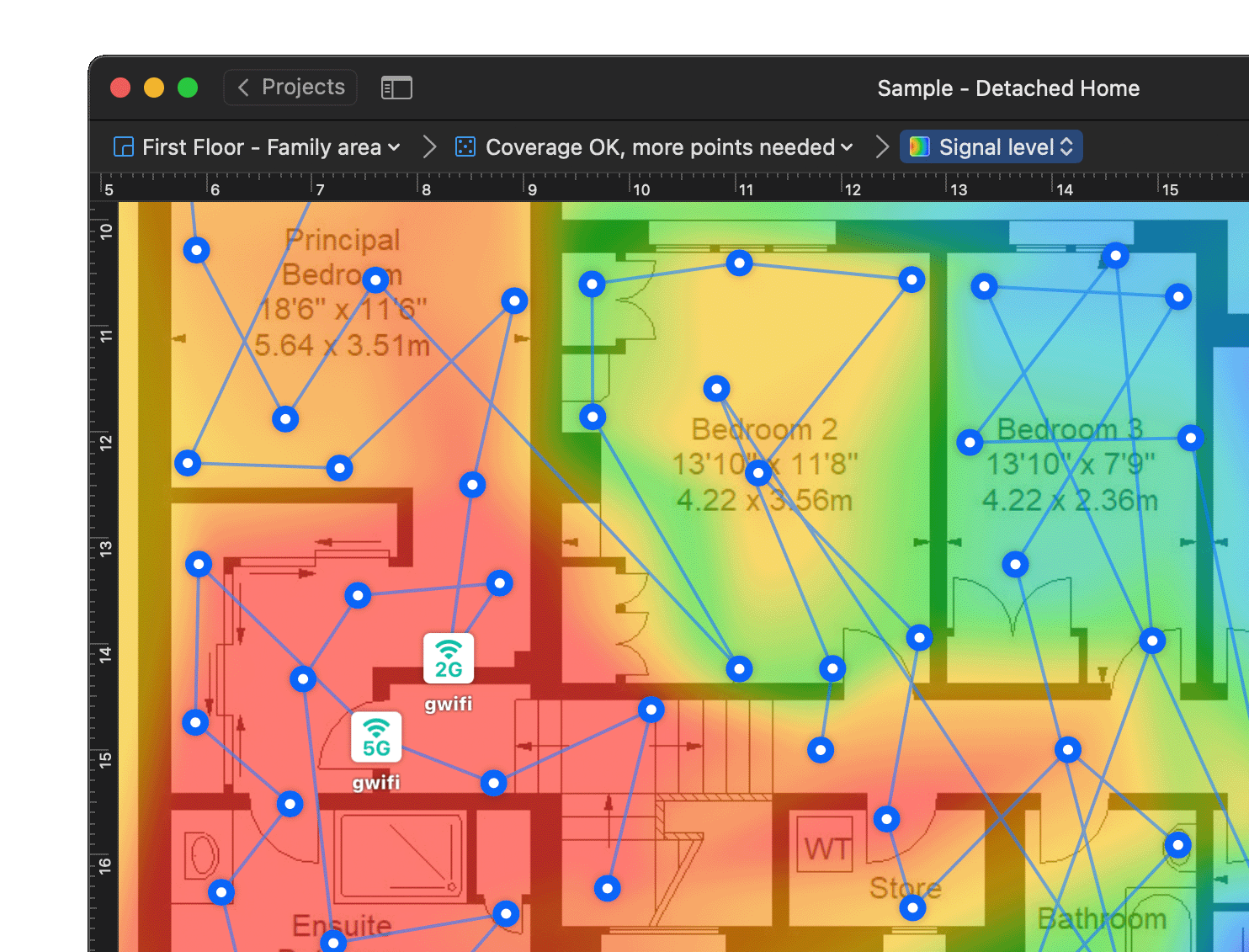
Wi-Fi Predictive Heat Map
Wi-Fi predictive heat mapping is a sophisticated tool used to visualize and optimize wireless network coverage before deployment. By simulating various parameters such as access point placement, signal strength, and potential interference, this technology enables network planners to anticipate and address connectivity issues proactively. The predictive heat map provides a detailed overview of expected Wi-Fi performance, allowing for strategic adjustments to enhance coverage and minimize dead zones. This foresight is invaluable for businesses aiming to implement reliable and efficient wireless networks that meet the demands of modern digital environments.
Wi-Fi Performance Heat Mapping Techniques
Wi-Fi performance heat mapping techniques are instrumental in diagnosing and optimizing live wireless networks. By collecting real-time data on signal strength, interference, and throughput, these techniques offer a comprehensive analysis of current network conditions. This information is crucial for identifying bottlenecks and optimizing access point configurations to improve overall network performance. By employing performance heat mapping, businesses can ensure that their wireless networks deliver consistent, high-quality connectivity, essential for supporting critical operations and maintaining user satisfaction in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Network Management Strategies
Effective network management strategies are vital for maintaining optimal performance and security across both wired and wireless infrastructures. These strategies encompass a range of practices, from regular monitoring and maintenance of network devices to implementing robust security measures against cyber threats. Leveraging advanced network management tools, such as automated configuration and centralized control systems, businesses can enhance visibility and streamline operations. Furthermore, adopting a proactive approach to network management ensures that potential issues are identified and resolved swiftly, safeguarding enterprise networks and supporting resilient, high-performance connectivity.
Vendor Comparison and Features
List of Leading Vendors
In the realm of networking infrastructure, several vendors stand out for their innovative solutions and robust product offerings. Companies such as Cisco, Juniper Networks, and HP’s Aruba lead the charge with their cutting-edge technologies in both Ethernet switch and wireless connectivity solutions. These vendors provide a range of products, from basic unmanaged switches for small businesses to advanced managed switches and PoE switches for complex enterprise environments. By leveraging their extensive expertise, these leaders in network technology continue to shape the future of data communication and the evolution of stackable switches.
Feature Table Comparison
When evaluating the features of network switches and wireless access points offered by top vendors, it is essential to consider factors such as network security, scalability, and ease of management, especially regarding how switches can forward data effectively. For instance, Cisco’s Catalyst series offers robust Layer 2 and Layer 3 capabilities with advanced network management features, while Aruba’s Instant On series emphasizes simplicity and ease of deployment.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| PoE Support | Aids in selecting the best fit for network needs |
| Maximum Throughput | Aids in selecting the best fit for network needs |
| Number of Ethernet Ports | Aids in selecting the best fit for network needs |
Evaluating Vendor Solutions
Assessing vendor solutions involves analyzing how well their products integrate into existing network infrastructures and meet specific business requirements. Factors to consider include the reliability of network connections, the flexibility of modular switches, and the ability of smart switches to adapt to evolving network demands. Additionally, vendors’ customer support and commitment to security updates play a crucial role in maintaining network integrity. By thoroughly evaluating these solutions, businesses can ensure they invest in technologies that deliver optimal performance and long-term value.
How Teamwin Can Help
Teamwin’s Role in Network Solutions
Teamwin Global Technologica Pvt Ltd plays a pivotal role in fortifying enterprise networks through its comprehensive suite of IT security solutions. With a focus on safeguarding data and intellectual property, Teamwin offers advanced technologies such as next-generation firewalls and privileged access management to secure network operations. Their expertise extends to both passive and active networking, providing clients with robust solutions that encompass everything from endpoint protection management to secure networking infrastructure, ensuring that enterprises remain resilient against evolving cybersecurity threats.
Benefits of Choosing Teamwin
Choosing Teamwin Global Technologica brings several advantages, especially for organizations across industries such as Banking, Healthcare, and Telecom. With a commitment to delivering reliable and efficient solutions, Teamwin emphasizes a custom-tailored approach to meet unique business needs, especially in the context of network switch work. Their 24/7 support and proactive monitoring ensure that IT environments are secure and operational. Clients commend Teamwin for its dedication to customer satisfaction and its ability to provide value for money, making it a trusted partner in achieving secure, scalable, and affordable IT solutions.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Teamwin Global Technologica boasts numerous success stories where their solutions have significantly enhanced clients’ network security and performance. In one instance, a major healthcare provider leveraged Teamwin’s advanced endpoint security and real-time threat detection to safeguard sensitive patient data, achieving compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Another client, a leading manufacturing firm, utilized Teamwin’s managed security services to streamline network operations, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced downtime. These case studies illustrate Teamwin’s capacity to deliver tangible results and drive business success through tailored IT solutions.
Network Switches and Wireless Solutions
In today’s interconnected world, network switches and wireless solutions play a critical role in ensuring seamless connectivity across various devices in a network. From managed switches to wired and wireless access points, the right combination of network devices can significantly enhance your business network.
Types of Network Switches
Understanding the types of network switches is essential for effective network management. There are several types of switches including:
- Unmanaged Switches: Basic switches that allow plug-and-play connectivity.
- Managed Switches: Offer advanced features for network security and management.
- Layer 2 Switches: Operate at the data link layer, forwarding data based on MAC addresses.
- Layer 3 Switches: Capable of routing data packets between different network segments.
- Stackable Switches: Allow multiple switches to be controlled as a single unit.
Wireless Solutions
Wireless networks have become increasingly popular, offering flexibility and mobility. Wireless access points (APs) enable Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing users to connect to the local area network (LAN) without physical cables. The deployment of PoE switches simplifies the installation of APs by providing power over Ethernet.
Network Performance
Optimizing your network connectivity involves understanding how different network switches work. A network switch connects devices by using switch ports to forward data packets between the source and destination devices. This process reduces network congestion and enhances overall performance.
Choosing the Right Solution
When selecting network switches and wired or wireless solutions, consider factors such as the number of ports, scalability, and the specific requirements of your data center. Incorporating Cisco products or smart switches can provide advanced features for managing your network infrastructure.
In conclusion, whether you are deploying basic switches or advanced modular switches, understanding the difference between a switch and a router, and the various types of switches available, is crucial for building a secure and efficient network.
Our Cyber Security & Secure networking Services
🔒 Why Enterprise CCTV & VMS? Enhanced Security & Compliance Centralized Monitoring & Control Real-Time Alerts & Smart Analytics Scalable Integration with Existing Infrastructure 📹 Supported [...]
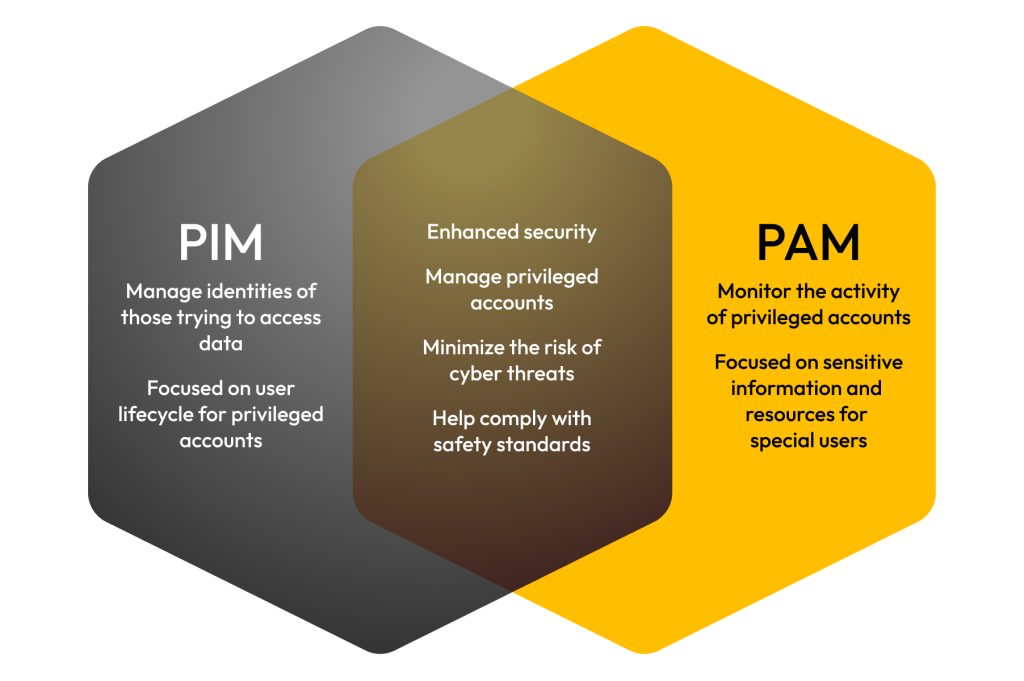
🛡️ PIM & PAM Solutions – Teamwin Global Secure, Monitor & Control Privileged Access.Protect critical assets with advanced Privileged Identity & Access Management solutions. 🔍 [...]
Accelerate innovation. Drive efficiency. Stay competitive. 🔹 Key Areas & Partners ☁️ Cloud Enablement Vendors: AWS | Azure | Google Cloud | Oracle Cloud 🤖 [...]
Articles from the latest news
Latest Tech Articles news
—–BEGIN PGP SIGNED MESSAGE—– Hash: SHA256 Multiple Vulnerabilities in Zyxel Indian – Computer Emergency Response Team (https://www.cert-in.org.in) Severity Rating: HIGH Systems Affected Zyxel devices 4G/5G [...]
—–BEGIN PGP SIGNED MESSAGE—– Hash: SHA256 Multiple Vulnerabilities in Trend Micro Apex One Indian – Computer Emergency Response Team (https://www.cert-in.org.in) Severity Rating: CRITICAL Software Affected [...]
—–BEGIN PGP SIGNED MESSAGE—– Hash: SHA256 Multiple Vulnerabilities in VMware Products Indian – Computer Emergency Response Team (https://www.cert-in.org.in) Severity Rating: HIGH Software Affected VMware Aria [...]