
Cyber Criminals Mimic Popular IT Tools.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cyber criminals have become masters of deception, adapting their tactics to exploit the very tools that organizations rely on to protect themselves. With an uncanny ability to mimic popular IT tools, these nefarious individuals are infiltrating networks, stealing sensitive data, and causing havoc without raising suspicion. From fake antivirus software that actually infects systems to counterfeit password managers that capture login credentials, the arsenal of deceptive techniques employed by cyber criminals is as vast as it is insidious. As businesses and individuals grapple with the ever-present threat of cyber attacks, understanding how these criminals emulate trusted technology becomes paramount in safeguarding our digital lives.
Cyber attackers Mimic Popular IT Tools to Deliver Malware Stealthily.
Threat actors are known to use several methods to lure victims into their websites and make them download their malicious payload, which will allow them to take full control of the system.
Malicious ad and cloaking
Threat actors continue to target certain IT programs such as remote access programs and scanners by creating ads that are displayed on popular search engines such as Google. The ad below is for the Advanced IP scanner tool and was found when performing a Google search from a US IP address.
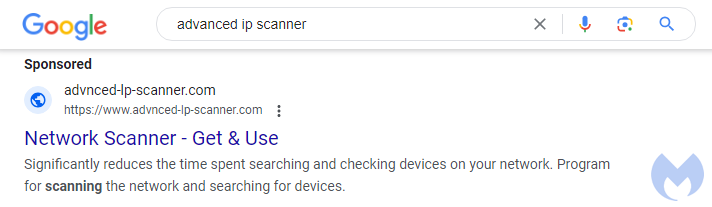
The domain name advnced-lp-scanner[.]com may look legitimate but it is not. It was registered on Jul 30 2023 and is hosted on a server in Russia at 185.11.61[.]65.
If you were to investigate this ad, you would likely open it up in a virtual machine and see what it leads to. One of the most common checks that is done by threat actors is a simple server-side IP check to determine whether you are running a VPN or proxy or have visited the site before. That means that as researchers we need to constantly find new IP addresses that look legitimate and then revisit the page again.
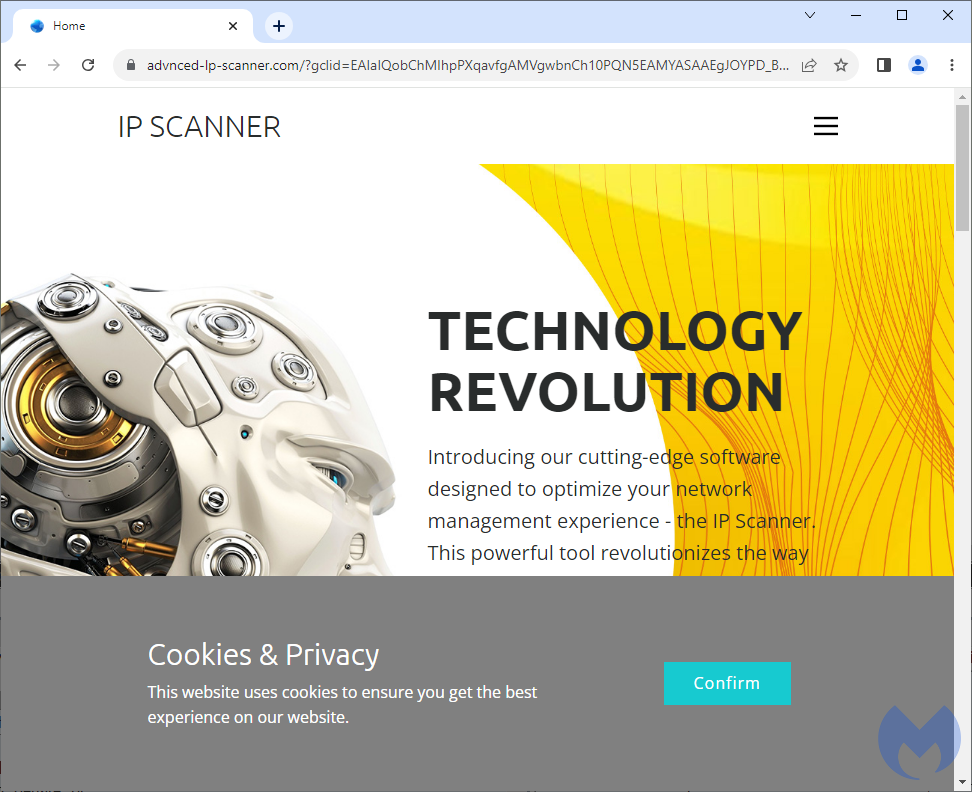
Interestingly, even with a fresh IP address the landing page looked innocent. This can happen for different reasons, for example if the threat actor is in the process of setting up the site and hasn’t finished swapping it to the malicious version. Or it could also be that the time of day is not in line with when the attacker is making the switch.
Enlighten:
The code was clarified, which revealed several functions that are performed by the JS code, which include,
- Browser properties like Screen and window size
- Time Zone details (Difference between UTC time and local time)
- Video card driver information and
- MIME type for MP4 file format.
When the server side confirms the IP is clean, it shows the original website that is shown to the victims, which has the option to download a malicious file.

Once this information is gathered from visitors, they are then sent to the attacker’s server through a POST request. Further passing the data will allow the threat actor to decide on what actions to take further.
Conflict with Other Advertising accounts
One of the major blockers for stopping these kinds of malware websites is that it is difficult to find and report these kinds of events. The platform serving this malicious website needs to validate the information from the malicious website before taking any action against the account.
This is due to the fact that other legitimate advertiser accounts must not be affected. However, finding these kinds of websites takes several hours, within which the threat actors can lure tens of thousands of victims and make them download the malware. A complete report has been published by Malwarebytes, which provides detailed information on this malware campaign. Users including security professionals are recommended to take precautions before visiting and downloading any scanners from an unknown website as it could be a potential malware.
In conclusion, cyber criminals are continuously evolving their tactics to deceive and infiltrate unsuspecting victims’ systems. By mimicking popular IT tools and using sophisticated techniques, they can now deliver malware stealthily without raising suspicion. This poses a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and even governments as it allows attackers to bypass traditional security measures. It is imperative for users to remain vigilant and skeptical of any unexpected or unusual emails, attachments, or software updates. Furthermore, organizations must invest in robust cybersecurity measures that go beyond standard antivirus software to detect and mitigate these advanced threats. Only through a proactive approach can we effectively combat the ever-evolving landscape of cybercrime.





