Over 600 Laravel Apps Exposed to Remote Code Execution Due to Leaked APP_KEYs on GitHub
In the intricate landscape of web application security, a seemingly innocuous leak can trigger a cascade of critical vulnerabilities. Recent findings by cybersecurity researchers have unveiled a perturbing issue: over 600 Laravel applications are currently exposed to remote code execution (RCE) due to the inadvertent disclosure of their APP_KEY on public platforms like GitHub. This isn’t merely a configuration oversight; it’s a direct pathway for attackers to seize control, emphasizing the profound impact of even minor missteps in application development and deployment.
The Critical Role of Laravel’s APP_KEY
At the heart of every Laravel application, the APP_KEY serves as a cryptographic cornerstone. This vital secret is instrumental in performing crucial security functions, including:
- Encrypting Sensitive Data: The
APP_KEYis used by Laravel’s encryption services to protect sensitive user data, sessions, and other confidential information stored within the application or transmitted. - Session Management: It plays a role in signing session cookies, ensuring their integrity and preventing tampering.
- CSRF Token Generation: While not directly generating CSRF tokens, a properly configured and secret
APP_KEYindirectly supports the overall security posture that CSRF protection relies upon.
As GitGuardian aptly notes, when this key, “essential for encrypting sensitive data,” is leaked publicly, it creates an immediate and severe security risk. Its exposure effectively disarms the application’s core cryptographic defenses, turning a robust framework into a vulnerable target.
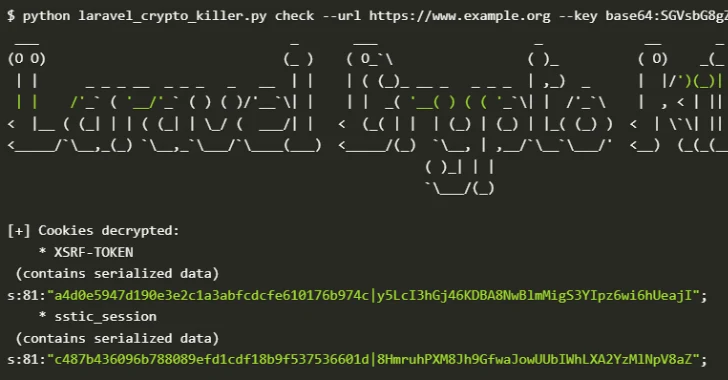
Weaponizing a Leaked APP_KEY: The Deserialization Exploit
The danger of a leaked APP_KEY extends beyond simple decryption. Attackers can leverage it to exploit a deserialization flaw inherent in PHP’s object handling. Deserialization is the process of converting a byte stream back into an object. If an attacker can control the serialized data that Laravel deserializes, and they possess the APP_KEY, they can craft malicious payloads.
This attack typically involves:
- Crafting Malicious Payloads: With the
APP_KEY, an attacker can create legitimate-looking but malicious serialized objects that, when deserialized by the application, trigger unintended behavior. - Exploiting PHP’s Object Instantiation: Upon deserialization, PHP will instantiate classes and call methods defined within the serialized string. By carefully crafting the `__destruct()` or `__wakeup()` methods of specific classes, an attacker can coerce the application into executing arbitrary commands. This often leverages known “gadget chains” within common PHP libraries or the Laravel framework itself.
- Achieving Remote Code Execution (RCE): The culmination of this process is RCE, allowing the attacker to run operating system commands on the server hosting the Laravel application. This grants them significant control, potentially leading to data theft, defacement, or further compromise of the underlying infrastructure.
While the specific mechanics of the deserialization flaw might resonate with past vulnerabilities, the repeated exposure of APP_KEYs on public repositories like GitHub highlights a persistent operational security challenge rather than a zero-day vulnerability in Laravel itself. This class of attack is often associated with PHP object injection vulnerabilities, which have been well-documented in the security community (e.g., in various CVEs related to deserialization of untrusted data).
The GitHub Vector: A Public Gallery of Secrets
The prevalence of these exposures on GitHub underscores a critical disconnect between development practices and security awareness. Developers often inadvertently commit sensitive configuration files directly into public repositories. Reasons include:
- Lack of understanding regarding the implications of public repositories.
- Overlooking
.gitignorefiles or having incomplete exclusions. - Relying on “private” repositories that are later mistakenly made public.
- Using automated deployment scripts that pull directly from public repos without proper secret management.
This public exposure transforms GitHub from a collaboration platform into a treasure trove for threat actors actively scanning for such leaks, turning a developer convenience into an enterprise risk.
Remediation Actions and Best Practices
Addressing this vulnerability requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on prevention, detection, and incident response.
Immediate Actions:
- Rotate Your
APP_KEYImmediately: If your Laravel application’sAPP_KEYhas ever been exposed, generate a new one. This invalidates all previous encrypted data and sessions, forcing users to re-authenticate. Usephp artisan key:generate. - Scan Public Repositories: Use secret scanning tools (see table below) to scour your organization’s public and private GitHub repositories for any leaked
APP_KEYsor other sensitive credentials. - Audit Access Logs: Investigate application and server access logs for any suspicious activity indicative of RCE attempts.
Long-Term Security Posture:
- Implement Strict
.gitignoreRules: Ensure.envand other configuration files containing secrets are explicitly excluded from version control systems. - Leverage Environment Variables or Secret Management Systems: Store sensitive keys and configurations outside of the application’s codebase, fetching them securely at runtime. Options include:
- Operating system environment variables.
- Cloud provider-specific secret managers (AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, Google Secret Manager).
- Dedicated secret management platforms (HashiCorp Vault).
- Educate Developers: Conduct regular security awareness training for development teams on secure coding practices, secret management, and the risks of public repositories.
- Utilize Pre-Commit Hooks: Implement Git pre-commit hooks that scan for common secret patterns before code is committed to a repository.
- Adopt a “Security by Design” Approach: Integrate security considerations throughout the entire Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC), from initial design to deployment and maintenance.
Relevant Tools for Detection and Mitigation:
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| GitGuardian | Real-time secret detection in Git repositories. | https://www.gitguardian.com/ |
| TruffleHog | Finds secrets in repositories (both history and current). | https://github.com/trufflesecurity/trufflehog |
| Gitleaks | Scans git repos for secrets. | https://github.com/zricethezav/gitleaks |
| SonarQube | Static application security testing (SAST) for code quality and security. | https://www.sonarqube.org/ |
| OWASP ZAP | Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) for finding vulnerabilities in running web apps. | https://www.zaproxy.org/ |
Conclusion: The Enduring Challenge of Secret Management
The exposure of Laravel APP_KEYs on GitHub and the resulting RCE risk serve as a stark reminder of the persistent and evolving challenges in application security. It underscores that even fundamental security components, when mishandled, can become critical vulnerabilities. For any organization developing or deploying web applications, meticulous secret management, a robust understanding of the underlying framework’s security mechanisms, and continuous developer education are not merely best practices—they are indispensable safeguards against potentially catastrophic breaches.
Proactive scanning for leaks, integrating security into the CI/CD pipeline, and fostering a security-conscious development culture are paramount to protecting digital assets in an increasingly interconnected and vulnerable landscape.





