CastleLoader Malware Infects 469 Devices Using Fake GitHub Repos and ClickFix Phishing
In an increasingly interconnected digital landscape, new malware strains emerge with disturbing regularity, evolving tactics to bypass traditional defenses. One such recent discovery demanding immediate attention is CastleLoader, a versatile malware loader that has successfully compromised hundreds of devices by leveraging sophisticated social engineering and technical evasion techniques. Its ability to distribute various information stealers and remote access trojans (RATs) underscores a critical threat to organizational and individual cybersecurity.
Understanding CastleLoader’s Modus Operandi
Cybersecurity researchers, including Swiss cybersecurity company PRODAFT, have meticulously analyzed CastleLoader’s campaigns, revealing a multi-pronged attack strategy. At its core, CastleLoader acts as a sophisticated distributor for more potent malware payloads, including prevalent information stealers and RATs. This modular approach allows its operators to adapt their attack goals based on the compromised environment.
The primary vectors for CastleLoader infections involve two highly deceptive methods:
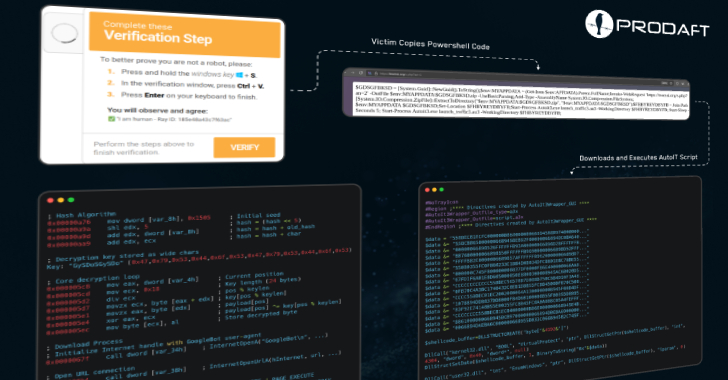
- Fake GitHub Repositories: Attackers create convincing counterfeit GitHub repositories mimicking legitimate applications. Users, trusting the perceived authenticity of GitHub, are lured into downloading malicious files disguised as benign software or updates. This method exploits the widespread use and trust in open-source development platforms.
- Cloudflare-Themed ClickFix Phishing: Beyond direct downloads, CastleLoader leverages elaborate phishing campaigns. These attacks, branded with Cloudflare’s familiar iconography, employ “ClickFix” social engineering lures. Victims are enticed to click malicious links or download tainted files under the guise of security fixes or necessary updates from a reputable service, thereby circumventing security awareness.
The Scope of the Compromise
The immediate impact of CastleLoader is stark: researchers have identified approximately 469 devices already infected. This number highlights the effectiveness of the malware’s distribution methods and the potential for rapid expansion if not countered promptly. The versatility of CastleLoader as a loader means that these 469 devices could be compromised with a range of secondary payloads, from keyloggers to ransomware, making the true extent of data exfiltration or system damage difficult to immediately ascertain without detailed forensic analysis.
The Threat Landscape: Info Stealers and RATs
CastleLoader’s primary function is to deliver secondary malware. The types of malware observed in these campaigns—information stealers and remote access trojans (RATs)—represent significant and pervasive threats:
- Information Stealers: These malicious programs are designed to exfiltrate sensitive data from compromised systems. This can include login credentials, financial information, personal identifiable information (PII), browser history, and crypto wallet data. The stolen data can then be sold on dark web marketplaces, used for identity theft, or leveraged for further targeted attacks.
- Remote Access Trojans (RATs): RATs grant attackers unauthorized remote control over a compromised device. This allows them to execute commands, access files, monitor user activity, and even install additional malware. The presence of a RAT can turn a user’s device into a persistent foothold for long-term espionage or large-scale network breaches.
Remediation Actions and Proactive Defense
Mitigating the threat posed by CastleLoader and similar versatile loaders requires a multi-layered approach, combining immediate remediation with proactive security measures.
For Organizations:
- Employee Training and Awareness: Conduct regular, up-to-date training on identifying phishing attempts, especially those mimicking trusted brands like Cloudflare or legitimate platforms like GitHub. Emphasize scrutiny of URLs, sender authenticity, and unexpected download requests.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Systems: Implement robust EDR solutions capable of detecting suspicious behaviors, process injections, and unauthorized network communications indicative of malware loaders and RATs.
- Email and Web Gateway Security: Utilize advanced email filtering and web proxies to block known malicious URLs, analyze email attachments, and identify phishing indicators.
- Software Supply Chain Security: Implement strict protocols for software acquisition. Verify the authenticity of application downloads from GitHub or other repositories. Prioritize official vendor channels and use checksums when available.
- Regular Software Updates and Patching: Ensure all operating systems, applications, and security software are regularly updated with the latest patches to close known vulnerabilities that malware might exploit.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems and sensitive data from general user networks to limit lateral movement in case of a breach.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Enforce the principle of least privilege for all users and applications, minimizing the potential damage from a compromised account.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test a comprehensive incident response plan for suspected malware infections, outlining containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis steps.
For Individuals:
- Be Skeptical of Unsolicited Communications: Approach emails, messages, or pop-ups requesting you to click links or download files with extreme caution, even if they appear to be from legitimate sources.
- Verify URLs: Always hover over links before clicking to check the actual destination URL. Look for subtle misspellings or unusual domain names.
- Download from Official Sources: Only download software directly from official vendor websites or trusted application stores. Avoid unverified third-party download sites.
- Use Reputable Antivirus/Anti-Malware Software: Keep your security software updated and perform regular scans.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Activate MFA on all critical accounts (email, banking, social media, GitHub) to add an extra layer of security.
- Regular Backups: Maintain regular backups of important data to an external drive or cloud service to facilitate recovery in case of ransomware or data loss.
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions | Advanced threat detection, incident response, and behavioral analysis on endpoints. Examples: CrowdStrike Falcon, SentinelOne, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. | CrowdStrike / SentinelOne |
| Next-Generation Antivirus (NGAV) | Signature-less detection methods, machine learning, and AI to identify polymorphic malware and zero-day threats. | Sophos Intercept X / Trend Micro Apex One |
| Email Security Gateways | Filters malicious emails, detects phishing attempts, and prevents malware delivery via email. | Proofpoint Email Protection / Mimecast Email Security |
| Web Application Firewalls (WAF) | Protects web applications from various attacks, including those originating from malicious downloads or compromised repositories (though less direct for client-side infection). | Cloudflare WAF / Akamai App & API Protector |
| Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs) | Aggregates and analyzes threat data to provide actionable intelligence for proactive defense. | Anomali ThreatStream / Recorded Future |
Conclusion
CastleLoader represents a significant example of modern malware threats that meticulously blend technical sophistication with highly effective social engineering. Its reliance on trusted platforms like GitHub and established security service brands like Cloudflare makes these campaigns particularly insidious. The compromise of nearly 500 devices serves as a stark reminder of the continuous need for vigilance, robust security infrastructure, and comprehensive user education. Staying informed about emerging threats, implementing strong preventative measures, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness are paramount to defending against such elusive and impactful malware campaigns.





