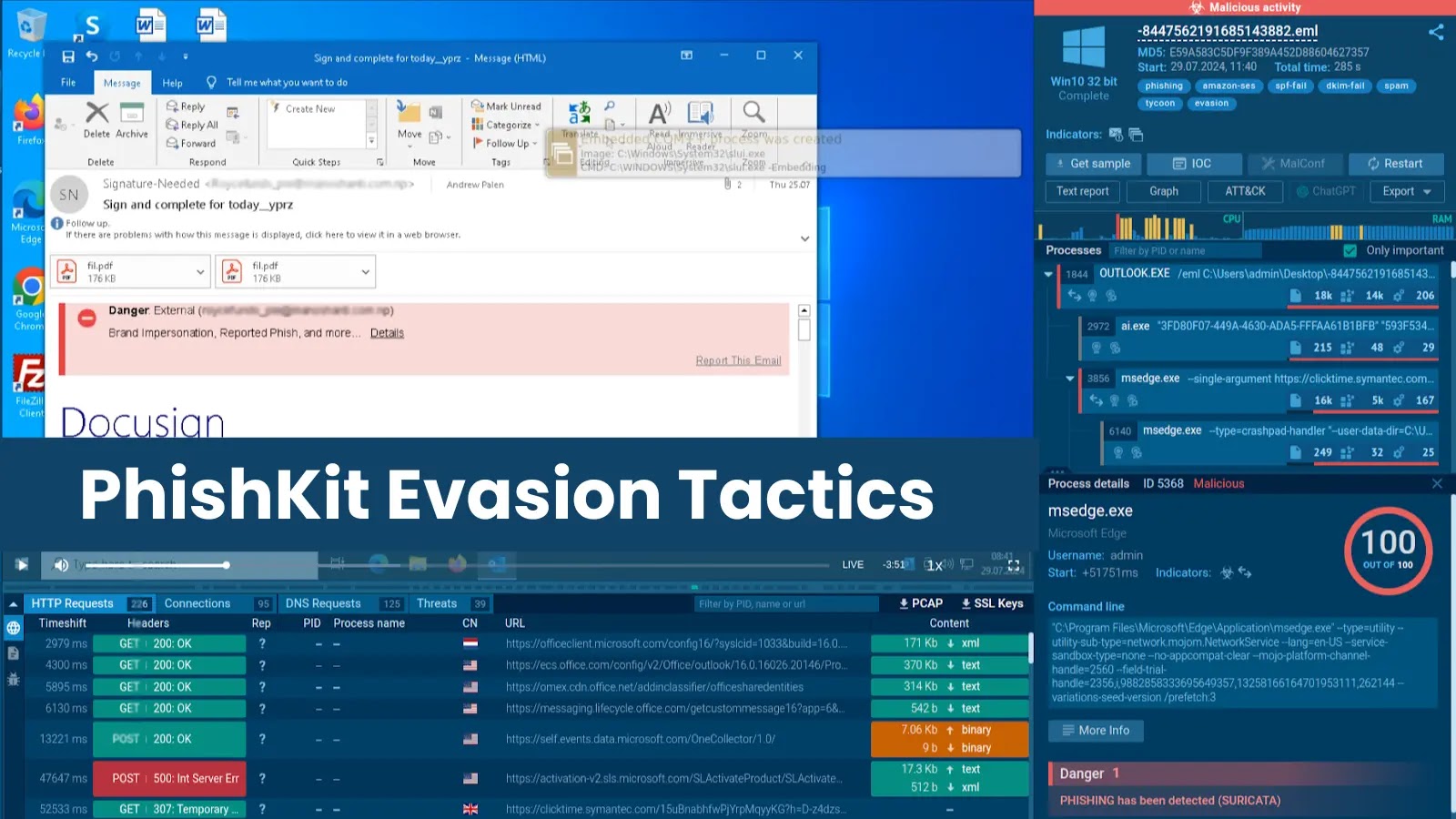
PhishKit Evasion Tactics: What You Need to Pay Attention to Right Now
The relentless evolution of cyber threats demands constant vigilance, especially when it comes to sophisticated phishing campaigns. Attackers are not just improving their lures; they’re refining their very infrastructure to evade detection. Phishing kits, once relatively simple, now incorporate advanced evasion tactics that make them incredibly difficult to spot and dismantle. This adaptive nature, exemplified by kits like Tycoon 2FA, presents a significant challenge for even the most robust cybersecurity defenses. Understanding these modern evasion strategies is no longer optional – it’s a critical imperative for every security professional.
The Adaptive Nature of Modern PhishKits
The landscape of cybercrime is characterized by rapid innovation. PhishKits, the tools used by threat actors to launch phishing campaigns, are at the forefront of this evolution. They’re no longer static tools but dynamic frameworks that regularly integrate new tricks to bypass security controls. This continuous refinement directly impacts an organization’s ability to detect and investigate threats. The alarming success of these kits in compromising companies underscores their remarkable adaptability, making them a top concern for security analysts and incident responders alike.
Tycoon 2FA: A Case Study in Evasion
While the provided reference highlights Tycoon 2FA, the article does not specify its particular evasion techniques. However, based on the general threat landscape and common PhishKit advancements, we can infer and discuss typical sophisticated evasion tactics that kits like Tycoon 2FA likely employ.
Common PhishKit Evasion Techniques
- Anti-Analysis and Anti-VM Capabilities: Sophisticated PhishKits often include code that detects whether they are running in a virtual machine (VM) or a sandboxed environment. If detected, they may alter their behavior, present benign content, or simply cease execution, thwarting automated analysis. This makes it challenging for security researchers to fully understand their malicious payload and mechanisms.
- Dynamic URL Generation and Obfuscation: Instead of static and easily blockable URLs, advanced PhishKits generate unique, dynamic URLs for each target or session. These URLs might incorporate random strings, encoded parameters, or even legitimate-looking subdomains to bypass reputation-based filtering and pattern matching. Furthermore, the URLs and the kit’s underlying code often employ various obfuscation techniques (e.g., JavaScript obfuscation, HTML entity encoding) to obscure their true intent from static analysis tools.
- Bypassing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Session Hijacking: While the name “Tycoon 2FA” directly suggests MFA bypass as a core capability, it’s a prevalent evasion tactic for many advanced kits. They often act as reverse proxies, sitting between the victim and the legitimate login page. This allows them to intercept and forward authentication credentials, including one-time passcodes (OTPs), in real-time. Once the victim authenticates, the kit can capture session cookies or tokens, enabling the attacker to hijack the legitimate session and bypass subsequent MFA prompts.
- IP Blacklisting and Geographic Restrictions: Some kits implement IP-based blacklisting to deny access from known security vendors, honeypots, or IP ranges associated with law enforcement. They might also restrict access based on geographic location, serving malicious content only to specific regions where their targets reside, further reducing their detection surface from global scanning efforts.
- Legitimate Service Integration and CDN Usage: To appear more legitimate and bypass web filters, attackers often host PhishKits on compromised legitimate websites or leverage reputable Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). This blends the phishing infrastructure with legitimate traffic, making it harder for security tools to distinguish malicious activity from benign interactions.
Remediation Actions and Proactive Defenses
Combating these advanced PhishKit evasion tactics requires a multi-layered and dynamic security strategy. Static defenses are no longer sufficient.
- Enhanced Email Security Gateways (ESGs): Implement ESGs with advanced threat intelligence feeds, machine learning capabilities, and behavioral analysis to detect subtle anomalies in incoming emails, even those with obfuscated URLs or legitimate-looking delivery methods.
- Advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)/Extended Detection and Response (XDR): Deploy EDR/XDR solutions that monitor endpoint behavior for suspicious activities indicative of phishing attempts, even if the initial email bypassed traditional filters. These tools can detect post-delivery activities like credential entry into suspicious forms or unusual network connections.
- User Awareness Training with Simulation: Regularly conduct in-depth security awareness training that specifically covers advanced phishing tactics, including MFA bypass attempts and the importance of verifying URLs and sender identities. Phishing simulations using up-to-date evasion techniques can help users identify real-world threats.
- Robust Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – FIDO2/Hardware Keys: While some kits bypass traditional MFA, adopting stronger, phish-resistant MFA methods like FIDO2 (e.g., YubiKeys) significantly mitigates the risk. These methods prevent session hijacking by tying authentication to hardware, making it impossible for attackers to simply intercept and replay credentials.
- Threat Intelligence and IoC Sharing: Subscribe to and actively leverage threat intelligence feeds that provide indicators of compromise (IoCs) related to emerging PhishKits and their evasion tactics. Share relevant IoCs within the security community to bolster collective defense.
- Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) and DNS Monitoring: Monitor network traffic for unusual request patterns, suspicious DNS queries, and connections to known malicious domains. NTA solutions can sometimes detect attempts to communicate with phishing infrastructure even if the initial lure was missed.
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Proofpoint / Mimecast | Advanced Email Security Gateway (ESG) for inbound email filtering, URL rewriting, and sandboxing. | https://www.proofpoint.com/
https://www.mimecast.com/ |
| Cisco Secure Endpoint / CrowdStrike Falcon | Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) for behavioral analysis and threat hunting on endpoints. | https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/secure-endpoint.html
https://www.crowdstrike.com/products/falcon-platform/ |
| KnowBe4 / Cofense | Security Awareness Training and Phishing Simulation Platforms. | https://www.knowbe4.com/
https://cofense.com/ |
| Yubico YubiKey | Hardware-based FIDO2/U2F security keys for phish-resistant MFA. | https://www.yubico.com/ |
| Splunk / Elastic (Security Information and Event Management) | SIEM platforms for centralized log management, correlation, and anomaly detection. | https://www.splunk.com/
https://www.elastic.co/security/ |
Key Takeaways for Cybersecurity Professionals
The battle against phishing is a constant arms race. Modern PhishKits, such as Tycoon 2FA, have evolved far beyond simple trickery, integrating sophisticated evasion tactics that bypass traditional defenses. For security analysts, this means moving beyond signature-based detection and embracing behavioral analysis, advanced threat intelligence, and a proactive stance on user education. Prioritizing phish-resistant MFA, continuously auditing security controls, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness are paramount to staying ahead of these adaptive and increasingly effective threats.





