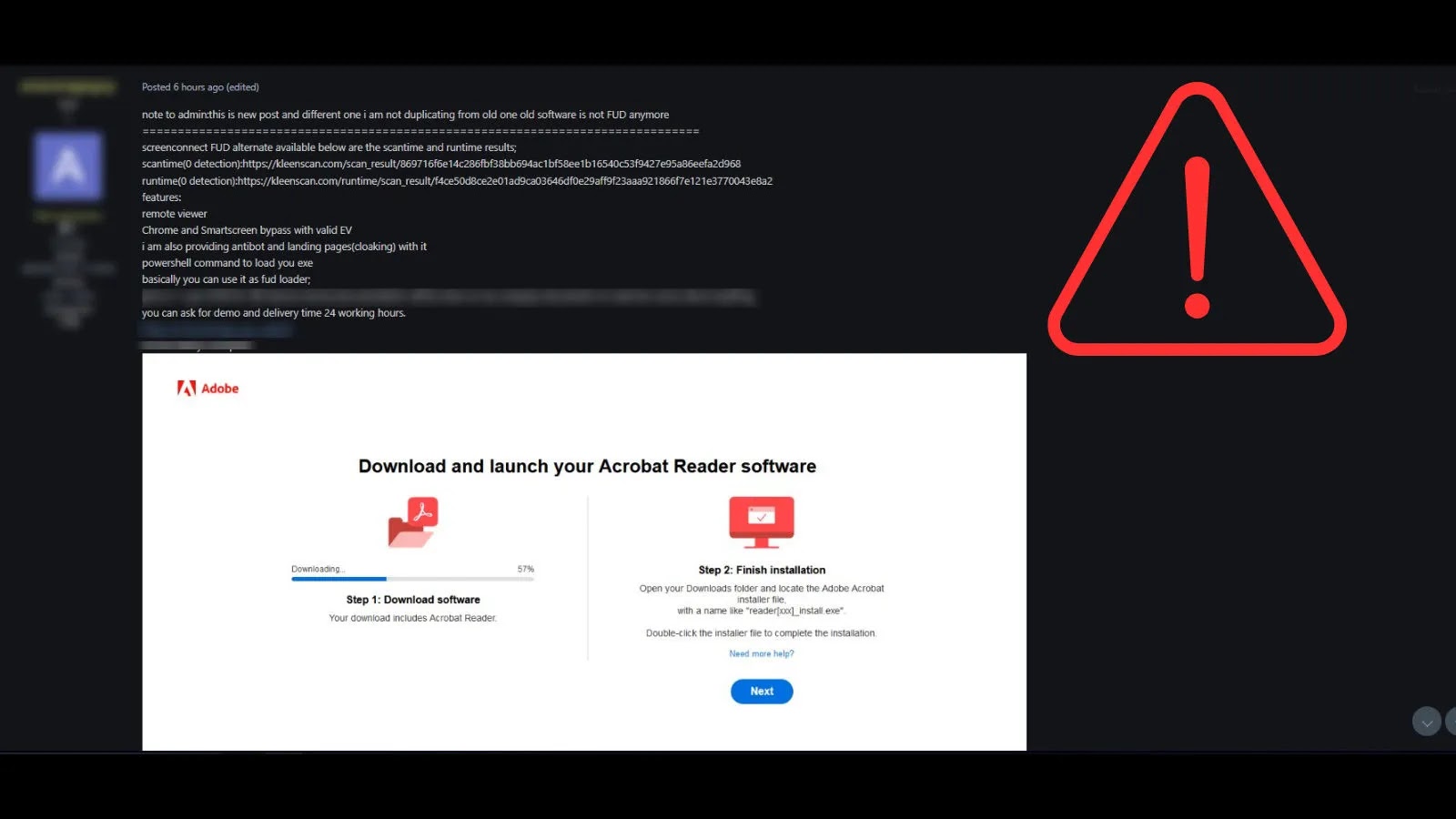
Threat Actors Selling New Undetectable RAT as ’ScreenConnect FUD Alternative’
The cybersecurity landscape is in a perpetual state of flux, with threat actors consistently innovating to bypass established defenses. A concerning new development has emerged from the underground forums: a novel Remote Access Trojan (RAT) is being aggressively marketed as a “Fully Undetectable” (FUD) alternative to legitimate remote access tools like ConnectWise ScreenConnect. This sophisticated offering poses a significant threat to organizations of all sizes.
The Rise of the “FUD ScreenConnect Alternative” RAT
Recent reports highlight a threat actor actively advertising a new RAT on clandestine online platforms. The core selling point? Its purported “fully undetectable” status and its positioning as a superior or unidentifiable replacement for ScreenConnect. This immediately raises red flags, as FUD claims are often a hallmark of advanced, evasive malware designed to sidestep traditional antivirus and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
The marketing strategy behind this RAT is particularly insidious. By leveraging the familiarity of a legitimate tool like ScreenConnect, threat actors aim to make their malicious offering seem more credible or to exploit potential misconfigurations or vulnerabilities in environments where such tools are commonly used. While the specific features of this new RAT are still emerging, the advertisement suggests a suite of advanced capabilities focused on stealth and persistence.
Understanding the Threat: Why This Matters
Remote Access Trojans are a formidable weapon in a cybercriminal’s arsenal. They grant unauthorized attackers persistent, covert access to compromised systems, enabling a wide array of malicious activities including:
- Data Exfiltration: Stealing sensitive information, intellectual property, or personal data.
- Lateral Movement: Spreading throughout a network to gain access to more critical systems.
- System Manipulation: Installing additional malware, disabling security controls, or launching further attacks.
- Espionage: Covertly monitoring user activities, keystrokes, and communications.
- Ransomware Deployment: Using the RAT as an initial foothold to deliver ransomware payloads.
The “fully undetectable” claim, if even partially true, is particularly alarming. It implies that the RAT employs advanced obfuscation techniques, polymorphic code, or novel evasion methods to bypass signature-based and behavioral detection mechanisms. This makes incident response significantly more challenging and increases the likelihood of prolonged compromise.
Remediation Actions and Proactive Defense
Given the emergence of this new, evasive RAT, organizations must take proactive steps to bolster their defenses. While specific CVEs related to this new RAT are not yet public, focusing on foundational security principles and robust incident response planning is paramount.
Key Remediation and Prevention Strategies:
- Enhanced Endpoint Protection: Deploy and maintain advanced EDR solutions with behavioral analysis capabilities that can detect anomalies even if signatures are unknown.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Limit user and system permissions to the absolute minimum required for operations. This reduces the blast radius of a successful compromise.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems and sensitive data on separate network segments to prevent lateral movement of attackers.
- Regular Software Updates and Patch Management: While this specific RAT is new, threat actors often chain exploits. Keep all operating systems, applications, and security software — including legitimate remote access tools like ConnectWise ScreenConnect (for which ConnectWise has addressed CVE-2024-1709 and CVE-2024-1708) — fully patched.
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all critical services and user accounts.
- User Awareness Training: Educate employees about phishing, social engineering, and the dangers of opening suspicious attachments or clicking malicious links.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Implement network intrusion detection/prevention systems (NIDS/NIPS) to detect unusual outbound connections or command-and-control (C2) communications.
- Regular Backups: Maintain tested, isolated backups of critical data to facilitate recovery in the event of a successful attack.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test a comprehensive incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective reaction to a security breach.
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
Organizations should leverage a combination of security tools to detect and mitigate the risks posed by advanced RATs.
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) Solutions | Advanced threat detection, behavioral analysis, incident response capabilities on endpoints. | Malwarebytes EDR (Example) |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity and blocking known threats. | Snort (Open Source Example) |
| Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) Tools | Deep packet inspection and behavioral analysis of network flows. | Zeek (Open Source Example) |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Centralized logging, correlation, and analysis of security events across the infrastructure. | Elastic Security SIEM (Example) |
| Vulnerability Management Solutions | Identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities in systems and applications. | Tenable.io (Example) |
Conclusion
The emergence of a new, supposedly undetectable RAT marketed as a “ScreenConnect FUD Alternative” underscores the continuous arms race in cybersecurity. Threat actors are keenly aware of the effectiveness of remote access tools and are adapting their malware to mimic and exploit legitimate functionalities while evading detection. Staying ahead requires a multi-layered security approach, persistent vigilance, and a commitment to proactive defense strategies. Organizations must prioritize robust endpoint security, network monitoring, and user education to defend against these evolving and increasingly sophisticated threats.





