Hackers Actively Scanning Internet to Exploit XWiki Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Urgent Alert: XWiki Remote Code Execution Vulnerability Under Active Exploitation
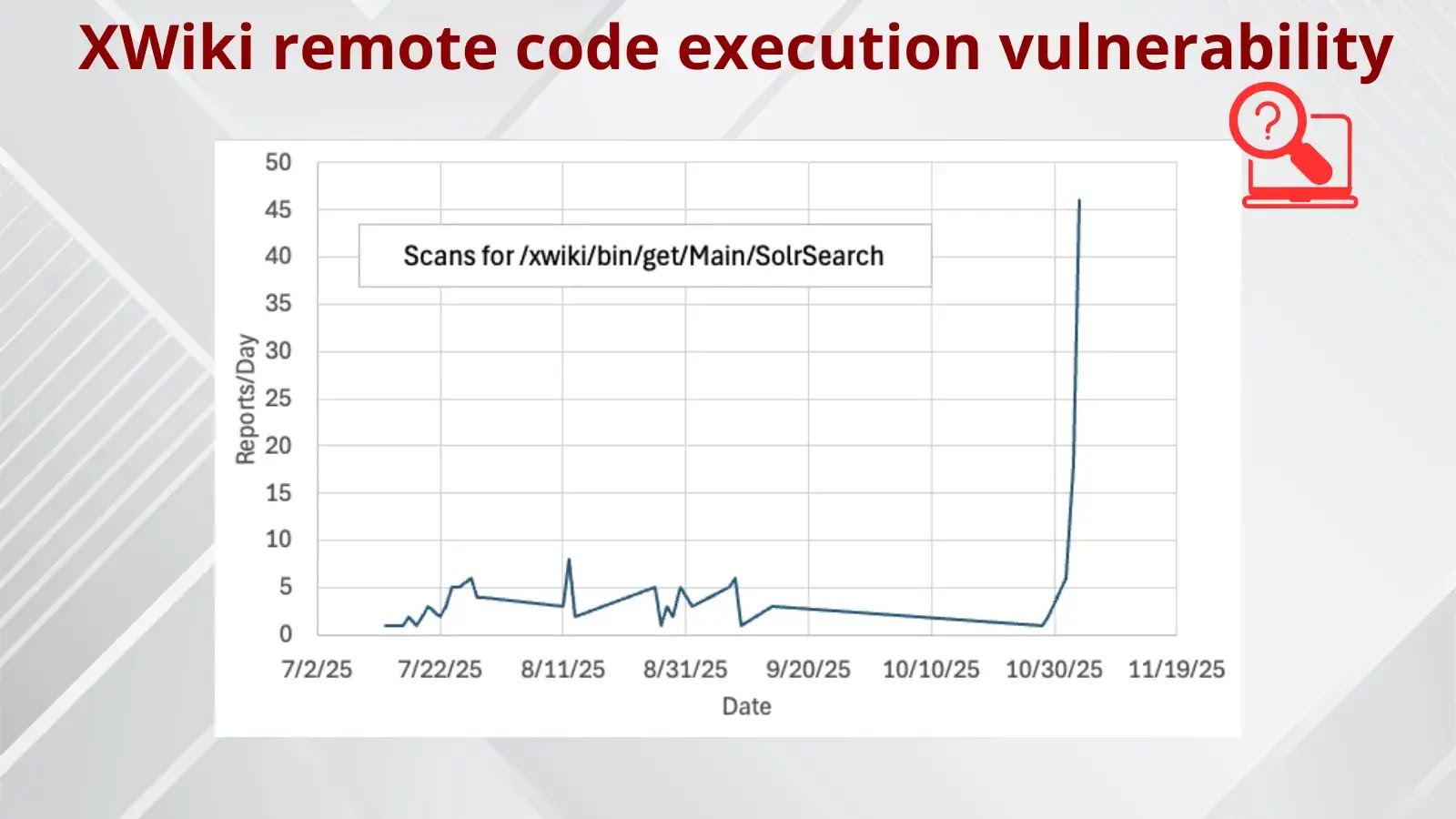
The digital landscape just became a little more perilous for organizations relying on XWiki. A critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, specifically impacting XWiki’s SolrSearch component, is no longer a theoretical threat. Cybersecurity authorities have escalated their warnings as widespread exploitation attempts are now actively targeting this flaw across the internet. This poses a significant and immediate risk to any enterprise utilizing this open-source wiki platform.
Understanding the XWiki RCE Vulnerability
The vulnerability in question allows attackers with even minimal guest privileges to execute arbitrary commands on vulnerable systems. This isn’t merely a data breach risk; it’s a doorway for complete system compromise. The ease of exploitation, requiring only guest-level access, dramatically lowers the bar for malicious actors to gain a foothold within an organization’s infrastructure.
This particular flaw resides within the SolrSearch component of XWiki. Solr is a powerful, open-source enterprise search platform, and its integration into XWiki provides robust search capabilities. However, a misconfiguration or weakness in this integration has created a critical Achilles’ heel. While specific CVE details were not provided in the original source, such vulnerabilities often stem from improper input validation, deserialization issues, or command injection flaws within the search query processing.
Who is at Risk?
Any organization currently running XWiki, particularly those where the SolrSearch component is enabled and accessible, is at immediate risk. Small and large enterprises alike use XWiki for knowledge management, collaboration, and internal documentation. The widespread nature of this platform means that a substantial number of organizations could be vulnerable to these active exploitation attempts.
The fact that attackers are actively scanning the internet suggests a well-orchestrated campaign aimed at identifying and compromising exposed XWiki instances. This elevates the threat from a theoretical concern to an urgent operational security matter.
Real-World Impact of RCE
Remote Code Execution is one of the most severe types of vulnerabilities an organization can face. If successfully exploited, an attacker gains the ability to:
- Install malware, including ransomware or backdoors.
- Steal sensitive data, intellectual property, or confidential user information.
- Deface websites or disrupt critical services.
- Gain persistence within the network, leading to further lateral movement and more extensive compromise.
- Use the compromised server as a pivot point for attacking other internal systems.
The implications for business continuity, data integrity, and regulatory compliance are severe and far-reaching.
Remediation Actions: Securing Your XWiki Instance
Given the active exploitation, immediate action is paramount. Organizations using XWiki should prioritize the following steps:
- Patch Immediately: The most crucial step is to apply any available security patches or updates released by the XWiki project maintainers that address this specific vulnerability. Monitor official XWiki security advisories for the latest information.
- Isolate and Segment: If immediate patching is not feasible, restrict network access to your XWiki instance. Implement strict firewall rules to limit access to only trusted IP addresses or internal networks.
- Review SolrSearch Configuration: Carefully review the configuration of your SolrSearch component within XWiki. Ensure that it adheres to security best practices and disable any unnecessary functionality.
- Monitor Logs: Enhance logging for your XWiki server and Solr instances. Look for unusual activity, suspicious Solr queries, or unexpected process execution.
- Conduct Vulnerability Scans: Utilize vulnerability scanners to identify if your XWiki instance is indeed vulnerable.
- Implement Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF can provide an additional layer of defense by detecting and blocking malicious requests targeting known exploit patterns.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Ensure that the XWiki application and its underlying services operate with the least necessary privileges.
While specific CVE information is pending or not yet publicly attributed to XWiki’s SolrSearch component in general databases, staying vigilant to XWiki’s official security announcements is key.
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
Organizations can leverage various tools to help detect potential exploitation attempts or strengthen their defenses:
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Nessus | Vulnerability Scanning | https://www.tenable.com/products/nessus |
| OpenVAS | Open-source Vulnerability Scanning | https://www.greenbone.net/en/community-edition/ |
| ModSecurity | Web Application Firewall (WAF) | https://modsecurity.org/ |
| ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) | Log Monitoring and Analysis | https://www.elastic.co/elastic-stack |
| Snort/Suricata | Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | https://www.snort.org/ / https://suricata.io/ |
Conclusion
The active exploitation of the XWiki SolrSearch remote code execution vulnerability serves as a stark reminder of the continuous threats facing open-source platforms. Organizations using XWiki must treat this with utmost urgency, implementing patches and employing defense-in-depth strategies to protect their systems. Proactive security measures, vigilant monitoring, and rapid response are essential to mitigating the severe risks posed by such critical flaws. Stay informed through official XWiki security channels and bolster your defenses now.





