New Android Bug Impacts Volume Buttons Functionality with “Select to Speak” Enabled
A recently identified critical bug affects Android devices, specifically impacting the functionality of volume buttons when the “Select to Speak” accessibility feature is enabled. This oversight can significantly disrupt user experience, transforming what should be a straightforward volume adjustment into a source of frustration, particularly for those relying on accessibility tools.
Overview of the Android Volume Button Bug
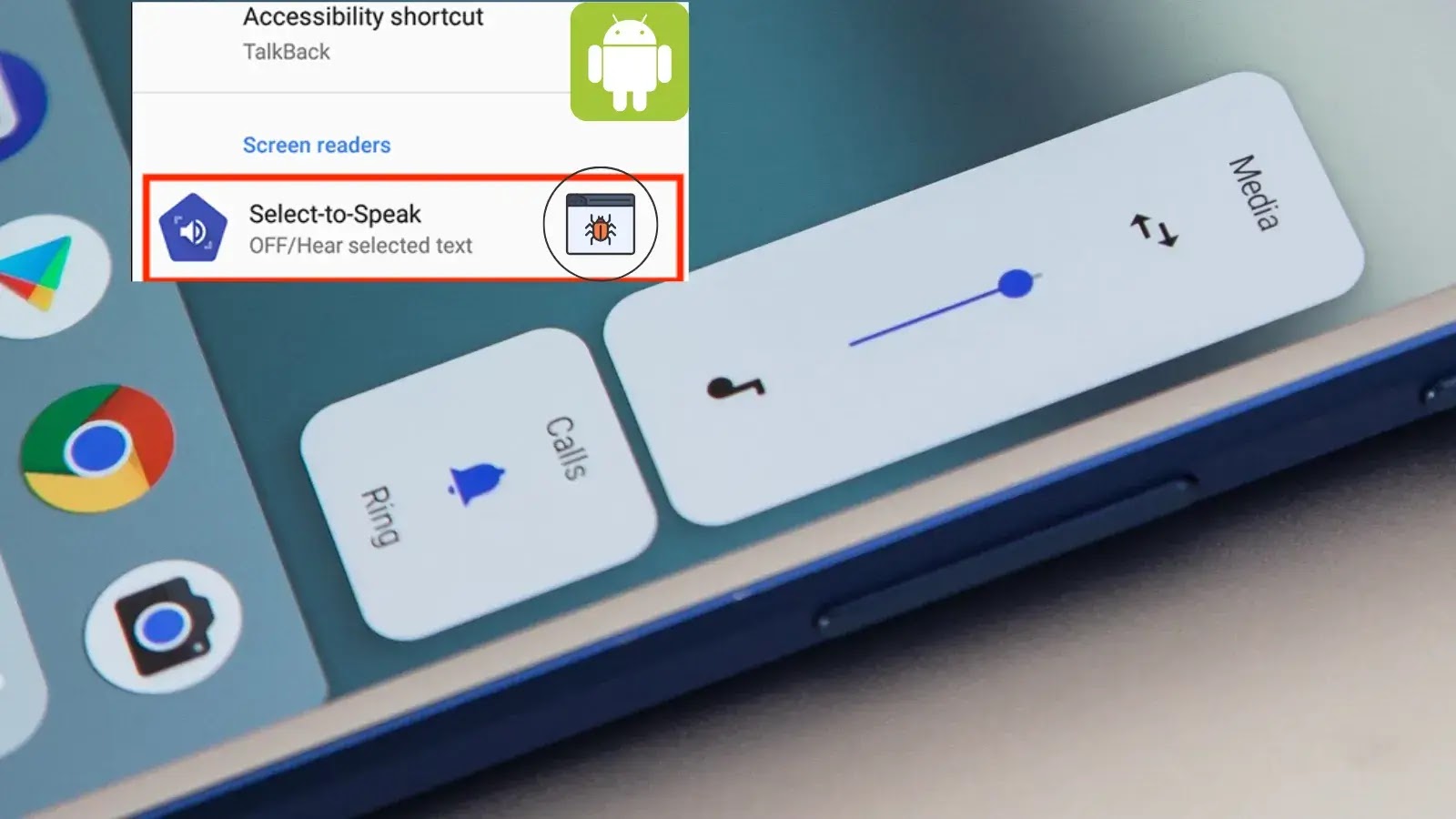
Google has acknowledged a significant issue within the Android operating system where enabling the “Select to Speak” accessibility feature inadvertently alters the primary function of physical volume buttons. Instead of controlling media volume as users would expect, these buttons begin to adjust the accessibility volume. This switch in functionality creates a confusing and often inconvenient experience, undermining the intuitive design of Android devices.
The impact extends beyond simple volume control. A notable side effect identified within this bug is the inability to capture photos using volume buttons during photography in certain scenarios. This capability, often favored for its tactile feedback and ease of use, becomes non-functional, hindering quick photo opportunities. The core of the problem lies in the misdirection of hardware button inputs, diverting them from their intended system-wide media control to a specific accessibility subset.
Technical Details and Impact
The “Select to Speak” feature is designed to assist users with visual impairments or reading difficulties by reading aloud selected text on the screen. While invaluable for accessibility, its interaction with core system functionalities like volume control reveals a software conflict. When “Select to Speak” is active, the system’s input handler for volume button presses prioritizes accessibility volume adjustments over the standard media volume. This effectively re-maps the hardware input, leading to unexpected behavior.
Users who rely on “Select to Speak” are particularly affected, as disabling the feature to regain normal volume control would defeat its purpose. The bug essentially forces a trade-off between critical accessibility functions and fundamental device operations. The lack of a clear prompt or warning about this change in button behavior further exacerbates the issue, leaving users to diagnose the problem themselves.
Remediation Actions
Addressing this Android volume button bug requires a direct approach, primarily through software updates. As this is a system-level issue, individual user workarounds are limited and often temporary.
- System Updates: The most crucial step is to ensure your Android device is running the latest available software. Google typically rolls out fixes for such bugs through system updates. Users should regularly check for and install these updates from their device settings. Navigate to
Settings > System > System update(or similar path depending on your device manufacturer) to check for pending updates. - Temporary Workaround (If Applicable): If an immediate software update is not available, and you are not actively using “Select to Speak,” temporarily disabling the feature may restore normal volume button functionality. This can be done via
Settings > Accessibility > Select to Speak. Re-enable it only when needed, acknowledging the potential impact on volume control. This is not a permanent solution but can alleviate immediate frustration. - Report the Issue: If you are experiencing this bug and your device is up-to-date, report the issue to Google through your device’s feedback mechanism or your phone manufacturer’s support channels. Such reports help prioritize fixes and ensure broader compatibility.
Future Implications and Accessibility Considerations
Bugs like this highlight the intricate challenges in integrating advanced accessibility features without introducing conflicts with core system functions. For IT professionals and developers, this serves as a reminder of the importance of comprehensive regression testing, especially when introducing new features or modifying existing system behaviors. Ensuring that accessibility tools enhance, rather than hinder, the overall user experience is paramount.
Moving forward, ongoing vigilance in software development and quality assurance is critical to prevent such regressions. This includes thorough testing across various configurations and user scenarios, with a particular focus on how accessibility features interact with fundamental hardware and software components. The goal remains a seamlessly integrated and universally accessible digital experience for all users.
Conclusion
The Android bug affecting volume button functionality when “Select to Speak” is enabled is a testament to the complexities of modern operating systems. While the feature itself is a vital accessibility tool, its current interaction with volume controls presents a significant usability challenge. Users are advised to keep their devices updated and apply any available software patches. This situation underscores the continuous need for rigorous testing and thoughtful integration of accessibility features to maintain a robust and user-friendly mobile ecosystem.





