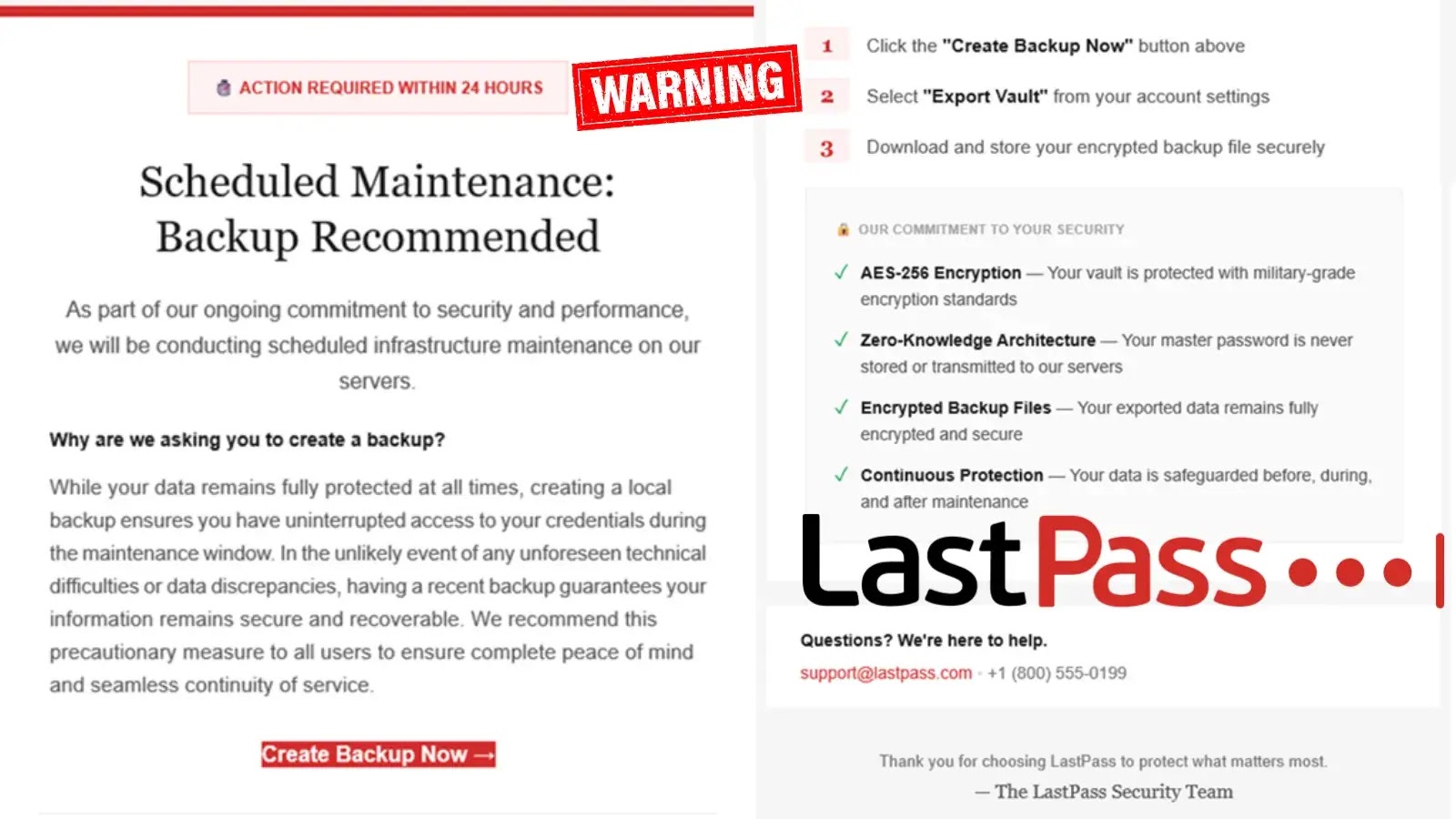
LastPass Warns of Fake Maintenance Message Tracking Users to Steal Master Passwords
A disturbing new phishing campaign is actively targeting LastPass users, leveraging highly convincing social engineering tactics to steal master passwords. This isn’t a theoretical threat; it’s an ongoing operation that commenced on January 19, 2026, and demands immediate attention from all LastPass account holders. Understanding the mechanics of this attack is crucial for safeguarding your digital vault.
The Anatomy of the Attack: Fake Maintenance and Urgent Backup
Malicious actors are impersonating LastPass support staff, sending fraudulent emails designed to create a false sense of urgency. The core of their deception revolves around a fabricated “maintenance” scenario and the purported need for an “urgent vault backup.” These emails are crafted to appear legitimate, leveraging brand impersonation to gain trust.
The attackers employ classic social engineering techniques. They falsely claim that LastPass is undergoing critical maintenance, which necessitates users back up their vaults immediately. The implicit threat is data loss or account compromise if the user fails to comply. This manufactured urgency is a hallmark of sophisticated phishing attempts, designed to bypass careful scrutiny and elicit a hasty response from the victim. The ultimate goal is to direct users to a malicious login page, where their master password will be harvested.
Understanding the Threat: Master Password Compromise
If successful, this phishing campaign directly compromises the most critical credential of a LastPass user: their master password. The master password is the single key that unlocks an entire digital vault, containing all stored usernames, passwords, secure notes, and other sensitive information. A compromised master password grants attackers unfettered access to all these stored credentials, leading to a cascade of potential identity theft, financial fraud, and unauthorized access to numerous online accounts.
There is no specific CVE associated with social engineering or phishing attacks directly, as they exploit human vulnerabilities rather than software flaws. However, the impact of such a breach can be as severe as a software vulnerability, if not more so, given the broad scope of data at risk.
Remediation Actions: Protecting Your LastPass Vault
Immediate and proactive steps are essential to protect your LastPass account and your digital identity from this and similar phishing attempts.
- Verify Sender Identity: Always scrutinize the sender’s email address. Phishing emails often come from domains that are similar to, but not exactly, the legitimate domain (e.g., “lastpax.com” instead of “lastpass.com”). When in doubt, navigate directly to the official LastPass website via your browser – do not click links in suspicious emails.
- Be Wary of Urgency: Legitimate service providers, especially those handling sensitive data like LastPass, rarely demand immediate action or threaten account suspension via unsolicited emails. Any message demanding immediate action should be treated with extreme suspicion.
- Never Share Your Master Password: LastPass will NEVER ask you for your master password via email, phone, or any other unsolicited communication. Your master password is known only to you.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): If you haven’t already, enable MFA on your LastPass account. This adds a critical layer of security, requiring a second verification step (e.g., a code from an authenticator app or a security key) even if your master password is compromised.
- Review LastPass Security Notifications: Familiarize yourself with how LastPass communicates legitimate security alerts. Typically, these would be announced on their official blog, within the application itself, or through clearly identifiable official channels.
- Stay Informed: Regularly check official LastPass channels and reputable cybersecurity news sources for updates on known threats and best practices.
Tools for Enhanced Security
While phishing primarily targets human judgment, various tools can aid in creating a more secure digital environment and help identify malicious indicators.
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| PhishTank | Community-based clearinghouse for verified phishing data. | https://www.phishtank.com/ |
| Google Safe Browsing | Identifies unsafe websites across the web and warns users. | https://safebrowsing.google.com/ |
| SPF/DKIM/DMARC Email Authentication | Protocols to detect email spoofing and phishing attempts. | Not a single tool; refer to email provider documentation for setup. |
| Authenticator Apps (e.g., Authy, Google Authenticator) | Generate time-based one-time passwords for MFA. | https://authy.com/ |
Key Takeaways for LastPass Users
The ongoing phishing campaign targeting LastPass users highlights the persistent and evolving nature of cyber threats. Impersonating support staff and fabricating urgent maintenance scenarios are effective social engineering techniques designed to trick even vigilant individuals. Your master password is your most critical credential; never divulge it in response to an unsolicited request. Proactive measures such as verifying sender identity, scrutinizing urgent requests, enabling MFA, and staying informed are your primary defenses against these sophisticated attacks. Remain skeptical of unexpected communications, and always, always cross-reference information with official sources.





