Google Announces Android Theft Protection Feature to Make Your Device Harder Target for Hackers
Google Fortifies Android: A New Era of Theft Protection Emerges
The modern smartphone is more than just a communication device; it’s a repository of our digital lives, holding sensitive data from financial applications to personal memories. The loss or theft of such a device can be devastating, leading to not only financial exploitation but also significant privacy breaches. Recognizing this escalating threat, Google has taken a significant stride forward, announcing a comprehensive update to Android’s theft protection capabilities. This initiative, rolled out on January 26, 2026, introduces a robust, multi-layered defense system designed to transform Android devices into considerably harder targets for opportunistic criminals and sophisticated hackers alike. This post delves into the specifics of Google’s latest security enhancements, detailing how these new features aim to safeguard users before, during, and after a theft attempt.
Strengthening the Digital Fortress: Enhanced Authentication Safeguards
At the core of Google’s updated security architecture are stronger authentication safeguards. These new measures aim to prevent unauthorized access to a stolen device, even if the thief manages to bypass initial lock screen protections. The advancements move beyond simple PINs and patterns, integrating more sophisticated methods to verify user identity securely.
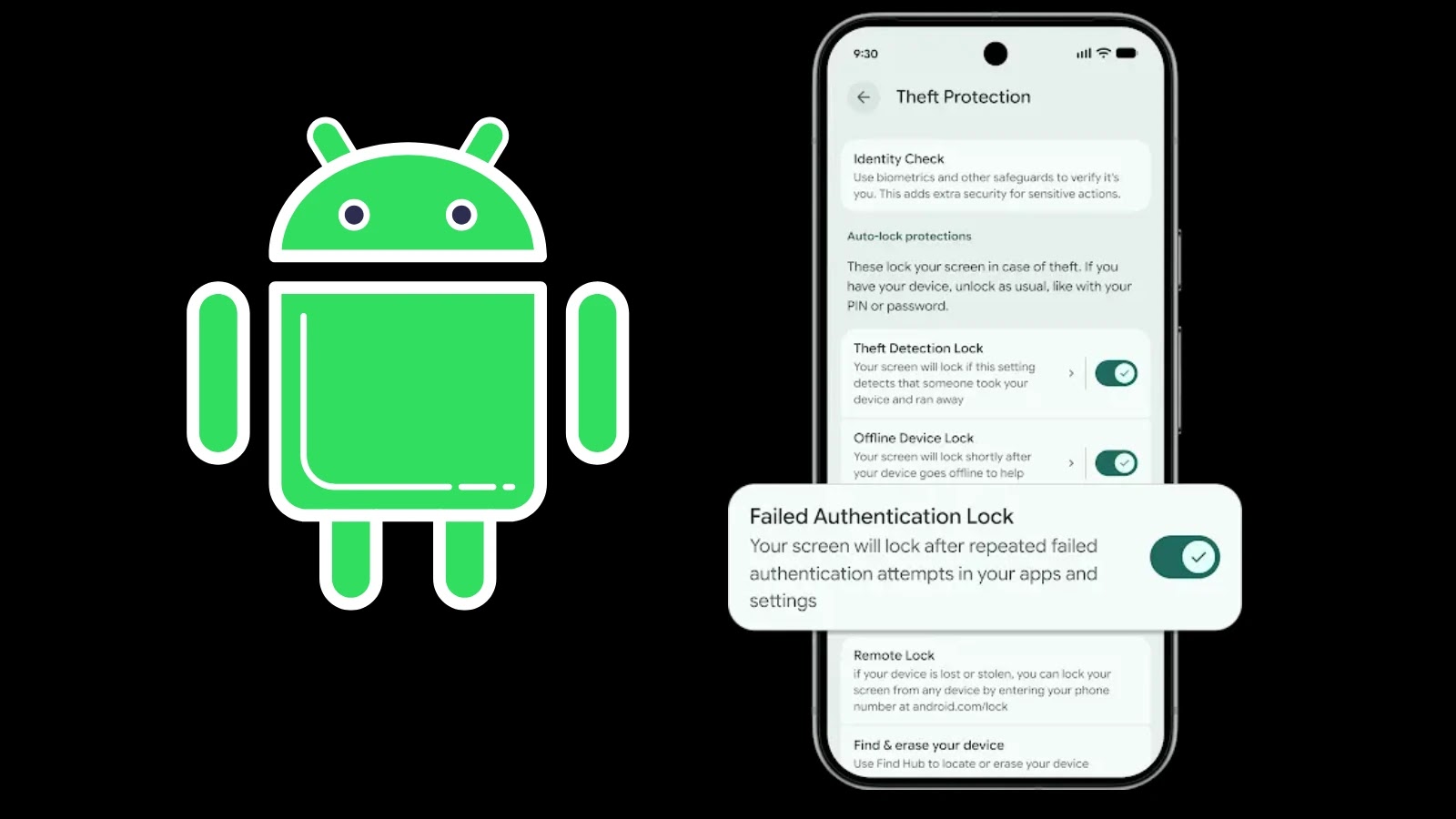
- Remote Lock & Wipe Enhancements: While remote wiping has been a staple, Google has refined its implementation, making it more resilient to common evasion tactics employed by thieves. The goal is to ensure a swift and irreversible data wipe, even under challenging network conditions.
- Device Binding & Account Security: New mechanisms will more tightly bind Android devices to their owner’s Google accounts, adding an extra layer of authentication for critical actions and making it far more difficult for a stolen device to be factory reset and reused by an unauthorized party.
- Proactive Theft Detection: Google is leveraging AI and machine learning to detect suspicious activity indicative of a theft. For instance, if a device is rapidly taken from a user and then moved to an unknown location, the system can automatically trigger heightened security protocols, such as requiring re-authentication for critical apps or even locking the device.
Beyond the Robbery: Advanced Recovery Tools
Beyond preventing initial access, Google’s new features also focus on enhancing the recoverability of stolen devices and securing data post-theft. The company understands that prevention is paramount, but recovery and data protection during an ongoing incident are equally crucial.
- Enhanced “Find My Device” Capabilities: The “Find My Device” service is receiving an overhaul, promising more accurate location tracking, even indoors, and improved capabilities to remotely ring, lock, or erase a device. These improvements are critical in the immediate aftermath of a theft.
- Secure Storage for Sensitive Data: Google is implementing stronger encryption protocols and secure enclaves for highly sensitive data, such as biometric information and payment details. This ensures that even if a device’s primary security is compromised, core personal information remains protected.
- Guest User & Locked Folder Enhancements: For situations where a device might be shared or temporarily lent, new features allow for more robust guest profiles and even more secure, password-protected folders, allowing users to move sensitive data out of immediate view and access.
Addressing Specific Threat Vectors
These updates specifically address common tactics used by criminals, often observed in opportunistic street robberies or more sophisticated phishing attempts that lead to device compromise. While no CVEs are directly associated with these feature enhancements (as they are architectural improvements rather than vulnerability patches), they indirectly mitigate risks associated with information disclosure and unauthorized access. For example, by making it harder to bypass lock screens and wipe devices without authorization, Google is reducing the impact of incidents that might otherwise lead to broader data breaches.
Key Takeaways for Android Users
Google’s commitment to enhancing Android’s security stature is evident in this latest update. For users, these changes translate into a significantly more resilient device against theft and unauthorized access. It’s a proactive step that leverages advanced technology to provide peace of mind in an increasingly connected, yet challenging, digital landscape. Users should ensure their devices are updated to the latest Android version to benefit from these new protections and always maintain strong, unique passwords for their Google accounts.





