Cybersecurity in Smart Cities.
Cybersecurity Challenges in Smart Cities: A Cyber Guide
As smart cities continue to evolve, integrating technology into every facet of urban life, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. This guide aims to explore the cybersecurity challenges in smart cities, offering insights and strategies to create a secure smart city. From understanding the infrastructure to implementing robust cybersecurity measures, we delve into the complexities of securing these interconnected environments.
Understanding Smart Cities and Their Infrastructure
Definition and Importance of Smart Cities
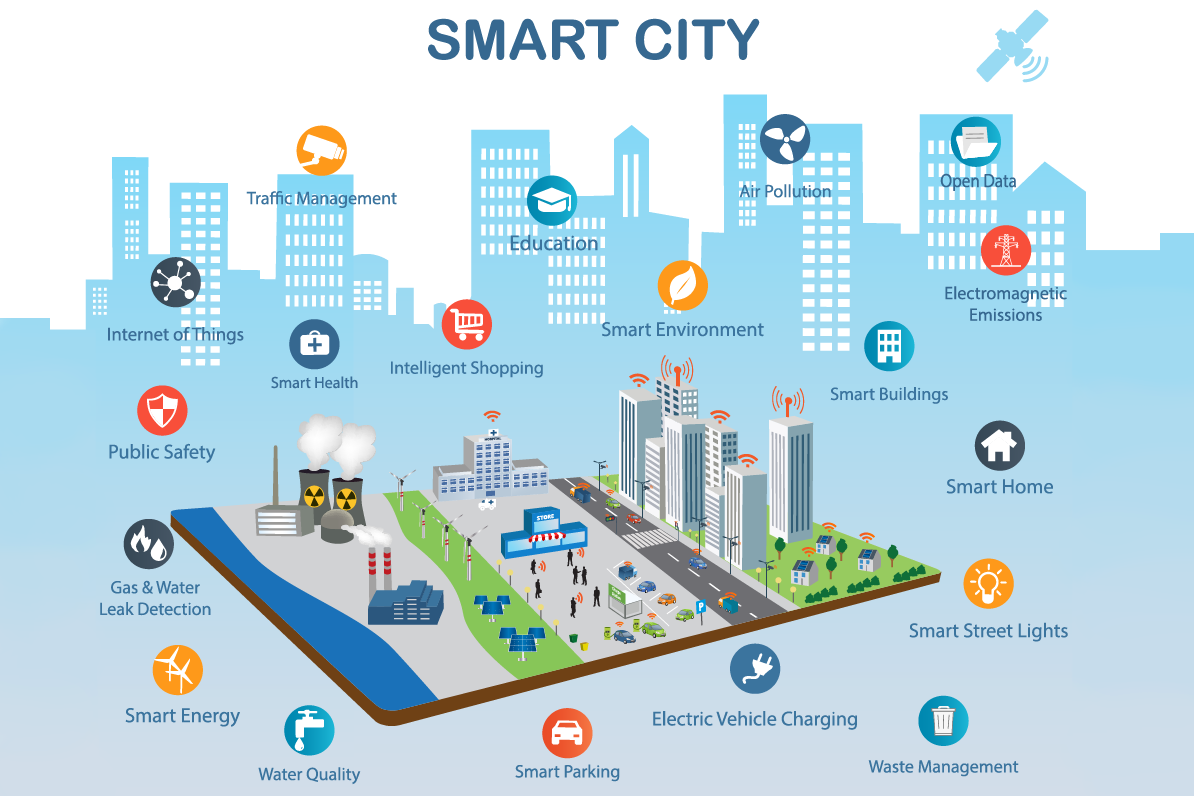
Smart cities leverage smart city technologies to enhance the quality of life for their citizens through optimized city services. These urban centers utilize the internet of things (IoT) devices and vast networks to collect and analyze data, improving efficiency and sustainability. However, this increased connectivity also introduces cybersecurity risks, making information security a top priority. cybersecurity for smart cities a paramount concern. The very essence of a smart city’s functionality hinges on its ability to maintain secure operations.
Key Technologies in Smart City Infrastructure
The digital infrastructure of smart cities encompasses a wide array of technologies, including smart grids, intelligent transportation systems, and interconnected public services. Each of these components relies on data exchange, making them potential targets for information security threats. Protecting this infrastructure requires a cybersecurity framework that addresses vulnerabilities and ensures the integrity of data. Cybersecurity solutions must be integrated at every level to safeguard against disruptions and data breaches, thereby securing smart city operations.
Role of IoT Devices in Smart Cities
IoT devices are integral to smart city systems, collecting and transmitting vast amounts of data that informs decision-making and drives automation. However, these devices often lack adequate security features, making them vulnerable entry points for cyber threat actors in the smart city ecosystem. Addressing these cybersecurity challenges requires implementing best practices for IoT device security, including regular updates, strong authentication, and network segmentation. Securing smart cities demands a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities associated with IoT deployments, ensuring security and privacy for all citizens.
Cybersecurity Risks in Smart Cities
Overview of Cybersecurity Threats
The landscape of cybersecurity threats in smart cities is constantly evolving, presenting significant challenges to maintaining a secure smart city. These threats range from ransomware attacks targeting critical infrastructure to sophisticated phishing campaigns aimed at gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data. Understanding the types and sources of these threats is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity strategies.
Common Cybersecurity Challenges in Smart Cities
Smart cities face unique cybersecurity challenges due to their interconnected nature. The proliferation of IoT devices creates numerous entry points for cyber threat actors. Moreover, the integration of legacy systems with modern technologies often introduces vulnerabilities that can be exploited. Addressing these cybersecurity challenges in smart cities requires a holistic approach that considers the entire ecosystem.
Impact of Cyber Threats on City Services
A successful cyber attack on smart city systems can have devastating consequences, disrupting essential city services and endangering the quality of life for residents. Imagine transportation networks being paralyzed, smart grids collapsing, or emergency services being hampered. Protecting city infrastructure from cyber threats is therefore paramount to ensuring the well-being and security of the urban population and to minimizing cybersecurity risks. A comprehensive cybersecurity framework is essential to safeguard these systems.
Best Practices for Securing Smart Cities
Implementing Cybersecurity Strategies
Securing smart cities requires the implementation of robust cybersecurity strategies that address the unique security challenges they face in the concept of smart cities. These strategies should include regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and incident response plans. By proactively identifying and mitigating cybersecurity risks, cities can enhance their resilience to cyber threats and ensure the continuity of essential services. Such smart cities and cybersecurity strategies should be comprehensive to ensure robust security solutions.
Securing Smart City Technologies
Securing smart city applications, especially IoT devices, is paramount to maintaining a secure urban environment. This involves implementing best practices for device security, such as strong authentication, encryption, and regular software updates. Additionally, network segmentation can help isolate critical systems within the smart city ecosystem, limiting the impact of a potential breach. Cybersecurity for smart cities’ infrastructure depends on the strength of each component.
Building Resilient Digital Infrastructure
Building resilient digital infrastructure is essential for ensuring that smart cities can withstand and recover from cyber attacks. This includes implementing redundancy and failover mechanisms, as well as establishing clear protocols for incident response and data privacy recovery. By investing in resilient infrastructure, smart cities can minimize the impact of cyber threats and maintain the security and privacy of their citizens and their amount of data, which is essential for their security and privacy.
Case Studies on Cybersecurity Challenges
Notable Cyber Attacks on Smart Cities
Examining specific instances of cyber attacks on smart city systems provides valuable insights into the potential vulnerabilities and impacts. These case studies often reveal common entry points exploited by cyber threat actors, such as unsecured IoT devices or outdated software. Analyzing these incidents helps in understanding the evolving cybersecurity challenges in smart cities and in developing more effective cybersecurity solutions.
Lessons Learned from Cyber Incidents
Each cyber incident serves as a learning opportunity for enhancing cybersecurity strategies. By dissecting the anatomy of these attacks, cities can identify weaknesses in their digital infrastructure and implement targeted security measures. The goal is to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future and ensuring that smart city infrastructure remains resilient. These lessons learned are invaluable for creating a more secure smart city’s infrastructure.
Successful Strategies for Mitigation
Despite the ever-present threat landscape, many cities have successfully mitigated cyber attacks through proactive cybersecurity measures. These successful strategies often involve a combination of technological solutions, policy frameworks, and public awareness campaigns. Highlighting these success stories can inspire other cities to adopt similar approaches, thereby strengthening the overall cybersecurity posture of smart cities.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Smart Cities
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The future of cybersecurity for smart cities will be shaped by emerging trends and technologies. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are playing an increasing role in threat detection and response. Blockchain technology can enhance data security and integrity within the smart city’s infrastructure. Staying abreast of these developments is crucial for maintaining a secure smart city environment in the face of evolving cybersecurity threats.
Preparing for the Rise of Smart Cities
As more cities embrace smart city technologies, the need for robust cybersecurity measures will only intensify. Preparing for this rise requires a proactive approach, including investing in cybersecurity training, developing comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks, and fostering collaboration between stakeholders. By anticipating future cybersecurity challenges, cities can minimize security risks and ensure the security and privacy for their residents.
Collaboration Between Stakeholders for Enhanced Security
Effective cybersecurity in smart cities requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including government agencies, technology providers, and the public. Sharing information about cyber threats and best practices can enhance the overall security posture of smart cities. Collaborative initiatives can also drive the development of innovative cybersecurity solutions tailored to the unique needs of smart cities. This comprehensive cybersecurity is vital for security in smart cities’ measures.
5 Surprising Facts About Cybersecurity in Smart Cities
- Connected infrastructure expands the attack surface: many smart-city systems use legacy devices with weak security, so a breach of a single sensor or traffic camera can cascade into broader network control.
- Physical safety depends on digital security: cyberattacks on smart grids, traffic management, or emergency response systems can create real-world hazards, from blackouts to accidents.
- Privacy risks are amplified by sensor fusion: combining data from cameras, IoT sensors, transit cards, and mobile signals can reveal detailed movement patterns and identities even when individual sources are anonymized.
- Supply-chain vulnerabilities matter more: third-party firmware, cloud services, and municipal vendor ecosystems introduce hidden risks where a compromise at a supplier can affect multiple cities simultaneously.
- Resilience requires interdisciplinary governance: effective cybersecurity in smart cities needs coordination across municipal departments, utility operators, private vendors, and citizens — technical fixes alone are insufficient.
How does cyber security impact security in smart cities?
Cyber security directly affects the security in smart cities by protecting smart city networks, smart meters, and iot-based smart systems from attacks that could disrupt smart city services and infrastructure. Implementing cybersecurity best practices preserves the cybersecurity and privacy of citizens and maintains the integrity of smart governance, smart transportation systems, and other digital technologies used in smart city projects.
What are the main threats to critical infrastructure and systems for smart cities?
Critical infrastructure in smart cities faces threats such as ransomware, supply-chain compromises, sensor spoofing, and denial-of-service attacks that target smart traffic controls, smart meters, and public safety systems. These threats can degrade services and infrastructure, undermining the operation of smart services and the integrity of smart city networks unless cybersecurity experts and robust defenses are in place.
Why are smart cities vulnerable and what challenges facing smart cities should planners expect?
Smart cities vulnerable status stems from broad connectivity, legacy systems, and widespread data collection. Challenges facing smart cities include securing heterogeneous devices, balancing cybersecurity and data privacy, and updating governance to address significant cybersecurity challenges associated with smart technologies. Cities become safer when they plan for these issues early in smart city projects.
How can cities become better at protecting and protect smart infrastructure?
Cities can protect smart infrastructure by adopting an approach to cybersecurity that includes risk assessments, segmentation of smart city networks, regular patching, strong identity and access management, and incident response planning. Training cybersecurity experts and promoting cybersecurity practices across agencies improves resilience of services and infrastructure.
What cybersecurity best practices should be used in smart city projects and services?
Cybersecurity best practices for smart city projects include encrypting data in transit and at rest, applying least-privilege access, using secure development lifecycles for iot-based smart applications, conducting regular penetration testing, and enforcing policies for smart city governance. These practices reduce risks to smart transportation systems, smart meters, and other systems for smart cities.
How does the context of smart cities change the approach to cybersecurity and privacy?
The context of smart cities — dense populations, integrated services, and extensive data collection — requires an approach to cybersecurity that emphasizes privacy-by-design, transparency, and community engagement. Balancing smart cities collect vast amounts of personal and operational data with citizens’ rights is essential for sustainable smart cities and trust in smart city services.
Who should be involved in securing smart city services and infrastructure?
Securing smart city services requires collaboration among municipal IT teams, cybersecurity experts, vendors, regulators, and community stakeholders. Multi-disciplinary coordination ensures that smart city networks, smart governance frameworks, and operation of smart services incorporate both technical defenses and policy measures to address significant cybersecurity challenges.
What are the implications of cybersecurity and data risks for the future of smart cities?
Cybersecurity and data risks can impact the future of smart cities by influencing adoption rates, investment in digital technologies, and public trust. If cities are becoming increasingly connected but fail to address cybersecurity practices, they risk disruptions to smart transportation systems, energy grids, and other services that make smart cities functional and sustainable.
How can smart city planners mitigate challenges associated with smart technologies used in smart city systems?
Planners can mitigate challenges associated with smart systems by designing resilient architectures, prioritizing vendor security requirements, investing in monitoring and threat intelligence, and ensuring interoperability standards. Emphasizing secure procurement and lifecycle management helps cities use technologies safely and supports the long-term integrity of smart city networks.