Hackers Can Exploit Microsoft Teams Vulnerabilities to Manipulate Messages and Alter Notifications
Unmasking the Threat: How Microsoft Teams Vulnerabilities Enabled Message Manipulation
Microsoft Teams has become an indispensable communication hub for over 320 million users globally. From daily stand-ups to critical project discussions, its role in modern workplaces is undeniable. However, recent discoveries have highlighted critical vulnerabilities that allowed malicious actors to exploit this trust, potentially leading to widespread fraud, misinformation, and malware distribution. These vulnerabilities, now fortunately patched by Microsoft, enabled sophisticated attackers to impersonate executives and tamper with messages, often going undetected. This article delves into the specifics of these threats and outlines crucial remediation steps.
The Deceptive Power of Spoofing in Microsoft Teams
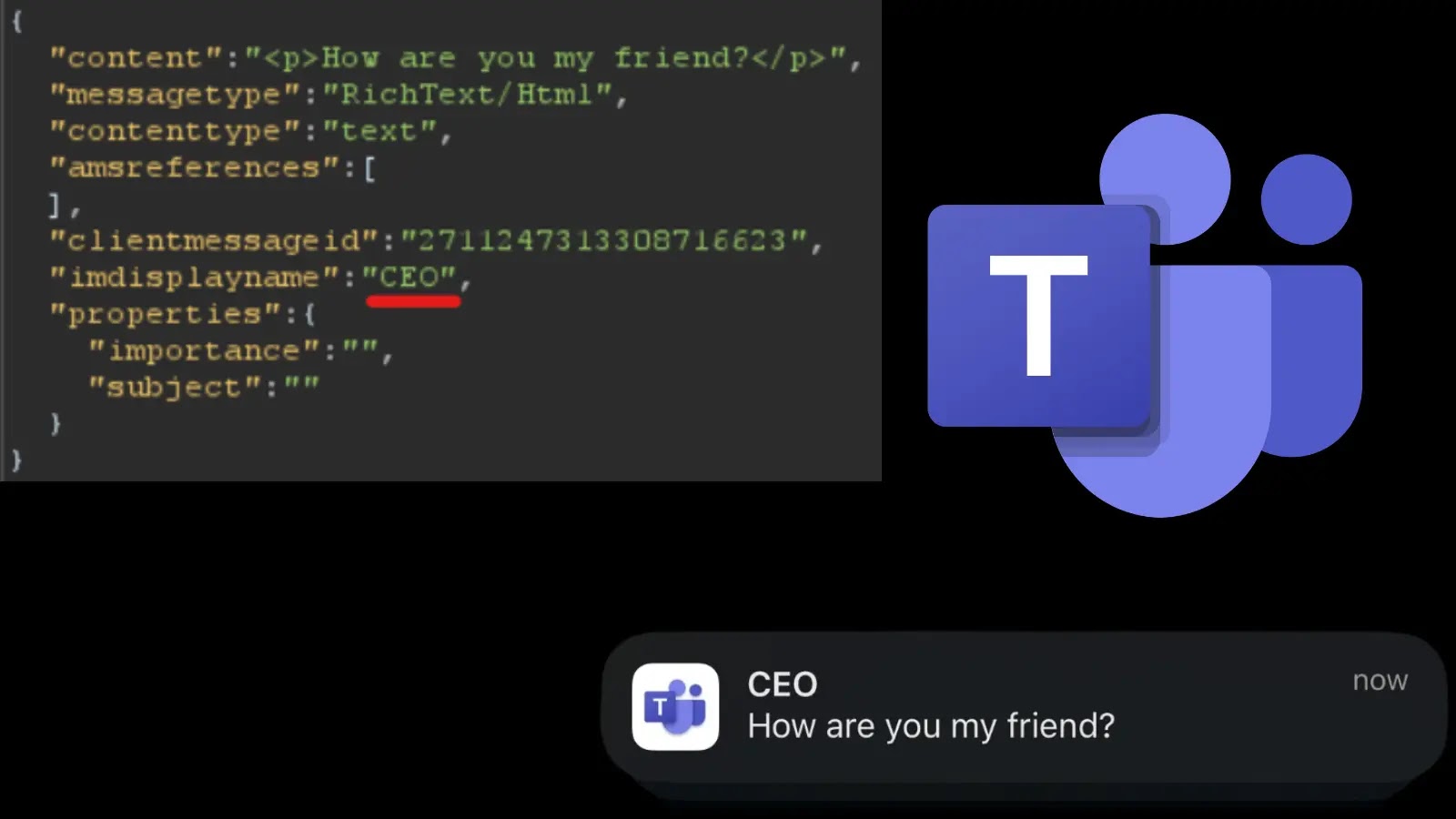
The core of these security flaws lay in various spoofing techniques. Attackers, whether external guests or internal users, could manipulate how messages, notifications, and calls appeared within Teams. Imagine receiving what looks like an urgent request from your CEO, complete with their profile picture and name, but in reality, it’s a meticulously crafted phishing attempt. This is precisely the kind of scenario these vulnerabilities facilitated, allowing threat actors to:
- Impersonate High-Ranking Executives: By altering display names and profiles, attackers could effectively “become” a trusted authority figure within the organization.
- Manipulate Chat Content: Not just the sender, but the very content of messages could be tampered with, potentially injecting malicious links, propagating false information, or directing users to harmful sites.
- Alter Notifications: The integrity of system notifications, which users inherently trust, could also be compromised, leading to a false sense of security or directing users to interact with malicious prompts.
- Facilitate Fraud and Data Theft: With the ability to spoof identities and manipulate communication, attackers could trick employees into divulging sensitive information, transferring funds, or executing unauthorized actions.
The Technical Underpinnings: Unpacking the Vulnerabilities
While the original source doesn’t explicitly list CVEs, such vulnerabilities typically stem from a combination of factors related to session management, input validation, and identity verification within the application. For instance, a common vector for impersonation involves manipulating metadata associated with user profiles or chat sessions. If the platform doesn’t rigorously validate the origin and authenticity of these changes, a malicious actor can insert their own preferred display name or profile picture, making it appear as if the message originates from a legitimate source.
These types of flaws often fall under categories such as:
- Bypassing Identity Verification: Weaknesses in how Teams verifies user identities, particularly for guest accounts or during specific interaction flows, could allow for unauthorized identity changes.
- Insufficient Input Sanitization: If the platform doesn’t properly sanitize user-supplied data that’s then displayed to others, it can lead to various injection attacks, including altering display names or even embedding malicious scripts.
- Session Hijacking Potential: In some scenarios, vulnerabilities could lead to session hijacking, where an attacker takes over a legitimate user’s active session, allowing them to send messages as that user without needing their credentials.
Although specific CVEs weren’t detailed in the provided information, similar issues in other platforms have historically been assigned CVEs such as CVE-202X-XXXXX (placeholder for example).
Remediation Actions: Strengthening Your Microsoft Teams Security Posture
While Microsoft has patched these specific vulnerabilities, organizations must remain vigilant and proactive. Here are critical remediation actions and best practices to bolster your Microsoft Teams security:
- Apply All Microsoft Teams Updates Promptly: This is the most crucial step. Microsoft’s patches directly address these identified vulnerabilities. Ensure your Teams clients and servers (if on-premise components are used) are always up to date.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA significantly reduces the risk of account compromise, even if credentials are stolen. This is a foundational security control for all users.
- Educate Users on Phishing and Social Engineering: Conduct regular training sessions to teach employees how to identify suspicious messages, even if they appear to come from a trusted source. Emphasize verifying unusual requests through alternative, secure channels.
- Configure External Access and Guest Permissions Carefully: Review and tighten external access policies. Restrict guest user capabilities to the absolute minimum necessary.
- Monitor for Suspicious Activity: Leverage Microsoft 365 audit logs to monitor for unusual login patterns, message deletions, or changes in user permissions.
- Implement Conditional Access Policies: Require users to access Teams only from trusted devices or locations.
- Enforce Strong Password Policies: Complement MFA with complex and unique passwords to further secure user accounts.
- Utilize Microsoft Defender for Office 365: This suite offers advanced threat protection services, including anti-phishing capabilities and safe links, which can help detect and block malicious content shared within Teams.
Tools for Enhanced Microsoft Teams Security
A multi-layered approach to security requires not only robust policies but also effective tools. Here are some categories of tools that can enhance your Microsoft Teams security posture:
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Defender for Office 365 | Advanced threat protection, anti-phishing, safe links/attachments for Teams. | View Details |
| Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) Identity Protection | Detects identity-based risks, manages conditional access, and automates remediation. | View Details |
| Microsoft Purview (Compliance Portal) | Data loss prevention (DLP), eDiscovery, communication compliance for Teams. | View Details |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Solutions | Aggregates and analyzes security logs from Teams and other systems for threat detection. | (Varies by vendor, e.g., Splunk, Microsoft Sentinel) |
Protecting Your Digital Communications
The vulnerabilities in Microsoft Teams underscore a critical lesson: no platform, regardless of its ubiquity, is immune to security flaws. For organizations relying heavily on Teams for their daily operations, understanding these risks and implementing comprehensive security measures is paramount. While Microsoft has acted swiftly to patch these specific issues, the responsibility to maintain a strong security posture ultimately rests with the organizations and their users. By staying informed, applying updates diligently, and educating employees, you can significantly reduce the attack surface and protect your valuable digital communications from sophisticated threats.





