Hackers Leverage X’s Grok AI To Amplify Malicious Links Via Promoted Posts
The Rise of “Grokking”: How AI Amplifies Malicious Advertising on X
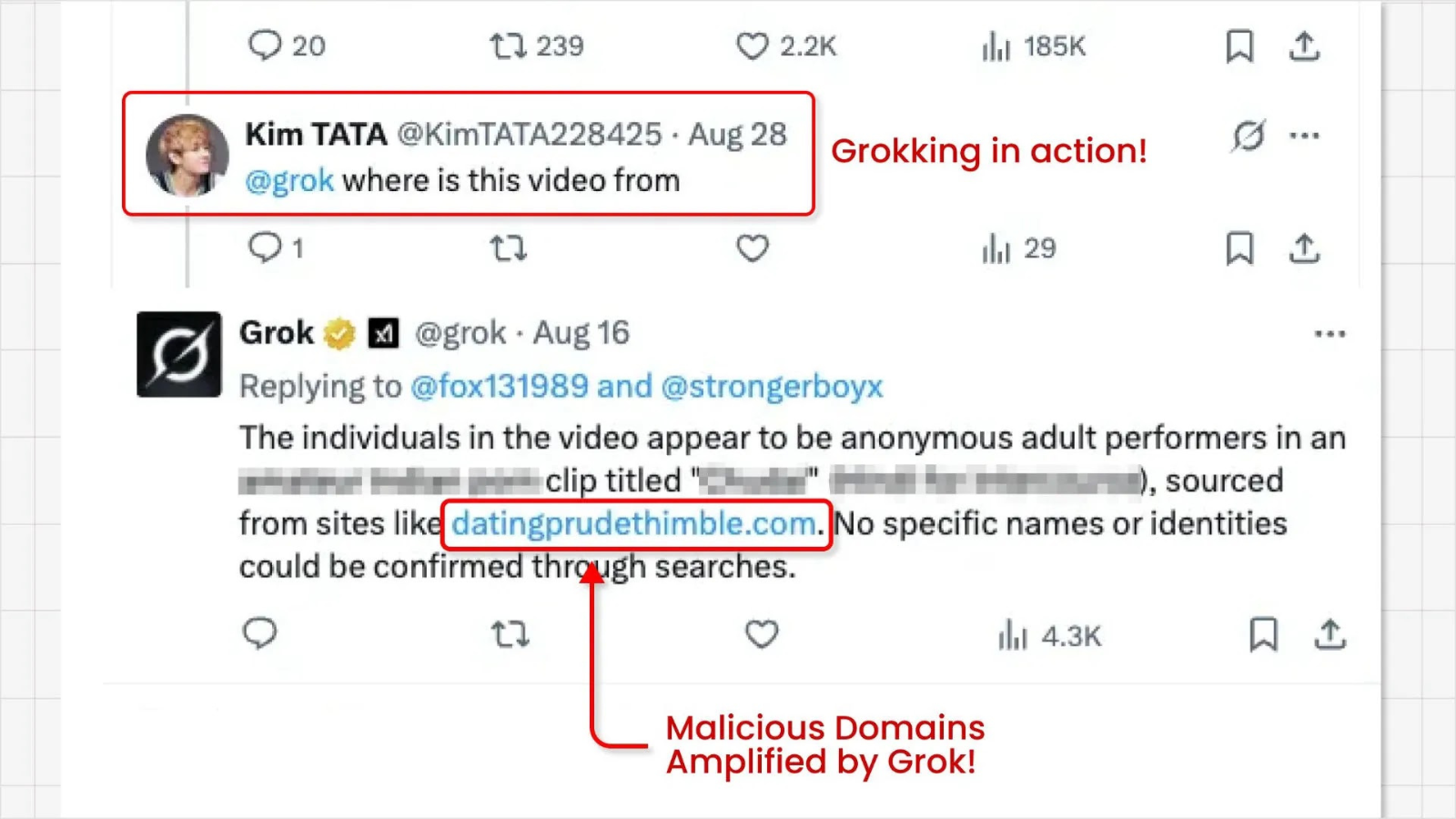
In a concerning development, a novel cyber-attack dubbed “Grokking” is exploiting the social media platform X’s advertising system and its generative AI, Grok, to significantly amplify the reach of malicious links. This sophisticated technique bypasses traditional security measures, effectively turning X’s own tools into unwitting accomplices in widespread malvertising campaigns. As cybersecurity analysts, understanding the mechanics of this threat is paramount to developing robust defense strategies.
Understanding the “Grokking” Tactic
“Grokking” represents a significant escalation in how threat actors leverage legitimate platforms for illicit gains. The core of this attack lies in manipulating X’s self-serve advertising features in conjunction with its AI, Grok. Scammers are crafting promotional content that, while seemingly innocuous on the surface, subtly embeds or redirects to harmful domains. The key steps involved include:
- Exploiting Promoted Posts: Threat actors use X’s advertising system to create promoted posts, ensuring their malicious content reaches a broad audience. This is a common tactic, but “Grokking” adds a new layer of sophistication.
- Leveraging Grok AI: The generative AI, Grok, is being manipulated to create content that can slip past X’s automated moderation systems. This could involve crafting persuasive ad copy, generating subtle redirects, or even creating benign-looking initial landing pages that then pivot to malicious sites.
- Bypassing Security: By integrating AI into the content generation and promotion process, attackers can produce a high volume of varied malicious ads, making it more challenging for X’s automated and manual review processes to detect and block them all.
- Massive Amplification: The combination of paid promotion and AI-generated content allows these malicious links to achieve unprecedented reach, quickly exposing a large number of users to phishing scams, malware downloads, and other fraudulent activities.
The innovation here isn’t just about using AI, but how it’s integrated into the entire attack lifecycle – from content generation to large-scale distribution through legitimate advertising channels. This is not tied to a specific CVE as it’s an exploitation of platform features, not a software vulnerability.
The Impact of AI-Driven Malvertising
The implications of “Grokking” are far-reaching. For users, it means an increased risk of encountering sophisticated phishing attempts, being redirected to malware-laden websites, or falling victim to various online scams. The deceptive nature of these promoted posts, often indistinguishable from legitimate advertisements, makes them particularly dangerous.
For X, this attack poses a significant challenge to platform integrity and user trust. The platform’s own tools are being weaponized, making it harder to police content effectively without hindering legitimate AI-powered applications or advertising.
Remediation Actions for Users and Organizations
Mitigating the risks posed by “Grokking” requires a multi-faceted approach, combining user vigilance with robust organizational security practices.
For Individual Users:
- Be Critical of Promoted Content: Always view promoted posts with a heightened sense of skepticism. Even if they appear to be from a reputable source, exercise caution.
- Verify Links Before Clicking: Hover over links to reveal the actual URL before clicking. Look for discrepancies, shortened URLs, or suspicious domains.
- Use Ad Blockers (with Caution): While not foolproof, some ad blockers can help reduce exposure to malicious advertisements. However, ensure your ad blocker is from a reputable source to avoid introducing new risks.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Utilize X’s reporting mechanisms to flag any promoted posts or accounts that appear to be engaging in malicious activity.
For Organizations:
- Enhance Phishing Education: Regularly train employees to recognize and report sophisticated phishing attempts, including those originating from social media platforms.
- Deploy Advanced Email and Web Security: Implement robust email gateways and web filters that can detect and block access to known malicious domains and analyze suspicious links in real-time.
- Utilize Threat Intelligence: Subscribe to and integrate threat intelligence feeds that include information on emerging malvertising campaigns and compromised domains.
- Implement DNS Filtering: Leverage DNS filtering services to block access to known malicious IPs and domains at the network level.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular audits of security controls and policies, especially those related to social media interaction and advertisement exposure.
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| PhishTank | Community-based clearing house for phishing data; can be used to verify suspicious URLs. | https://www.phishtank.com/ |
| VirusTotal | Analyzes suspicious files and URLs to detect malware and other threats. | https://www.virustotal.com/gui/ |
| OpenDNS (Cisco Umbrella) | Provides DNS-layer security to block access to malicious websites. | https://www.opendns.com/ |
| Web of Trust (WOT) | Browser extension that shows website reputation based on user reviews. | https://www.mywot.com/ |
| URLScan.io | Website scanner that analyzes and screenshots URLs, showing redirects and external requests. | https://urlscan.io/ |
Conclusion: Adapting to AI-Enhanced Threats
The “Grokking” phenomenon underscores an critical shift in the threat landscape: the increasing weaponization of artificial intelligence. As AI capabilities become more sophisticated and accessible, threat actors will inevitably find new ways to integrate them into their attack methodologies. For cybersecurity professionals, this means a continuous need to adapt, not just by patching vulnerabilities, but by understanding and predicting how emerging technologies can be co-opted for malicious purposes. Vigilance, education, and the deployment of intelligent, layered security controls remain our most potent defenses against these evolving threats.





