How Threat Intelligence Feeds Help Organizations Quickly Mitigate Malware Attacks
The Relentless Evolution of Malware Threats
Organizations today grapple with an unprecedented surge in sophisticated malware attacks. Ransomware cripples critical infrastructure, phishing campaigns compromise credentials, and zero-day exploits silently breach defenses, often before security teams even realize an attack is underway. The speed at which these threats evolve and proliferate makes traditional, reactive security measures increasingly insufficient. To stay ahead, a proactive defense strategy is no longer optional; it’s a fundamental necessity.
Threat Intelligence Feeds: Your Proactive Defense Nexus
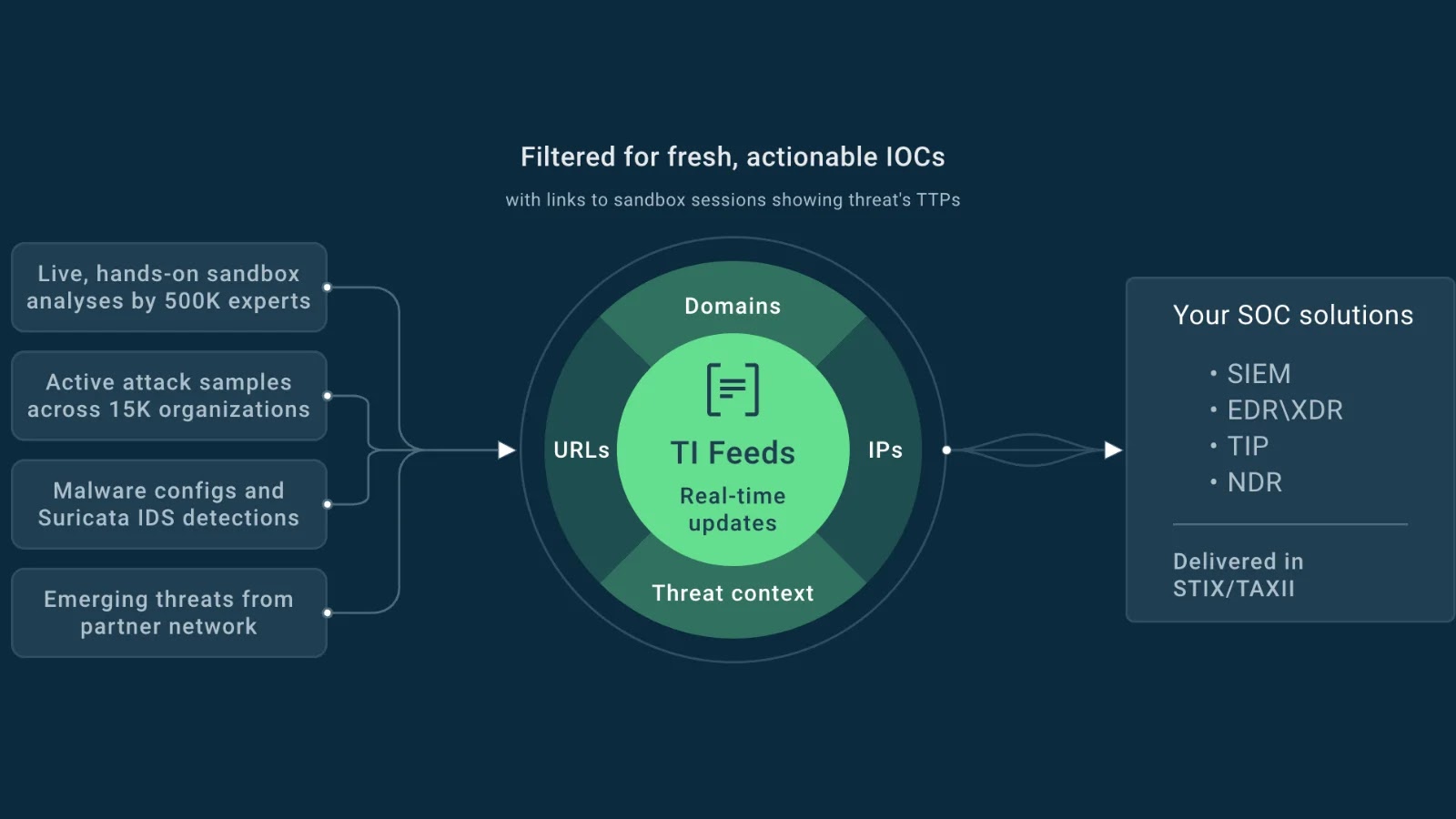
In this high-stakes environment, threat intelligence feeds have emerged as a pivotal resource. These feeds are not merely data dumps; they are dynamic conduits of real-time, actionable insights designed to empower security teams. By aggregating a wealth of indicators of compromise (IoCs), threat intelligence feeds enable organizations to detect and neutralize malicious activity with remarkable speed, often before widespread damage can occur. Think of them as an early warning system, filtering out the noise to deliver critical, context-rich information directly to your security operations center (SOC).
What Constitutes a Threat Intelligence Feed?
A robust threat intelligence feed is built upon a foundation of diverse data points, meticulously collected and analyzed. Key components typically include:
- Malicious IP Addresses: Known command-and-control servers, botnet participants, or sources of attack traffic.
- Malware Hashes: Unique digital fingerprints of known malware variants, allowing for rapid identification.
- Phishing Domains and URLs: Websites and links associated with credential harvesting or malware distribution.
- Email Headers and Sender Information: Patterns and anomalies indicative of phishing or spam campaigns.
- Vulnerability Information: Details on recently discovered weaknesses in software and hardware, including relevant CVEs like CVE-2023-3881 (WinRAR SFX vulnerability exploited by threat actors) or CVE-2023-46805 (Ivanti Connect Secure authentication bypass).
- Threat Actor Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs): Behavioral patterns and methodologies used by specific threat groups.
How Threat Intelligence Feeds Drive Rapid Malware Mitigation
The core value of threat intelligence feeds lies in their ability to operationalize information, transforming raw data into tangible security actions. This happens through several critical mechanisms:
- Early Detection and Blocking: By integrating feeds into firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and SIEM platforms, organizations can automatically block communication with known malicious IPs or domains, preventing malware from establishing beachheads or exfiltrating data.
- Enhanced Incident Response: During an active incident, threat intelligence provides crucial context. If an internal system communicates with a suspicious IP, cross-referencing it with a feed instantly flags it as potentially malicious, accelerating investigation and containment efforts.
- Proactive Vulnerability Management: Feeds often highlight actively exploited vulnerabilities, prompting security teams to prioritize patching or implement compensating controls for specific CVEs before they are leveraged in an attack.
- Improved Threat Hunting: Security analysts can leverage feed data to actively search for IoCs within their network, uncovering dormant threats or identifying early stages of compromise that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Reduced Mean Time To Respond (MTTR): By providing immediate insights and context, threat intelligence significantly reduces the time it takes to detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents, thereby mitigating the potential impact of a malware attack.
Integrating Threat Intelligence into Your Security Ecosystem
Effective utilization of threat intelligence requires seamless integration into existing security infrastructure. This typically involves:
- SIEM Platforms: Ingesting feeds directly into Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems for correlation with internal log data and alert generation.
- Firewalls and IDS/IPS: Configuring these perimeter defenses to automatically block traffic to and from blacklisted entities identified by the feeds.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions: Using IoCs from feeds to enhance endpoint monitoring and malware detection capabilities.
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) Platforms: Automating responses based on intelligence feed triggers, such as isolating compromised hosts or blocking malicious hashes.
Remediation Actions: Implementing a Threat-Intelligent Defense
To fully leverage threat intelligence for rapid malware mitigation, organizations should implement the following remediation actions:
- Select Reputable Feeds: Choose threat intelligence providers known for their accuracy, timeliness, and relevant coverage to your industry. Consider both open-source and commercial options.
- Automate Integration: Configure automated ingestion of threat intelligence feeds into your existing security tools (SIEM, firewall, EDR) to ensure real-time updates and proactive blocking.
- Establish Incident Response Playbooks: Develop clear, predefined procedures for responding to alerts generated by threat intelligence, outlining steps for verification, containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Regularly Review and Tune Feeds: Periodically assess the effectiveness of your feeds and adjust sources or filtering rules to minimize false positives and ensure relevance.
- Educate and Train Staff: Ensure your security team understands how to interpret and act upon threat intelligence data, fostering a proactive security posture.
Conclusion: Strengthening Defenses with Actionable Intelligence
The landscape of cyber threats, particularly malware, demands a dynamic and intelligent defense. Threat intelligence feeds are not just another security tool; they are a strategic asset that transforms an organization’s ability to anticipate, detect, and mitigate attacks. By delivering real-time, actionable data, these feeds empower security teams to transition from a reactive stance to a proactive defense, significantly reducing the window of opportunity for attackers and bolstering overall resilience against the ever-evolving malware threat.