How to choose between NAS and SAN
How to Choose Between SAN and NAS: Storage Area Network vs Network Attached Storage
In the rapidly evolving domain of data management, understanding storage options is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their IT infrastructure. SAN and NAS are two popular storage solutions that cater to different storage needs. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we recognize the paramount importance of selecting the right storage architecture to empower your enterprise, ensuring seamless operations and secure data management. By shedding light on SAN vs NAS, we aim to provide clarity and guidance for businesses seeking reliable and efficient storage resources. Safeguarding your enterprise is our mission, and we are dedicated to offering expert insights into these technologies.
Understanding SAN and NAS
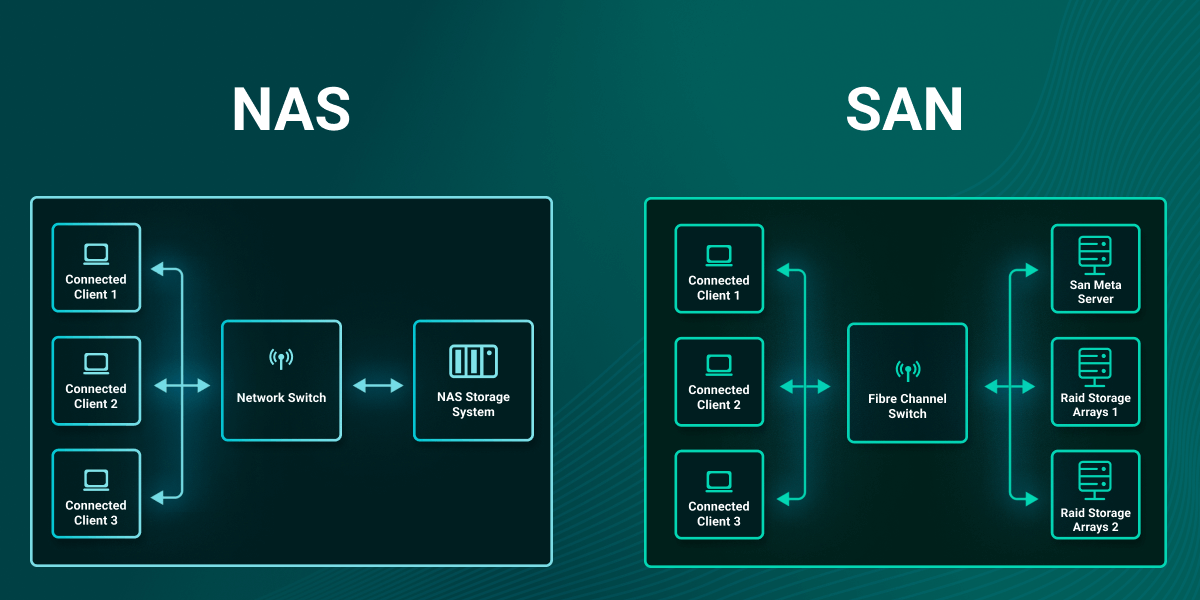
In the realm of data storage, SAN and NAS represent distinct approaches to managing and accessing storage resources. Both NAS and SAN provide unique benefits and are designed to meet different organizational requirements. As a centralized storage solution, SAN offers block-level storage through a dedicated network, enabling high-speed access to a network of storage devices. On the other hand, NAS, or network attached storage, is a file-level data storage device connected to a local area network, facilitating file storage and sharing across multiple users. Understanding these storage architectures is essential for making informed decisions about your business’s data storage needs.
What is a Storage Area Network (SAN)?
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a high-performance, dedicated network that provides block-level storage, designed to improve the accessibility and management of large volumes of data. SAN solutions are ideal for environments that demand high-speed, reliable access to data, such as enterprise-level applications and databases. By utilizing SAN protocols, such as Fibre Channel, a storage area network ensures that data is efficiently transferred between servers and storage devices. SAN storage is a preferred choice for organizations that require centralized and scalable storage capacity, offering robust data management capabilities to fortify your business infrastructure against potential threats.
What is Network Attached Storage (NAS)?
Network Attached Storage (NAS) refers to a type of storage system that connects directly to an Ethernet network, enabling seamless file storage and sharing. A NAS device provides file-level storage, making it an ideal solution for businesses that require easy access to shared files and documents over a local area network. NAS systems are renowned for their simplicity and efficiency, offering a cost-effective way to enhance data accessibility while ensuring data integrity. By using NAS, organizations can empower their teams to collaborate more effectively, enhancing productivity and streamlining workflows, all while maintaining a high level of data security.
Key Differences Between SAN and NAS
The key differences between SAN and NAS lie in their architecture, functionality, and intended use cases.
| Aspect | SAN | NAS |
|---|---|---|
| When choosing a storage type, organizations must consider their specific requirements for performance and cost, particularly in the context of NAS vs SAN storage. | Block-level storage | File-level storage |
| Network | Dedicated network | Standard Ethernet network |
| Main Priority | High-speed data transfers and scalability | Ease of use and accessibility for file sharing are significant advantages of network-attached storage, appealing to businesses prioritizing cost-effectiveness. |
| Complexity | More complex setup and investment | More economical and straightforward |
Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right storage solution for your organization’s unique needs.
Technical Aspects of SAN and NAS
Architecture of SAN
The architecture of a network-attached storage (NAS) system is designed to facilitate easy access to shared storage across a local area network. Storage Area Network (SAN) A SAN is designed to provide a dedicated storage solution that enhances data throughput and reliability, making it suitable for high-performance storage needs. SANs utilize a dedicated network to interconnect multiple storage devices with servers, enabling high-speed data transfers that are essential for enterprise environments with demanding storage needs. SAN protocols, such as Fibre Channel and iSCSI, ensure efficient communication between the servers and the storage devices, offering block-level storage access. This architecture allows for centralized storage management, providing a scalable storage capacity that can be expanded as business requirements grow, particularly through the use of a storage pool. By leveraging SAN solutions, organizations can ensure their critical data remains accessible and secure, supporting uninterrupted operations and robust data management.
Architecture of NAS
Network Attached Storage (NAS) architecture is centered around simplicity and accessibility, making it a favored storage system for many organizations seeking a user-friendly solution. A NAS device connects directly to an Ethernet network, facilitating seamless file-level data storage and sharing across a local area network. Unlike SAN, which requires a dedicated network, NAS uses the existing network infrastructure to provide storage resources, making it a cost-effective option. The architecture of NAS systems often includes multiple drives configured for redundancy and data protection, ensuring continuous data availability and integrity. This setup empowers businesses to efficiently manage file storage and sharing, enhancing collaboration and productivity while maintaining a secure data environment.
Performance Considerations
When evaluating SAN vs NAS for performance considerations, it is crucial to understand the specific storage needs of your organization, including whether a NAS file solution may be more appropriate.
| Storage Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| SAN |
|
| NAS |
|
The choice between SAN and NAS ultimately depends on the balance between performance and ease of use required by your business, with SAN being suited for high-demand scenarios and NAS offering a more straightforward, economical approach. By carefully assessing these performance aspects, organizations can select the appropriate storage architecture to maximize efficiency and ensure data security.
Use Cases for SAN and NAS
When to Use SAN Storage
In environments where high performance and reliability are non-negotiable, Storage Area Networks (SAN) stand out as the ideal storage solution. SAN is particularly advantageous for businesses managing large-scale databases or applications that demand swift data access and block-level storage. With its dedicated network, SAN provides unparalleled data throughput, making it indispensable for industries such as finance and healthcare, where data integrity and speed are critical. Organizations seeking centralized storage that can seamlessly scale with growing data storage needs will find SAN storage solutions to be robust, secure, and reliable, ensuring continuous operations without compromise.
When to Use NAS Storage
Network Attached Storage (NAS) Network-attached storage emerges as an optimal choice for businesses prioritizing ease of use and cost-effectiveness in their data management strategies, especially when compared to SAN. Ideal for small to medium-sized enterprises, NAS systems facilitate effortless file storage and sharing across a local area network, leveraging the existing Ethernet network infrastructure. This type of storage is particularly beneficial for organizations with collaborative teams, offering a straightforward approach to accessing and sharing documents. NAS devices deliver reliable file-level storage, ensuring data integrity while empowering users with secure and efficient data access. For businesses seeking a practical and economical storage solution, NAS provides the simplicity and accessibility required to enhance productivity.
Comparing Use Cases: NAS vs SAN
The decision between NAS and SAN storage solutions hinges on specific organizational needs and infrastructure demands.
| Storage Type | Features |
|---|---|
| SAN | Offers a dedicated network capable of handling high-speed, block-level data transfers. Suitable for environments with intensive data processing requirements. Requires higher investment and setup complexity but delivers unmatched performance and scalability. |
| NAS | Prioritizes user-friendly file storage and sharing solutions. Ideal for organizations with collaborative, team-oriented environments. Provides a more economical and accessible option, simplifying data management. |
By carefully evaluating these use cases, businesses can strategically select the storage architecture that best aligns with their operational needs and future growth plans.
Cost Analysis of SAN vs NAS
Initial Investment for SAN Solutions
When considering the initial investment for SAN solutions, organizations must account for the substantial costs associated with deploying a dedicated network. SAN requires specific hardware components, such as Fibre Channel switches and storage area network devices, which are essential for delivering high-speed, block-level storage capabilities. The complexity of SAN architecture demands skilled personnel for installation and maintenance, further adding to the initial expenditure, making it more expensive than NAS. However, the investment in SAN solutions is justified by its robust performance, scalability, and reliability, making it an invaluable asset for enterprises with demanding storage needs and a focus on centralized storage management.
Cost of NAS Solutions
NAS solutions present a more cost-effective alternative to SAN, particularly suitable for small to medium-sized enterprises. The initial investment in NAS systems is generally lower because they leverage existing Ethernet networks and require less specialized equipment. A NAS device is typically easier to set up and manage, reducing the need for extensive IT resources. While NAS may not offer the same level of performance as SAN, it provides an economical option for file-level data storage and sharing across a local area network. For businesses seeking a practical network storage solution without compromising on data accessibility and security, NAS is an advantageous choice.
Long-term Cost Considerations
Over the long term, the cost considerations for SAN and NAS solutions extend beyond initial investments. SAN offers significant advantages in scalability and performance, which can lead to cost savings as businesses grow and their storage needs evolve. However, ongoing maintenance and upgrades for SAN systems can be costly. NAS solutions, while less expensive upfront, may incur costs related to expanding storage capacity or integrating additional NAS devices as data storage demands increase. Ultimately, businesses must weigh the long-term benefits of SAN’s robust architecture against the affordability and simplicity of NAS when planning their storage infrastructure strategies, especially considering that SAN doesn’t tell the whole story.
Future Trends in Storage Solutions
Evolution of SAN and NAS Technologies
The landscape of SAN and NAS technologies is continually evolving, driven by advancements in data storage and network protocols. SAN solutions are increasingly adopting newer technologies such as NVMe over Fabrics, enhancing speed and data throughput. Meanwhile, NAS systems are incorporating AI and machine learning capabilities to optimize file-level storage management. As storage needs grow more complex, both SAN and NAS are evolving to offer greater efficiency, reliability, and security. This evolution underscores the importance of staying abreast of technological developments to ensure that storage architectures remain aligned with organizational objectives and data management strategies.
Hybrid Storage Solutions
Hybrid storage solutions are emerging as a compelling option for organizations seeking the best of both SAN and NAS technologies. By integrating the high-performance block-level storage of SAN with the accessible file-level storage of NAS, hybrid systems provide a versatile approach to data management. These solutions allow businesses to customize their storage architecture based on specific needs, balancing speed, capacity, and cost-effectiveness. Hybrid storage enables seamless data movement and scalability, making it an attractive choice for enterprises aiming to optimize their IT infrastructure while ensuring robust data security and availability across different storage environments.
Impact of Cloud Storage on SAN and NAS
The rise of cloud storage is significantly impacting the dynamics of SAN and NAS solutions. Cloud storage offers scalable, on-demand resources that complement traditional storage architectures, enabling businesses to extend their storage capacity without significant hardware investments. As organizations increasingly adopt hybrid cloud strategies, SAN and NAS solutions are evolving to integrate with cloud environments, offering flexibility and redundancy. This integration allows businesses to leverage the strengths of both on-premise and cloud storage, ensuring comprehensive data management and protection. The impact of cloud storage is reshaping storage strategies, emphasizing the need for adaptable and forward-thinking infrastructure solutions.
5 Surprising Facts About How to Choose Between NAS and SAN
- NAS (Network Attached Storage) is typically easier to set up and manage than SAN (Storage Area Network), making it ideal for small to medium-sized businesses.
- SAN offers higher performance and scalability, which is crucial for data-intensive applications, whereas NAS may struggle under heavy loads.
- NAS devices often use standard file protocols like NFS and SMB, while SAN relies on block-level storage, allowing for more complex data management.
- While NAS is often seen as a more affordable option, the total cost of ownership for SAN can be justified in environments where speed and reliability are paramount.
- Some hybrid solutions combine NAS and SAN capabilities, offering flexibility for businesses that require both file and block storage.
What are the main differences between NAS and SAN?
The main difference between NAS and SAN lies in their architecture and functionality. NAS, or Network Attached Storage, is a file-level data storage device connected to a network, providing file-based data storage services to other devices. In contrast, SAN, or Storage Area Network, is a tightly coupled system that offers block-level storage, often used in enterprise environments for dedicated storage solutions. Understanding these key differences can help you choose the right option for your needs.
How does NAS provide file-based data storage services?
NAS systems offer file-based data storage services through a dedicated server that connects to a network. This allows multiple users and devices to access a shared pool of storage, facilitating collaboration and data sharing. NAS is a good choice for environments where file sharing and easy access to data are essential.
When should I use NAS over SAN?
Choosing NAS over SAN is ideal when your primary need is file-level storage rather than block-level storage. NAS is also typically more cost-effective and easier to manage, making it suitable for small to mid-range environments. If your organization primarily requires file access and collaboration, NAS is a strong contender.
What are the advantages of SAN solutions?
The primary strength of a SAN lies in its ability to provide high-speed, block-level storage, making it suitable for applications that require fast access to data, such as databases and virtual machines. SAN storage can be summed up as a powerful solution for organizations needing dedicated storage for a group of servers, providing efficient data management capabilities.
Can NAS replace large tape backups?
Yes, NAS can replace large tape backups, particularly in environments where fast data access and recovery are necessary. High-end NAS systems offer native data protection features, enabling organizations to efficiently manage backups and recover data without the delays associated with traditional tape storage.
What storage technologies are used in NAS and SAN?
Both NAS and SAN utilize different storage technologies tailored to their specific use cases. NAS typically uses standard protocols such as NFS or SMB for file sharing, while SAN employs Fibre Channel or iSCSI for block-level storage. Understanding these technologies can help in comparing these two popular storage architectures.
What types of applications benefit from SAN vs NAS?
When comparing SAN vs NAS, it’s important to consider the types of applications that benefit from each. SAN is typically used for high-performance applications requiring low latency, such as transactional databases, while NAS is suited for file-sharing applications, such as media streaming or collaborative work environments.
Are NAS and SAN storage solutions complementary?
Yes, NAS and SAN are as complementary solutions in many IT environments. Organizations often implement both systems to take advantage of the strengths of each. While SAN provides high-speed block storage for critical applications, NAS offers cost-effective file storage for general use, making them ideal for diverse workloads.