MAD-CAT Meow Attack Tool to Simulate Real-World Data Corruption Attacks
Data corruption attacks pose a severe threat to organizations, capable of crippling operations and eroding trust. Imagine a cyberattack where critical data simply vanishes or becomes irretrievably scrambled. This isn’t theoretical; it’s a stark reality, famously exemplified by the “Meow attacks” that targeted numerous unsecured databases in 2020, wiping countless records.
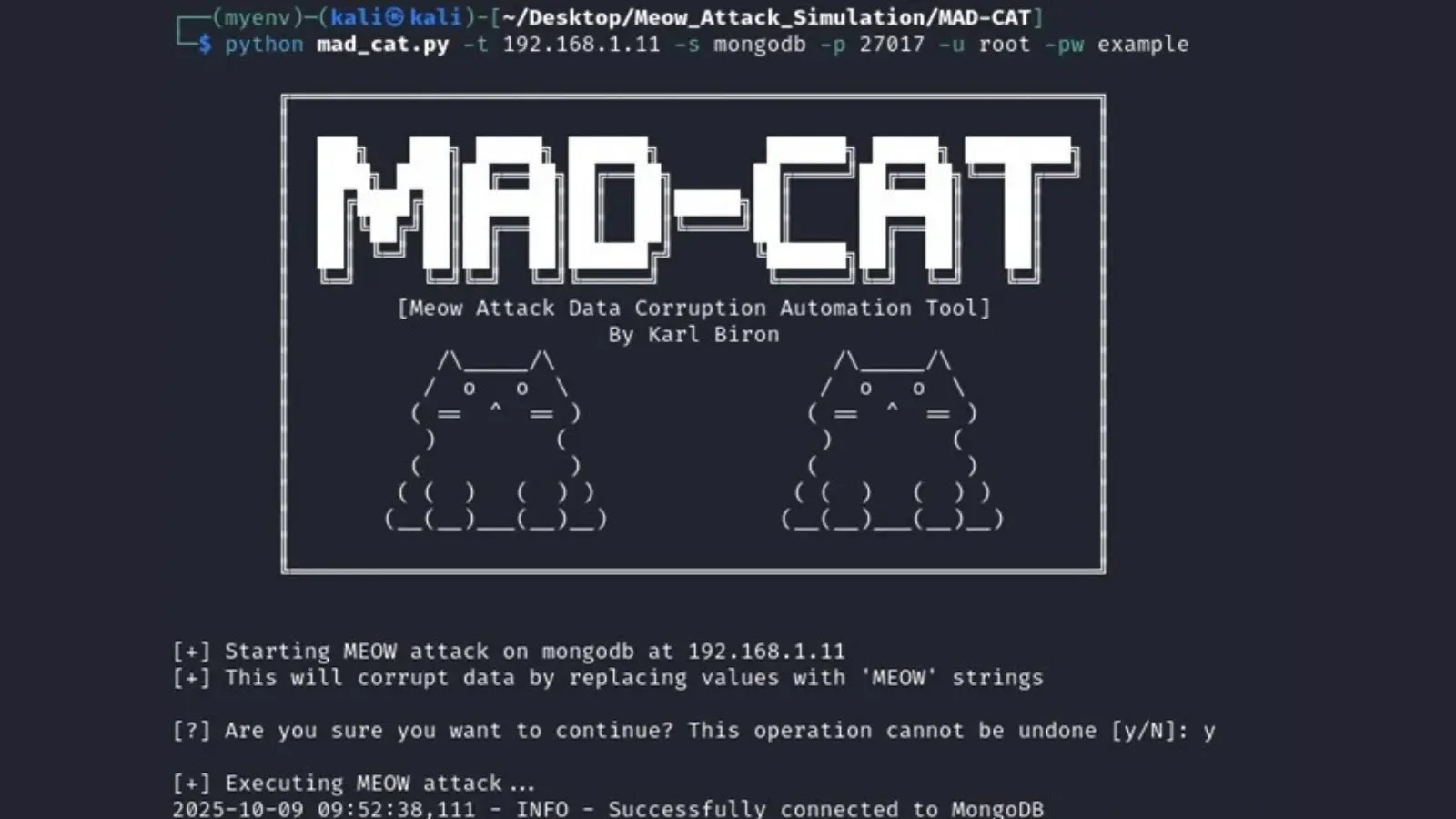
To help organizations better understand and defend against such destructive campaigns, security researcher Karl Biron of Trustwave developed MAD-CAT (Meow Attack Data Corruption Automation Tool). This Python-based tool empowers security professionals to simulate these real-world data corruption scenarios, effectively acting as an adversary to test an organization’s defenses and resilience.
Understanding the Meow Attacks and Their Legacy
The original Meow attacks, which surfaced prominently in 2020, were characterized by their straightforward yet devastating approach. Attackers scanned the internet for publicly exposed and unsecured NoSQL databases, primarily MongoDB and Elasticsearch. Once identified, they would initiate a rapid, automated deletion of all data within these databases, often replacing the database names with the word “meow.”
These attacks underscored a critical vulnerability: misconfigured or unauthenticated database instances. The impact was immediate and profound, leading to significant data loss for affected entities. While not always directly monetized through ransomware, the operational disruption and data integrity compromise were substantial. MAD-CAT directly targets the very platforms that were most vulnerable to these original attacks, providing a direct and relevant simulation experience.
Introducing MAD-CAT: The Meow Attack Data Corruption Automation Tool
MAD-CAT is a robust, open-source Python tool designed to replicate the destructive mechanisms of the Meow attacks across a range of popular database platforms. Developed by Karl Biron, it serves as a critical resource for penetration testers, security auditors, and developers looking to fortify their data storage systems against similar threats. The tool’s modular design allows it to interact with:
- MongoDB: A widely used NoSQL document database.
- Elasticsearch: A distributed search and analytics engine.
- Cassandra: A scalable NoSQL database for large data sets.
- Redis: An in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache, and message broker.
- CouchDB: A NoSQL document-oriented database.
- Hadoop HDFS: The Hadoop Distributed File System, a core component of big data processing.
By simulating data deletion or corruption on these platforms, MAD-CAT helps identify weak points in access controls, network segmentation, and authentication mechanisms before malicious actors exploit them.
How MAD-CAT Works: Simulating Destruction Safely
MAD-CAT operates by leveraging the client libraries for each supported database. When pointed at a target database, it attempts to connect without authentication or with weak default credentials, mirroring the methods employed by the original Meow attackers. Upon successful connection, it executes commands to delete or corrupt data, depending on the specific database’s architecture and the simulation parameters. This process helps to:
- Identify Open Ports and Services: Uncover databases exposed to the public internet without proper firewall rules.
- Test Authentication Mechanisms: Verify if default or weak credentials are in use.
- Assess Data Backup and Recovery Procedures: Challenge an organization’s ability to recover from a data-wiping event.
- Evaluate Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Determine if security tools can detect and block such destructive activity.
It’s crucial to emphasize that MAD-CAT is a powerful tool designed for authorized security testing within controlled environments. Misuse can lead to actual data loss. Always obtain explicit permission and operate within a sandboxed or test environment when using such tools.
Remediation Actions: Fortifying Your Databases
Defending against data corruption attacks like those simulated by MAD-CAT requires a multi-layered approach focusing on fundamental security hygiene. Proactive measures are far more effective than reactive scrambling after a breach.
- Implement Strong Authentication: Never use default credentials. Enforce strong, unique passwords for all database users and administrative accounts. Where possible, use multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Restrict Network Access: Databases should ideally not be directly exposed to the public internet. Use firewalls to restrict access to only trusted IPs and internal networks. Implement VPNs for remote access.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users and applications only the minimum necessary permissions to perform their functions. Avoid giving administrative privileges unnecessarily.
- Regular Backups: Implement a robust, tested backup strategy. Ensure backups are stored securely, are immutable where possible, and are regularly tested for restorability. Consider air-gapped or offsite backups.
- Regular Patching and Updates: Keep all database software, operating systems, and underlying infrastructure patched and up-to-date to address known vulnerabilities (e.g., potential CVE-2021-39232 for MongoDB or CVE-2021-34429 for Elasticsearch that could enable unauthorized access scenarios in certain configurations).
- Security Auditing and Logging: Enable comprehensive logging for all database activities, especially authentication attempts and data modifications. Regularly review these logs for suspicious activity.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Deploy and configure IDS/IPS solutions to monitor network traffic for anomalous patterns indicative of attack attempts.
- Security Scans and Penetration Testing: Regularly conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration tests, including using tools like MAD-CAT, to identify and rectify security weaknesses.
Tools for Database Security and Hardening
Integrating various tools into your security posture can significantly enhance your defense against data corruption attacks.
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| MAD-CAT | Simulates Meow-style data corruption attacks for penetration testing. | GitHub |
| OpenVAS/Greenbone | Vulnerability scanning for identifying exposed services and misconfigurations. | Greenbone.net |
| Nmap | Network discovery and port scanning to identify open database ports. | Nmap.org |
| Tenable Nessus | Comprehensive vulnerability assessment and compliance auditing. | Tenable.com |
| Grafana Loki | Centralized logging for analyzing database audit logs effectively. | Grafana.com |
Conclusion
The emergence of tools like MAD-CAT serves as a critical reminder of the persistent and evolving threat landscape. Data corruption attacks, though often simple in their execution, can have catastrophic consequences for any organization reliant on data integrity. By leveraging MAD-CAT, security professionals gain invaluable insight into their infrastructure’s resilience, transforming potential vulnerabilities into fortified defenses.
Proactive security measures, including robust authentication, stringent network segmentation, regular backups, and continuous security testing, are not optional but essential. Embracing a defensive posture that anticipates and simulates real-world threats is the most effective way to safeguard critical data against destructive campaigns.





