Microsoft Entra ID Vulnerability Let Attackers Escalate Privileges to Global Admin Role
A Critical Alert: Microsoft Entra ID Vulnerability Exposes Global Admin Privileges
The digital defense perimeter of countless organizations is under significant scrutiny following the discovery of a critical vulnerability within Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory). This weakness, if exploited, enables attackers to escalate privileges to the highly sensitive Global Administrator role. For IT professionals, security analysts, and developers managing hybrid environments, this revelation demands immediate attention and a clear understanding of the risks involved.
Understanding the Entra ID Vulnerability: Privilege Escalation Defined
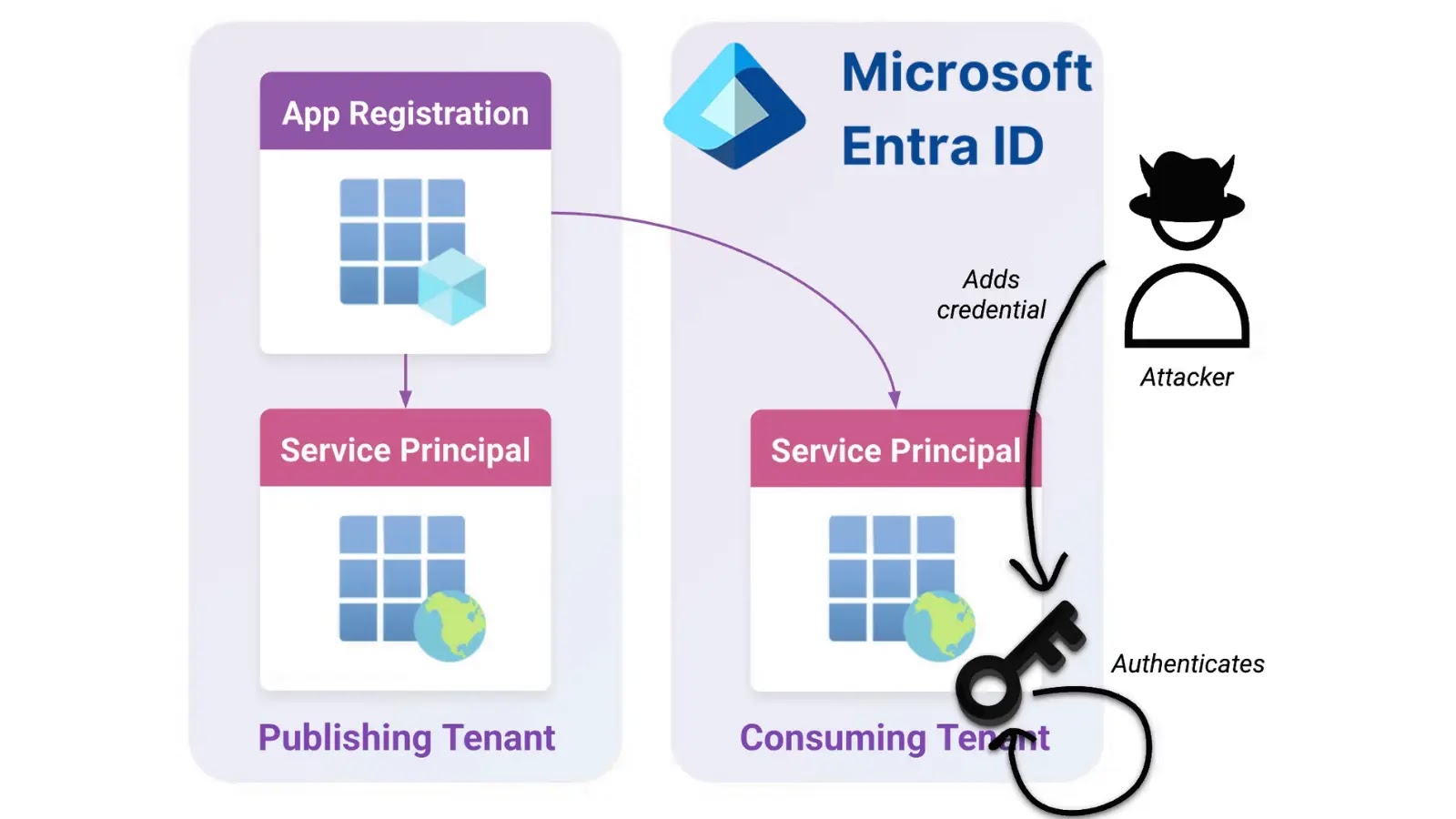
The core of this vulnerability lies in the potential for privilege escalation through the exploitation of first-party applications. Specifically, the risk is amplified for organizations operating with hybrid Active Directory environments that utilize federated domains. While details regarding a specific CVE are pending public release, the vulnerability was reportedly disclosed to the Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) in January 2025.
The implications are stark: an attacker who gains a foothold with certain administrative or application permissions can leverage this flaw to elevate their access to Global Administrator. This level of access grants complete control over an organization’s Entra ID tenant, including user management, application registrations, security policies, and much more. Such a compromise could lead to widespread data breaches, system disruption, and substantial reputational damage.
Impact on Hybrid Active Directory Environments
Organizations with hybrid Active Directory setups, where on-premises AD is synchronized with Microsoft Entra ID, are particularly susceptible. The vulnerability leverages the intricate trust relationships and synchronization mechanisms inherent in these configurations. Federated domains, often used for single sign-on (SSO) and identity management across diverse systems, introduce additional complexity and potential vectors for exploitation. This interconnectedness means a compromise in one part of the identity ecosystem can cascade throughout the entire infrastructure.
Key Tactics and Attack Vectors (Hypothetical)
- Exploitation of First-Party Applications: Attackers could target misconfigurations or vulnerabilities within applications developed by Microsoft that interact with Entra ID. This could involve manipulating application permissions or authentication flows.
- Leveraging Existing Admin/App Permissions: An adversary who has already compromised an account with lower-level administrative or application-specific permissions can use this vulnerability as a springboard to achieve Global Admin rights. This underscores the importance of the principle of least privilege.
- Federated Domain Abuse: In environments with federated domains, attackers might exploit weaknesses in the trust relationships or federation services (e.g., ADFS) to gain unauthorized access that can then be escalated within Entra ID.
Remediation Actions and Mitigations
Given the severity of a potential Global Administrator compromise, proactive and immediate remediation is crucial. While specific patches are awaited from Microsoft, several general security best practices can significantly reduce exposure:
- Implement Least Privilege: Scrutinize all administrative roles and application permissions within Entra ID. Ensure no user or application has more privileges than absolutely necessary to perform their function. Regularly review and revoke unnecessary permissions.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for All Admins: Enforce MFA for all administrative accounts, especially those with elevated privileges like Global Administrator, Application Administrator, and Cloud Application Administrator.
- Regular Auditing and Logging: Continuously monitor Entra ID audit logs for suspicious activities, including privilege escalation attempts, unusual application registrations, or changes to administrative roles. Utilize Microsoft Purview or third-party SIEM solutions for alert generation.
- Review Federation Trust Relationships: If using federated domains, regularly audit and harden your federation services (e.g., ADFS) – ensure they are patched, configured securely, and monitored for unusual activity.
- Conditional Access Policies: Implement robust Conditional Access policies to restrict sign-in to administrative roles based on location, device compliance, and identity risk.
- Secure Application Registrations: Periodically review all registered applications in Entra ID. Ensure that application permissions are scoped correctly and that no rogue or unused applications are present.
- Stay Updated with Microsoft Advisories: Continuously monitor Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) advisories and apply patches/updates as soon as they become available. This vulnerability, while reported, may soon have a public CVE and associated guidance.
Recommended Security Tools and Resources
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Entra ID Protection | Detects identity-based risks, offers automated remediation, and enforces MFA for conditional access. | Microsoft Learn |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps | Provides cloud app security broker (CASB) capabilities for discovering and controlling shadow IT, protecting sensitive information, and detecting threats. | Microsoft Learn |
| BloodHound (with AzureHound) | Visualizes complex relationships in Azure AD and on-premises AD, helping identify privilege escalation paths. | BloodHound Enterprise |
| Orca Security / Wiz / Tenable.io | Cloud security posture management (CSPM) and cloud workload protection platforms (CWPP) for continuous monitoring of cloud environments for misconfigurations and vulnerabilities. | Orca Security / Wiz / Tenable.io |
Conclusion
The reported Microsoft Entra ID vulnerability underscores the persistent threat of privilege escalation in modern cloud and hybrid environments. While specific details and official patches are pending, the cybersecurity community must act preemptively. By adhering to the principles of least privilege, strengthening authentication, robustly monitoring identity systems, and leveraging security tools, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience against such sophisticated attacks. Remain vigilant, stay informed, and prioritize your identity infrastructure’s security posture.





