New CastleLoader Attack Using Cloudflare-Themed Clickfix Technique to Infect Windows Computers
CastleLoader Emerges: Unpacking the Cloudflare-Themed Clickfix Attack Against Windows
The digital landscape is under perpetual siege, with adversaries constantly refining their tactics. A recent and particularly insidious threat, dubbed CastleLoader, has surfaced, leveraging sophisticated social engineering and highly deceptive techniques to compromise Windows environments. This rapidly evolving loader, first identified in early 2025, has already gained significant traction within underground networks, raising urgent concerns for IT professionals, security analysts, and developers alike.
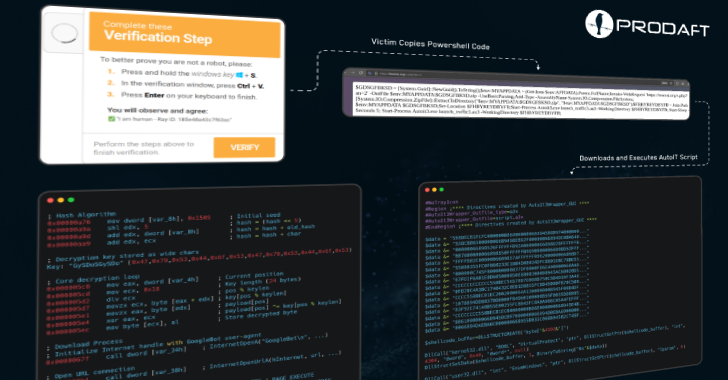
CastleLoader’s ingenuity lies in its weaponization of legitimate-looking platforms, particularly Cloudflare-themed “Clickfix” phishing pages and skillfully doctored GitHub repositories. By masquerading as benign developer resources, essential browser updates, or critical meeting portals, CastleLoader lures unsuspecting users into executing a seemingly innocent PowerShell command. This command, deceptively promising to “verify” or “repair” system issues, is the gateway to infection, establishing a foothold for the loader on the victim’s machine.
Understanding the CastleLoader Modus Operandi
The CastleLoader attack chain is a masterclass in deception, preying on user trust and familiarity with common online services. Here’s a breakdown of its primary vectors and techniques:
- Cloudflare-Themed “Clickfix” Phishing Pages: Attackers craft highly convincing phishing pages that mimic Cloudflare’s legitimate security checks. These pages often present a fabricated “click to verify” or “fix” prompt, creating a sense of urgency. The underlying malicious intent is to trick users into copying and executing a supplied PowerShell command.
- Doctored GitHub Repositories: CastleLoader also exploits the credibility of GitHub. Malicious actors create or compromise repositories that appear to host legitimate developer tools, software updates, or project assets. Within these forged repositories, they embed instructions or scripts that, when followed, lead to the execution of the loader.
- Masquerading as Benign Software: The malware often disguises itself as common and trusted applications, such as browser updates, developer utilities (e.g., Node.js, Python installers), or even meeting software logins. This broad appeal increases the likelihood of a successful initial compromise.
- Social Engineering through PowerShell: The core of the infection relies on a user-executed PowerShell command. This command is presented as a crucial step for verification, repair, or installation. Users, unaware of the command’s true nature, copy and paste it into their system’s command line interface, initiating the download and execution of the CastleLoader payload.
The “Clickfix” Deception: A Closer Look
The “Clickfix” technique is central to CastleLoader’s success. Attackers leverage the visual design and user flow of Cloudflare’s legitimate security challenges to create highly effective phishing decoys. When a user encounters one of these fake pages, they are presented with a prompt that typically indicates a problem requiring a “fix” or “verification.” The page then instructs the user to copy and paste a specific PowerShell command into their terminal to resolve the issue. This creates an immediate bypass of traditional browser download warnings, as the victim directly initiates the malicious script.
Impact on Infected Windows Computers
Once CastleLoader successfully infects a Windows machine, the consequences can be severe. As a loader, its primary function is to establish persistence and download additional malicious payloads. This can lead to:
- Further Malware Installation: CastleLoader can serve as a conduit for a wide range of secondary infections, including ransomware, info-stealers (e.g., for credentials, financial data), backdoors, and cryptocurrency miners.
- Data Exfiltration: Sensitive personal and corporate data can be exfiltrated from the compromised system.
- Remote Access: Attackers can gain unauthorized remote access to the infected machine, enabling them to control the system, deploy further attacks, or move laterally within a network.
- System Degradation: Resource-intensive malware payloads can cause significant performance degradation, leading to system crashes or slowdowns.
Remediation Actions and Prevention Strategies
Protecting against CastleLoader and similar social engineering attacks requires a multi-layered approach focusing on user education, robust security tools, and diligent monitoring.
Immediate Remediation if Suspected Infection:
- Isolate Infected Systems: Disconnect any potentially compromised machines from the network immediately to prevent lateral movement and further infection.
- Full System Scan: Perform a comprehensive scan using a reputable antivirus/anti-malware solution. Ensure definitions are up-to-date.
- Review PowerShell History: Check PowerShell command history for suspicious commands.
- Change Credentials: Assume any credentials stored or used on the compromised system are compromised and change them immediately, especially for critical accounts.
- Wipe and Reinstall: For critical systems or high-confidence infections, a complete wipe and reinstallation of the operating system is the safest course of action to ensure complete removal of the threat.
Proactive Prevention:
- User Awareness Training: Continuously educate users about the dangers of phishing and social engineering. Emphasize critical thinking before executing any commands or clicking suspicious links. Teach them to verify the legitimacy of requests, especially those asking to run system commands.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Implement the principle of least privilege for all users and applications. Restrict administrative rights to only those who absolutely need them.
- PowerShell Script Execution Policies: Configure PowerShell execution policies to restrict the execution of unsigned scripts. Consider setting it to `AllSigned` or `RemoteSigned` and enforce it via Group Policy.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)/Antivirus: Deploy and maintain robust EDR and antivirus solutions on all endpoints. Ensure they are configured for real-time protection and automatic updates.
- Network Monitoring: Implement network monitoring tools to detect unusual outbound connections or suspicious activity that might indicate Command and Control (C2) communication.
- Email Filtering and Web Security Gateways: Use advanced email filtering to block known phishing attempts and web security gateways to prevent access to malicious sites.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep operating systems, browsers, and all applications patched and up-to-date to mitigate vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Github Repository Verification: Advise developers and users to verify the authenticity of GitHub repositories. Look for signs of legitimacy, such as a strong commit history, community engagement, and official links.
Relevant Tools for Detection and Mitigation
Deploying the right tools can significantly enhance an organization’s defense posture against threats like CastleLoader.
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Defender for Endpoint | Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR), Antivirus, Behavioral Analysis | Microsoft Defender for Endpoint |
| Sysinternals Process Explorer | Process Monitoring, Identifying Suspicious Processes/DLLs | Process Explorer |
| PowerShell Remoting & Logging | Monitoring and logging of PowerShell activity for forensic analysis | PowerShell Logging |
| Cloudflare DNS/Security Offerings | Web Application Firewall (WAF), DNS filtering to block malicious sites (though attackers impersonate Cloudflare, Cloudflare’s own services can help defense) | Cloudflare Security |
| Any.run / VirusTotal | Online Sandbox for analyzing suspicious files/URLs; Malicious file/URL database lookup | Any.run / VirusTotal |
Conclusion
CastleLoader represents a growing trend in sophisticated attack vectors that combine technical prowess with cunning social engineering. The use of legitimate services like Cloudflare and GitHub as a front highlights the need for heightened vigilance and continuous security awareness training. Organizations and individual users must adopt a skeptical mindset when presented with unsolicited commands or prompts, even from seemingly trusted sources. By integrating robust endpoint protection, comprehensive user education, and proactive threat intelligence, we can collectively build stronger defenses against this evolving threat landscape.





