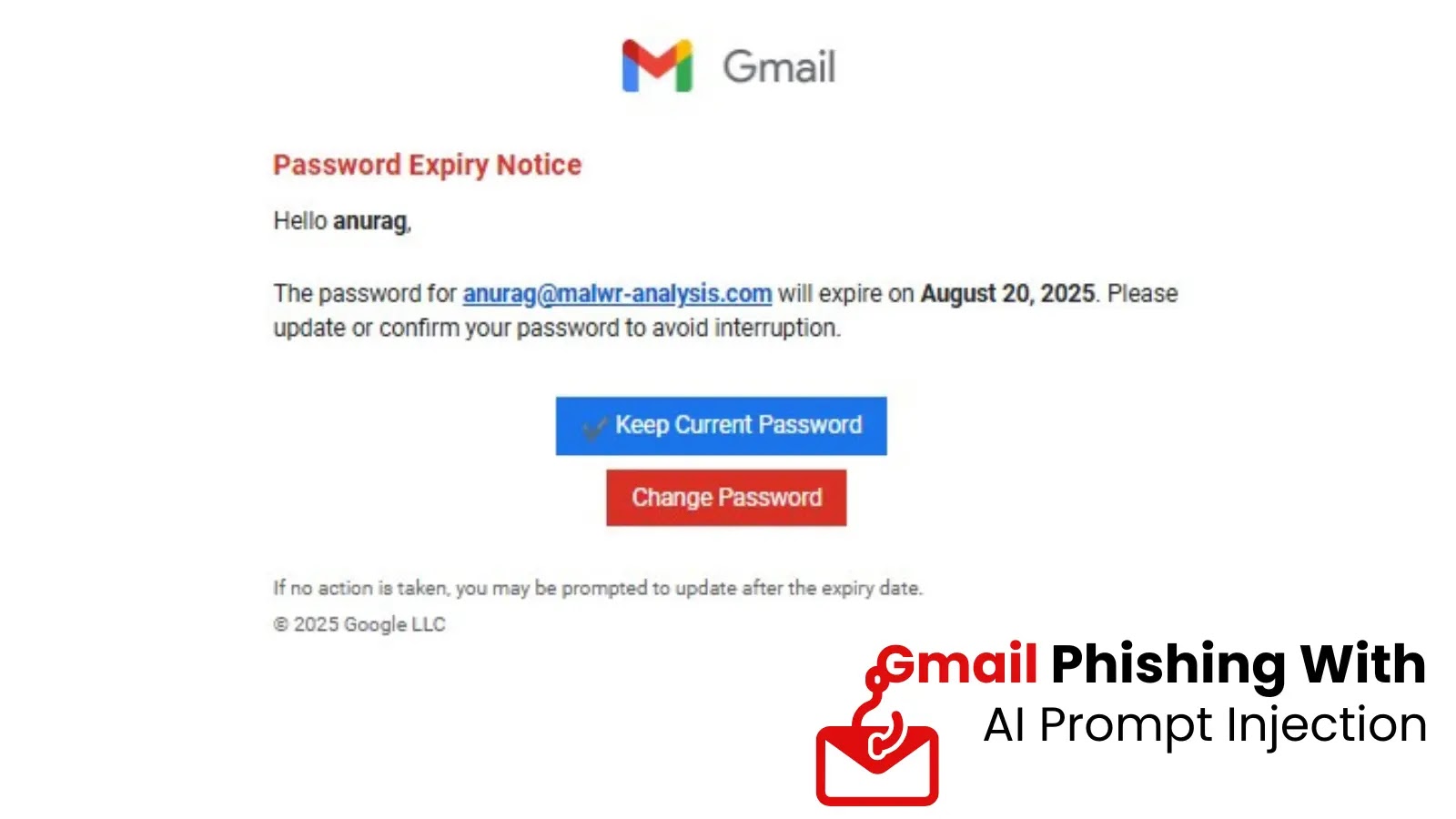
New Gmail Phishing Attack Uses AI Prompt Injection to Evade Detection
The landscape of cyber threats is constantly evolving, with attackers perpetually seeking new avenues to bypass traditional defenses. A recent and particularly insidious development in the realm of phishing attacks has emerged, targeting not only human vigilance but also the very artificial intelligence systems designed to protect us. This new Gmail phishing campaign represents a significant escalation, employing AI prompt injection techniques to evade detection and increase its success rate. For cybersecurity professionals, understanding this advanced tactic is paramount to developing effective countermeasures.
The Evolution of Phishing: Beyond Human Deception
Phishing has historically leveraged social engineering to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information. Tactics range from urgent requests for password resets to fake invoices, all designed to exploit human psychology. However, this latest Gmail phishing chain introduces a sophisticated layer of deception: it attempts to manipulate AI-based security defenses. While previous variants of this campaign relied on classic urgency and redirection techniques, the current iteration incorporates hidden AI prompts. These prompts are meticulously crafted to confuse automated systems, allowing malicious emails to slip through filters that would typically flag them as suspicious.
Understanding AI Prompt Injection in Phishing
AI prompt injection, in the context of this phishing attack, refers to the inclusion of specially formatted text within the email that is designed to be interpreted by an AI detection system, rather than or in addition to the human recipient. Imagine an email containing seemingly innocuous text that, when parsed by an AI, acts as an instruction to disregard certain suspicious elements or to classify the email as legitimate. This represents a novel approach to bypassing AI-powered email gateways and spam filters that rely on machine learning models to identify threats. The attackers are not just sending a malicious payload; they are actively trying to “jailbreak” or misdirect the protective AI.
The Mechanics of Evasion
While specific details of the prompt injection techniques used in this campaign are under ongoing analysis, the general principle involves embedding instructions that can subvert the AI’s detection logic. These could be subtle linguistic cues, specific character sequences, or even data patterns that, when processed by the AI, lead to a false negative. The goal is to make the email appear benign to the automated system, even if it contains elements that would otherwise trigger an alert. This makes it incredibly challenging for traditional signature-based or even behavior-based detection systems to accurately identify the threat.
Risks Associated with AI-Evading Phishing
The implications of AI-evading phishing attacks are far-reaching. Organisations that rely heavily on AI-driven security solutions may find themselves vulnerable if their systems are not adequately prepared for such nuanced attacks. The primary risks include:
- Increased Success Rates: Bypassing AI defenses directly translates to more malicious emails reaching user inboxes, significantly increasing the likelihood of successful compromises.
- Data Breaches: Successful phishing attacks often lead to credential theft, which is a common precursor to larger data breaches.
- Financial Loss: Business Email Compromise (BEC) schemes, often initiated via sophisticated phishing, can result in substantial financial losses.
- Reputational Damage: Being a victim of a cyberattack can severely impact an organization’s reputation and customer trust.
- Difficult Detection and Remediation: Because these attacks are designed to be stealthy, their detection and subsequent remediation become far more complex.
Remediation Actions and Mitigations
To combat this advanced form of phishing, organizations must adopt a multi-layered security strategy that goes beyond relying solely on AI detection. Here are critical remediation actions:
- Enhance Email Gateway Defenses: Implement advanced email security gateways that include robust anti-phishing capabilities, anomaly detection, and sandboxing for suspicious attachments and links. Regularly update and configure these systems.
- AI/ML Model Reinforcement: Security vendors and an organization’s internal security teams need to continuously train and retrain their AI and machine learning models with new threat intelligence, specifically focusing on examples of prompt injection and evasion techniques.
- User Awareness Training: The human element remains a critical line of defense. Conduct regular, sophisticated security awareness training for all employees. Emphasize the importance of scrutinizing email sender details, unexpected requests, and suspicious links. Educate users about the evolving nature of phishing attacks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Mandate MFA for all user accounts, especially for access to critical systems and sensitive data. This adds a crucial layer of security, even if credentials are compromised via phishing.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test a comprehensive incident response plan for phishing attacks. This includes clear procedures for reporting suspicious emails, isolating compromised accounts, and forensic analysis.
- Phishing Simulations: Conduct regular simulated phishing campaigns to test employee resilience and identify areas where further training is needed.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Adopt a Zero Trust security model, where no user or device is inherently trusted, and access is granted on a least-privilege basis with continuous verification.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Participate in threat intelligence sharing communities to stay abreast of the latest attack methodologies and indicators of compromise (IoCs).
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
While no tool is a silver bullet, a combination of the following can significantly enhance your defensive posture against advanced phishing attacks:
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Avanan (Check Point) | Cloud Email Security, API-based integration for M365/Google Workspace | https://www.checkpoint.com/cloudguard/cloud-email-security/ |
| Proofpoint Email Protection | Advanced threat protection for email, including phishing and imposter defense | https://www.proofpoint.com/us/products/email-protection |
| Microsoft Defender for Office 365 | Integrated email security for Microsoft 365 environments | https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/business/microsoft-365-defender/microsoft-defender-for-office-365 |
| Mimecast Email Security | Comprehensive email security, archiving, and continuity | https://www.mimecast.com/products/email-security/ |
| KnowBe4 Security Awareness Training | Phishing simulations and security awareness training platform | https://www.knowbe4.com/ |
Conclusion
The emergence of AI prompt injection in phishing campaigns marks a critical juncture in cybersecurity. Attackers are not just targeting human vulnerabilities; they are actively attempting to subvert the very AI systems designed to defend against them. This necessitates a proactive and adaptive approach from security professionals. By combining robust technological defenses, continuous AI model refinement, comprehensive user education, and a strong incident response posture, organizations can build resilience against these increasingly sophisticated and stealthy threats. Vigilance and adaptability are key in safeguarding digital assets in the face of evolving cyber adversary tactics.





