New Gmail Phishing Attack With Weaponized Login Flow Steals Login Credentials
Unmasking the Imposter: A New Gmail Phishing Attack Exploits Legitimate Infrastructure
In the evolving landscape of cyber threats, attackers constantly refine their tactics. A recent and particularly insidious phishing campaign targeting Gmail users has surfaced, demonstrating a sophisticated multi-layered approach that weaponizes legitimate infrastructure to bypass standard security measures and pilfer login credentials. This attack highlights a critical shift in adversary techniques, moving beyond simple spoofing to exploit trusted services.
The Anatomy of the Attack: Weaponizing Trust
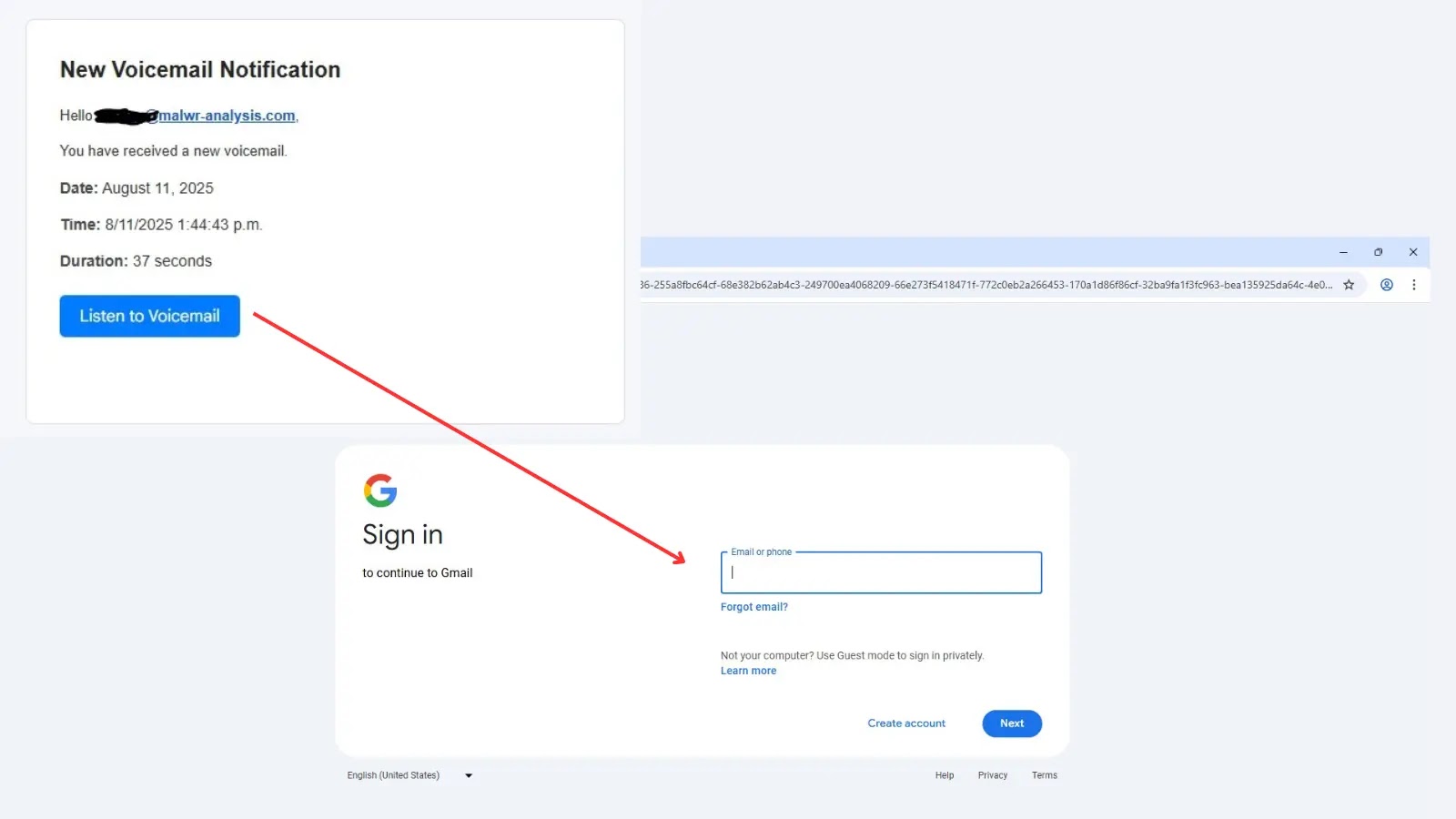
This novel phishing campaign commences with highly deceptive email lures. Disguised as “New Voice Notification” alerts, these emails meticulously spoof sender information, creating the illusion that they originate from legitimate voicemail services. The primary call to action within these emails is a prominent “Listen to Voicemail” prompt, designed to entice the recipient into clicking.
However, the cunning doesn’t end there. Upon clicking this seemingly innocuous link, victims are not redirected to a malicious spoofed website, but rather to a legitimate Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales site. This crucial step is what elevates the attack’s sophistication. By leveraging Microsoft’s trusted infrastructure, the attackers effectively bypass many traditional email security gateways and content filters that are less likely to flag traffic to a legitimate domain as malicious.
Once on the Microsoft Dynamics page, victims are presented with a series of redirects that ultimately lead to a convincing, yet entirely malicious, Gmail login page. This final page, meticulously crafted to mimic Google’s authentic authentication portal, is where the credential harvesting occurs. Unsuspecting users, seeing the familiar Google interface and having already navigated through seemingly legitimate channels, are prone to entering their Gmail usernames and passwords, which are then immediately captured by the attackers.
Key Characteristics and Sophistication
- Legitimate Infrastructure Abuse: The most significant factor differentiating this attack is its reliance on legitimate Microsoft Dynamics infrastructure. This technique, known as “redirection as a service” or “open redirect exploitation,” allows threat actors to leverage the reputation and trust associated with established domains to deliver their phishing payloads.
- Multi-layered Approach: The attack is not a single-stage event but a carefully orchestrated sequence involving deceptive emails, legitimate service redirection, and a convincing spoofed login page. This complexity makes it harder for automated systems and even discerning users to identify the threat.
- Bypassing Security Controls: By routing traffic through trusted domains, the attackers significantly increase their chances of bypassing spam filters, URL reputation checks, and other security mechanisms designed to identify and block malicious links.
- Targeting Gmail Users: While the method could potentially be adapted for other services, the current campaign specifically targets Gmail users, leveraging the ubiquity of Google’s email platform.
Remediation Actions and Prevention Strategies
Protecting against such sophisticated attacks requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing technical controls, user education, and proactive threat intelligence.
- Enhanced Email Security Gateways (ESGs): Organizations should ensure their ESGs are configured to perform advanced anomaly detection, looking beyond simple blacklists to identify unusual redirection chains originating from legitimate but unexpected sources.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing and enforcing MFA across all user accounts, especially for critical services like email, is paramount. Even if credentials are stolen, MFA acts as a vital secondary defense layer, preventing unauthorized access.
- User Awareness Training: Regular, comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training is crucial. Employees must be educated on the nuances of phishing, including sophisticated techniques like legitimate domain abuse. Key points to emphasize include:
- Always Verify URLs: Before entering credentials on any login page, users should meticulously inspect the URL in the browser’s address bar. Look for inconsistencies, misspellings, or unusual subdomains, even if the initial link seemed legitimate.
- Hover Before Clicking: Teach users to hover their mouse over links, especially in suspicious emails, to reveal the true destination URL before clicking.
- Report Suspicious Emails: Establish clear procedures for reporting suspicious emails to the IT security team.
- Exercise Caution with “Voice Notification” Emails: Advise users to be particularly wary of unsolicited “voicemail” or “missed call” notifications, especially if they are not expecting them or if they come from unfamiliar senders.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Deploying robust EDR solutions can help detect post-compromise activities, such as suspicious network connections initiated from compromised systems.
- Conditional Access Policies: Implement conditional access policies that restrict access to sensitive applications based on factors like geographic location, device health, and IP address reputation.
- Regular Penetration Testing and Phishing Simulations: Conduct frequent penetration tests and simulated phishing campaigns to assess the effectiveness of security controls and identify weaknesses in user awareness.
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Proofpoint Email Security | Advanced threat protection, URL defense, and email filtering. | https://www.proofpoint.com/us/products/email-protection |
| Microsoft Defender for Office 365 | Comprehensive email and collaboration security, anti-phishing, and safe attachments. | https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/business/microsoft-365-defender/microsoft-defender-for-office-365 |
| KnowBe4 Security Awareness Training | User education platform with simulated phishing and training modules. | https://www.knowbe4.com/ |
| Okta Adaptive MFA | Multi-Factor Authentication and adaptive access policies. | https://www.okta.com/products/adaptive-mfa/ |
| Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR | Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) for threat detection and response. | https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/cortex/cortex-xdr |
Looking Ahead: The Persistent Threat of Malicious Innovation
This new Gmail phishing campaign underscores a critical reality: cybercriminals are constantly innovating, adapting their techniques to circumvent existing security measures. The exploitation of legitimate infrastructure represents a significant escalation in phishing sophistication. Organizations and individual users must remain vigilant, prioritize robust security practices, and foster a culture of skepticism towards unsolicited communications. Proactive security measures, coupled with ongoing user education, are the most effective defenses against these evolving threats.





