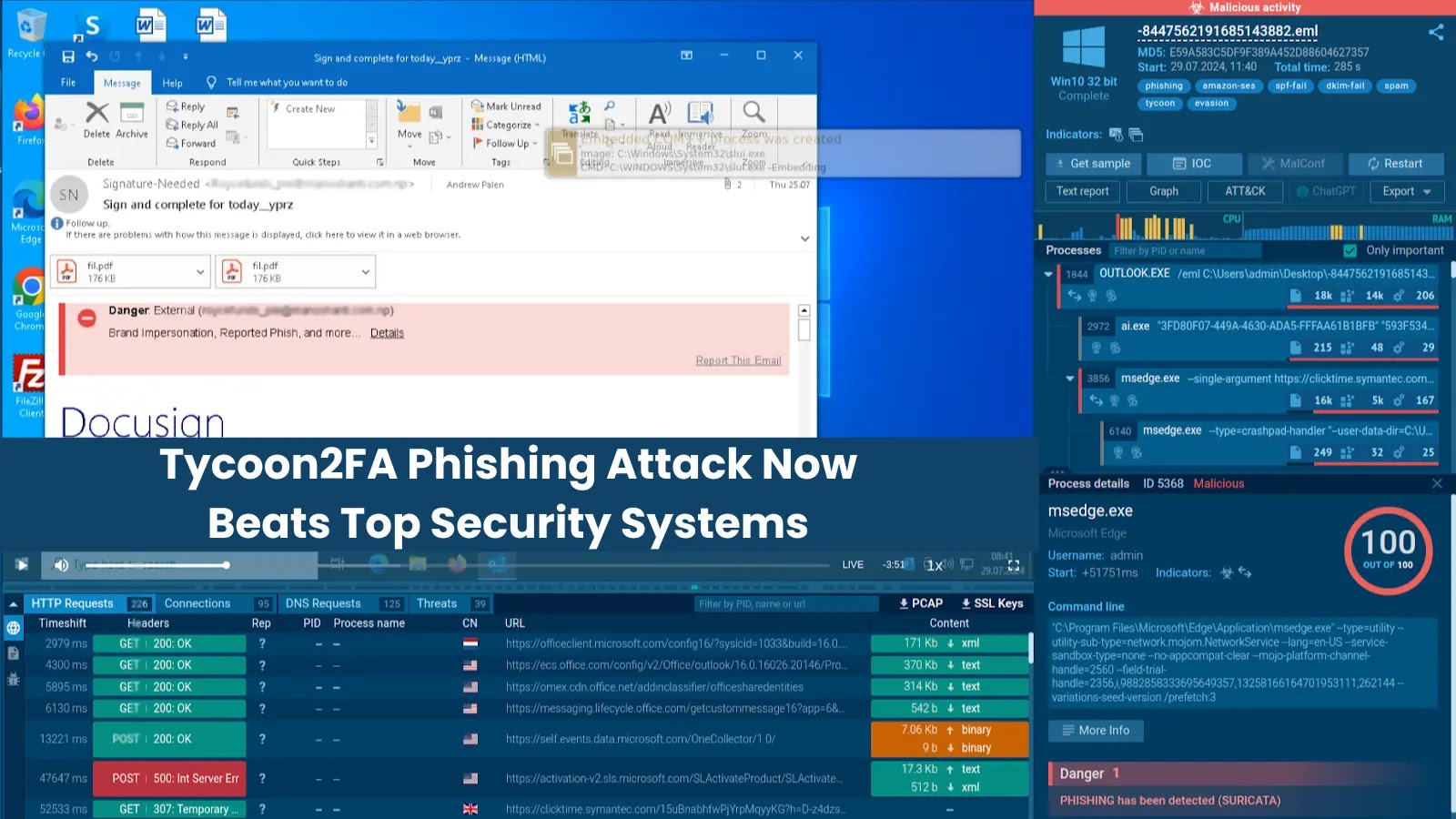
New Multi-Stage Tycoon2FA Phishing Attack Now Beats Top Security Systems
The End of Easy Phishing: Tycoon2FA Attacks Defy Traditional Security Defenses
The landscape of cyber threats is witnessing an audacious evolution. Forget the simplistic phishing attempts of yesteryear, where a bad link led to an obvious fake login page. A new, sophisticated adversary has emerged, pushing the boundaries of what we understand as a phishing attack: Tycoon2FA. This multi-stage “phishing-as-a-service” (PhaaS) offering is not merely an improvement on old tactics; it’s a complete paradigm shift, already demonstrating its ability to bypass leading security systems and challenge even the most vigilant human defenses. If your organization relies on conventional security postures, Tycoon2FA is a clear signal that the rules have changed.
What is Tycoon2FA and Why is it Different?
Tycoon2FA represents a new frontier in complex social engineering and technical evasion. Unlike single-stage phishing campaigns, Tycoon2FA orchestrates a sophisticated, multi-stage attack sequence – reportedly up to seven distinct stages – designed to intricately wear down both automated security tools and human awareness. This extended engagement period provides numerous opportunities for attackers to harvest credentials, session tokens, and bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA).
The key differentiators of Tycoon2FA include:
- Multi-Factor Evasion: Specifically engineered to circumvent common MFA protections, it often acts as a proxy or harvests session cookies post-authentication.
- Adaptive Techniques: Its modular nature allows operators to adjust tactics based on victim behavior or security tool responses, making it highly resilient to detection.
- Highly Concealed Infrastructure: Leveraging legitimate services and complex redirection chains, Tycoon2FA makes tracing its origins and infrastructure significantly more challenging.
- Phishing-as-a-Service Model: This accessibility lowers the barrier to entry for less sophisticated threat actors, democratizing advanced phishing capabilities.
The Seven-Stage Gauntlet: How Tycoon2FA Operates
While the exact stages can vary, a typical Tycoon2FA attack might involve:
- Initial Lure: A seemingly legitimate email or message, often from a spoofed trusted entity (e.g., IT support, HR, a known vendor), containing a link designed to initiate the attack chain.
- Redirection Chain: The victim is redirected through a series of legitimate-looking but compromised or controlled intermediary sites, making it difficult for reputation-based security tools to block the ultimate destination.
- Credential Harvesting Landing Page: A highly convincing, pixel-perfect replica of a legitimate login page (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, financial institutions) is presented to the victim.
- MFA Prompt Proxying/Bypass: As the victim enters credentials, the attacker’s infrastructure proxies the login attempt to the legitimate service, potentially capturing MFA codes or session tokens in real-time.
- Session Hijacking: If successful, the attacker gains access to the victim’s live session, bypassing future MFA prompts.
- Post-Exploitation Actions: Depending on the attacker’s goals, this could involve data exfiltration, internal lateral movement, or further phishing attempts against the victim’s contacts.
- Covert Channel Maintenance: Establishing persistence or backdoors for future access, often leveraging legitimate services or common protocols.
The primary reason Tycoon2FA beats top security systems is its ability to mimic legitimate user behavior through its multi-stage approach, making it appear less malicious to automated defenses that are often configured to flag immediate redirects to known malicious domains. Its use of legitimate infrastructure or compromised reputable sites adds another layer of evasion.
Tycoon2FA and Its Implications for Organizations
The rise of Tycoon2FA signals a critical need for organizations to re-evaluate their cybersecurity strategies:
- MFA is No Longer a Silver Bullet: While still essential, MFA alone is insufficient against these sophisticated attacks. Additional layers of security are crucial.
- Behavioral Analytics are Paramount: Detecting anomalies in user behavior, even after successful authentication, becomes vital.
- Heightened User Awareness: Employees must be trained to recognize subtle cues of advanced phishing, understanding that even seemingly legitimate sites can be part of an attack.
- Supply Chain Risks: Tycoon2FA often targets individuals to gain access to an organization, but it could also compromise vendors, adding supply chain risk.
Remediation Actions and Proactive Defenses Against Sophisticated Phishing
Countering threats like Tycoon2FA requires a multifaceted and adaptive security posture. Organizations must move beyond basic link analysis and focus on a defense-in-depth strategy that incorporates both technical controls and human elements.
- Enhanced Email Security Gateways (ESG): Implement advanced ESG solutions with capabilities for URL rewriting, post-delivery retraction, and deep content analysis that goes beyond simple static blacklisting. Look for solutions using AI/ML for anomaly detection in email patterns and sender behavior.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Reinforcement: Move towards FIDO2/WebAuthn-based phishing-resistant MFA methods where possible. For less resistant MFA, monitor for suspicious MFA approval requests or concurrent login attempts.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)/Extended Detection and Response (XDR): Deploy robust EDR/XDR solutions that can detect suspicious activity on endpoints even if the initial phishing attempt bypasses email filters. This includes monitoring for unusual process execution, network connections, and file access patterns.
- Security Awareness Training (SAT) with Phishing Simulations: Regularly conduct advanced phishing simulations that mimic Tycoon2FA’s multi-stage nature. Train users to scrutinize URLs, look for discrepancies in login pages beyond just the domain, and to report suspicious emails immediately. Emphasize verification processes for unusual requests.
- Network Traffic Analysis and DNS Monitoring: Implement solutions that monitor outbound network traffic for connections to unusual or suspicious domains, even after initial email gateways are bypassed. DNS monitoring can help identify look-alike domains or suspicious DNS requests.
- Conditional Access Policies: Leverage conditional access policies (e.g., in Azure AD, Google Workspace) to enforce stricter access controls based on user location, device health, and risk scores. Require re-authentication for sensitive actions or from high-risk locations.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Auditing: Regularly audit user accounts, permissions, and session activity for anomalies. Implement strong password policies and monitor for credential stuffing attempts.
- Incident Response Plan Review: Ensure your incident response plan is updated to handle sophisticated phishing attacks, including steps for rapid account lockout, session termination, and forensic analysis to understand the compromise’s full scope.
Tools for Enhanced Phishing Defense
| Tool Category | Purpose | Example Tool & Link |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Email Security | Detects and blocks sophisticated phishing, spoofing, and BEC attempts using AI/ML models. | Proofpoint Email Security |
| Phishing-Resistant MFA | Provides strong authentication that resists common phishing attacks like credential harvesting and session hijacking. | YubiKey / FIDO2 Standard |
| Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) | Monitors endpoint activity to detect and respond to suspicious behaviors post-email delivery. | CrowdStrike Falcon Insight |
| Security Awareness Training | Educates employees on latest phishing tactics and provides simulation exercises. | KnowBe4 Security Awareness Training |
| Proxy/DNS Protection | Filters web traffic and DNS requests, blocking access to malicious or suspicious sites. | Cisco Umbrella |
Looking Ahead: The Evolving Threat Landscape
Tycoon2FA is a harsh reminder that cybersecurity is a perpetually evolving struggle. The emergence of sophisticated PhaaS offerings like this one signifies a democratized access to advanced attack capabilities, putting more pressure on organizations of all sizes. The future of cybersecurity depends on adapting swiftly, embracing advanced detection methodologies, and fostering a culture of hyper-vigilance among all users. Protecting against these advanced threats requires a blend of cutting-edge technology, continuous education, and an unwavering commitment to a proactive security posture.





