New Salty 2FA PhaaS Attacking Microsoft 365 Users to Steal Login Credentials
Salty 2FA: Unmasking the Advanced Phishing-as-a-Service Threat to Microsoft 365
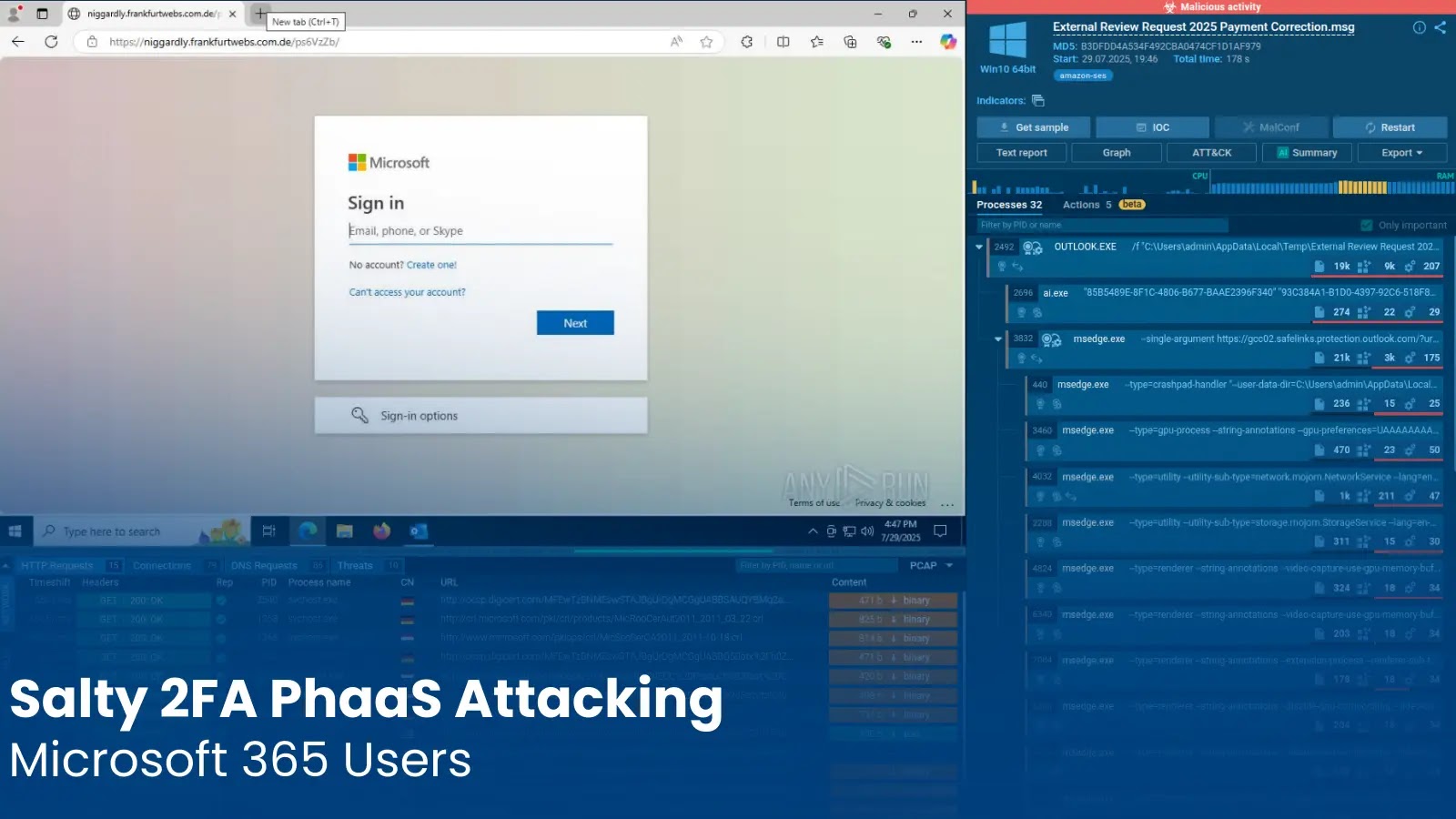
The digital landscape is under relentless assault, and a sophisticated new threat has emerged, specifically targeting Microsoft 365 users with advanced phishing techniques. Dubbed “Salty 2FA,” this previously undocumented Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) framework poses a significant risk, employing cutting-edge methods to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) and steal critical corporate credentials. Understanding this evolving threat is paramount for IT professionals, security analysts, and organizations relying on Microsoft 365 for their operations.
What is Salty 2FA?
“Salty 2FA” represents a new frontier in PhaaS platforms. Unlike simpler phishing kits, this framework demonstrates a heightened level of sophistication. It’s designed not just to mimic login pages but to actively circumvent security measures like 2FA, a common defense against credential theft. The platform’s name itself, “Salty 2FA,” hints at its primary objective: to ‘salt’ (or bypass) two-factor authentication, fooling users and systems alike.
How Salty 2FA Operates: A Multi-Stage Attack
Salty 2FA’s effectiveness lies in its intricate, multi-stage execution chain and advanced obfuscation techniques. This isn’t a spray-and-pray operation; it’s a targeted and stealthy approach. While specific technical details of its operation are still emerging, the core principle involves:
- Advanced Obfuscation: The phishing pages and underlying code are heavily obfuscated to evade detection by traditional security solutions and make analysis difficult for security researchers.
- Realistic Impersonation: Phishing lures are highly convincing, often mimicking legitimate Microsoft 365 login portals, password reset pages, or collaboration platform interfaces.
- 2FA Bypass Mechanisms: This is the hallmark of Salty 2FA. The platform is engineered to intercept and relay 2FA codes or tokens in real-time, effectively bypassing the second layer of security as the victim attempts to log in. This allows attackers to immediately gain access to accounts after credentials have been entered.
- Credential Harvesting: Once credentials and 2FA tokens are captured, they are exfiltrated to the attackers, granting unauthorized access to sensitive corporate data and systems.
- Targeted Campaigns: The framework is reportedly used in highly targeted campaigns, specifically aimed at organizations within the finance and telecommunications sectors across both the US and Europe.
The Impact on Microsoft 365 Users
Microsoft 365, being a widely adopted platform for business productivity and collaboration, becomes a prime target for such advanced PhaaS platforms. A successful Salty 2FA attack can lead to:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to emails, documents, OneDrive, SharePoint, and other sensitive corporate data.
- Financial Fraud: Compromised financial accounts, enabling fraudulent transactions or Business Email Compromise (BEC) schemes.
- Reputational Damage: Loss of customer trust and severe damage to an organization’s brand image.
- Further Compromise: Stolen credentials can be used for lateral movement within a compromised network, escalating the attack.
Remediation Actions and Proactive Defenses
Defending against advanced PhaaS platforms like Salty 2FA requires a multi-layered security strategy. Organizations using Microsoft 365 must prioritize the following actions:
- Strengthen MFA Implementations: While Salty 2FA aims to bypass 2FA, not all 2FA methods are equally vulnerable. Prioritize FIDO2/hardware-based security keys (e.g., YubiKey) or certificate-based authentication where possible, as these are significantly more resilient to phishing than SMS or time-based one-time passwords (TOTP). Implement number matching for Microsoft Authenticator push notifications.
- Advanced Phishing Detection: Deploy and configure email security gateways (ESG) with advanced threat protection, sandboxing, and URL rewriting capabilities to detect and block sophisticated phishing lures before they reach inboxes.
- User Awareness Training: Conduct regular, realistic phishing simulations and provide continuous training to employees on identifying phishing attempts, even highly sophisticated ones. Emphasize verification procedures for suspicious login prompts or links.
- Conditional Access Policies: Leverage Microsoft 365 Conditional Access policies to enforce strict access controls based on user location, device compliance, risk levels, and application. For example, block access from untrusted locations or enforce MFA for high-risk sign-ins.
- Monitor Sign-in Logs and Audit Trails: Regularly review Microsoft 365 sign-in logs and audit trails for unusual activity, such as sign-ins from new locations, unusual times, or multiple failed login attempts. Implement security information and event management (SIEM) solutions for centralized logging and anomaly detection.
- Least Privilege Access: Ensure users only have the necessary permissions to perform their job functions. Regularly review and revoke excessive privileges.
- Regular Security Posture Assessment: Utilize tools like Microsoft Secure Score to continuously assess and improve your Microsoft 365 security posture.
Detection and Mitigation Tools
Organizations can leverage specific tools and features integrated within or complementary to Microsoft 365 to enhance their defense against threats like Salty 2FA:
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Defender for Office 365 | Advanced phishing and malware protection for email and collaboration. | Learn more |
| Microsoft 365 Conditional Access | Policy-based access control based on user, device, and location. | Learn more |
| Microsoft Secure Score | Measures and helps improve an organization’s security posture. | Learn more |
| Phishing Simulation Platforms | Trains employees to identify and report phishing attempts. | (Varies by vendor, e.g., KnowBe4, Proofpoint) |
| FIDO2 Security Keys | Hardware-based, phishing-resistant MFA. | (Varies by vendor, e.g., YubiKey, Feitian) |
Conclusion
The emergence of Salty 2FA underscores the growing sophistication of cyber threats and the critical need for robust, adaptive security measures. Its ability to bypass traditional 2FA mechanisms highlights that even with MFA enabled, a layered security approach remains indispensable. By combining advanced technical controls, stringent policy enforcement, and continuous user education, organizations can significantly bolster their defenses against this new wave of PhaaS attacks and protect their valuable Microsoft 365 assets.





