NVIDIA Triton Bugs Let Unauthenticated Attackers Execute Code and Hijack AI Servers
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly becoming the backbone of many modern applications, from medical diagnostics to autonomous vehicles. The infrastructure supporting these AI models, such as NVIDIA’s Triton Inference Server, is therefore a critical component of digital security. A newly disclosed set of vulnerabilities, however, has revealed a significant exposure, allowing unauthenticated attackers to gain complete control over susceptible AI servers. This post delves into these critical flaws, explaining their impact and outlining essential remediation steps for organizations leveraging Triton.
NVIDIA Triton: A Key AI Infrastructure Component
NVIDIA Triton Inference Server is an open-source platform designed to deploy and run AI models at scale, supporting various deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and ONNX Runtime. Its robust architecture allows for efficient inference across multiple GPUs and CPUs, making it a popular choice for enterprises integrating AI into their operations. The widespread adoption of Triton underscores the severity of any security vulnerabilities affecting it, as a compromise could have far-reaching implications for AI-driven services.
The Critical Vulnerabilities: Unauthenticated RCE Explained
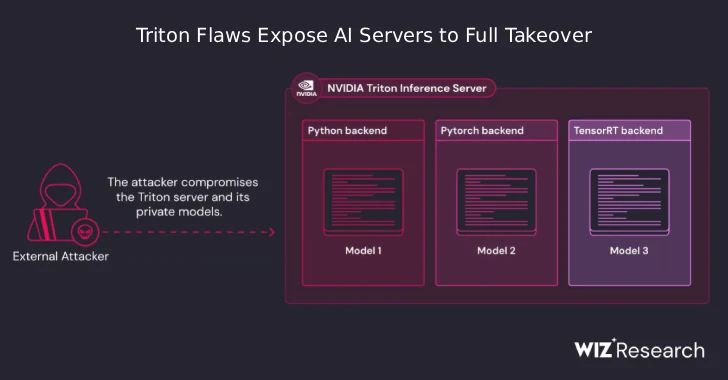
The recently identified security flaws, impacting Triton Inference Server for both Windows and Linux, are particularly alarming due to their potential for remote code execution (RCE) without requiring any authentication. When chained together, these vulnerabilities present a severe threat: a remote, unauthenticated attacker can achieve complete server takeover.
While specific CVE numbers often detail individual vulnerabilities, the report highlights a critical chain of exploits. This means that no single flaw might grant RCE, but the sequence of exploiting multiple weaknesses cumulatively leads to full compromise. Such pre-authentication RCE vulnerabilities are among the most dangerous, as they allow an attacker to bypass initial security layers and directly execute malicious code on the target system. This could lead to data exfiltration, service disruption, or the establishment of persistent backdoors within an organization’s AI infrastructure.
Impact and Exposure for AI Servers
The implications of these Triton vulnerabilities are substantial. Organizations relying on Triton Inference Server for their AI operations are at risk of:
- Data Breach: Attackers could access sensitive data processed or stored by AI models.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Proprietary AI models themselves, often the result of significant investment, could be stolen.
- Service Disruption: AI inference services could be shut down, leading to operational paralysis for dependent applications.
- Supply Chain Compromise: If an attacker gains control of an AI server, they could potentially inject malicious models or tamper with existing ones, affecting downstream applications and users.
- Resource Hijacking: Compromised servers could be repurposed for illicit activities, such as cryptocurrency mining or launching further attacks.
Remediation Actions and Best Practices
Given the severity of these unauthenticated RCE vulnerabilities, immediate action is paramount for any organization using NVIDIA Triton Inference Server. The primary and most critical step is to apply security updates as soon as they become available from NVIDIA.
- Patch Immediately: Always prioritize and apply official security patches and updates released by NVIDIA. Monitor NVIDIA’s official security advisories and announcements for specific patch details and instructions.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate AI inference servers from other critical network segments. Implement robust firewall rules to restrict access to Triton Inference Server only from necessary internal systems and authorized personnel.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Ensure that the Triton Inference Server and the user accounts it operates under have only the minimum necessary permissions to perform their functions.
- Regular Auditing and Monitoring: Implement comprehensive logging and monitoring for your AI infrastructure. Look for unusual network activity, unexpected process executions, or unauthorized configuration changes on Triton servers.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan your network and systems for known vulnerabilities, including those affecting AI inference servers and their underlying operating systems.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Deploy EDR solutions on servers running Triton to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real-time.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Consider placing a WAF in front of web-exposed interfaces of Triton (if applicable to your deployment) to filter malicious traffic.
Tools for Detection and Mitigation
While specific tools for detecting these exact chainable flaws may evolve, general cybersecurity tools are crucial for maintaining the security posture of systems running NVIDIA Triton.
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Nessus | Vulnerability Scanning and Assessment | https://www.tenable.com/products/nessus |
| OpenVAS | Open Source Vulnerability Scanner | https://www.greenbone.net/en/community-edition/ |
| Wireshark | Network Protocol Analyzer (for traffic monitoring) | https://www.wireshark.org/ |
| Snort/Suricata | Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | https://www.snort.org/ https://suricata.io/ |
| Lynis | Security Auditing and Hardening Tool (Linux) | https://cisofy.com/lynis/ |
Conclusion
The disclosure of critical vulnerabilities in NVIDIA’s Triton Inference Server serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing need for robust security practices in AI deployments. The potential for unauthenticated remote code execution underscores the urgency for organizations to act swiftly, applying necessary patches and reinforcing their security postures. Protecting AI infrastructure is not just about safeguarding data or intellectual property; it’s about ensuring the integrity and reliability of the AI-driven services that are increasingly critical to modern business operations.





