Role of Layer 2 Switches in Zero Trust Architecture.
Role of Layer 2 Switches in Zero Trust Architecture: Layer 2 Segmentation, Zero Trust Security Use Cases & Verification
In today’s dynamic threat landscape, a robust security architecture is paramount. The zero trust architecture emerges as a critical framework for cloud security, fundamentally shifting the conventional security paradigm from implicit trust to explicit verification. This article explores the pivotal role of Layer 2 switches in the zero trust security model, highlighting how they facilitate enhanced security through network segmentation, support various zero trust security use cases, and enable rigorous verification processes. Discover how Layer 2 switches contribute to a more secure and resilient network environment, aligning with the core zero trust principles.
Understanding Zero Trust Architecture
Definition and Principles of Zero Trust Security
Zero trust security represents a transformative security approach predicated on the “never trust, always verify” principle. Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models, zero trust architecture eliminates implicit trust and mandates that every user and device be authenticated and authorized before gaining network access. This approach drastically reduces the attack surface and limits lateral movement within the network. Key zero trust principles include least privilege access, microsegmentation, continuous monitoring, and adaptive security policies. By implementing zero trust, organizations enhance security across multiple dimensions, minimize risks, and ensure compliance with stringent regulatory requirements, safeguarding their critical assets and data.
Components of a Zero Trust Security Model
A zero trust security model comprises several critical components working in concert to enforce stringent security policies. Authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, are essential to verify the identity of users and devices. Access control solutions, including granular permissions and role-based access, regulate network access to only authorized resources. Several other important components contribute to this model, including:
- Network segmentation, which further divides the network into isolated segments, limits the blast radius of potential breaches and enhances secure access.
- Security devices, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, which continuously monitor network traffic and detect malicious activities.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools provide real-time threat detection and response capabilities, ensuring comprehensive endpoint security. These components collectively enhance security posture and mitigate risks across the network.
Importance of Layer 2 in Zero Trust Architecture
The role of Layer 2, or the data link layer, is often underestimated in zero trust implementations, yet it is crucial for effective network segmentation and security enforcement. Layer 2 switches provide the foundational infrastructure for microsegmentation. By creating isolated network segments at Layer 2, organizations can significantly reduce the potential for lateral movement and contain security breaches across multiple attack vectors. Layer 2 segmentation complements Layer 3 security measures, such as firewalls and routing policies, to create a comprehensive zero trust network. Leveraging Layer 2 security features enhances security solution effectiveness, improves network security, and supports zero trust policies, making it an indispensable element of a robust security architecture. We assure your infrastructure is secure across multiple layers of security.
Layer 2 Segmentation in Zero Trust
What is Layer 2 Segmentation?
Layer 2 segmentation divides a network into smaller, isolated network segments at the data link layer, typically using VLANs. By logically separating the network into distinct segments, organizations can control and limit network access, restricting the potential for lateral movement in the event of a security breach. Layer 2 segmentation enhances network security, making it more difficult for attackers to traverse the entire network from a single compromised endpoint. This approach complements Layer 3 security measures, providing a more comprehensive defense strategy within a zero trust model. Layer 2 segmentation is essential to implement zero trust architecture.
Benefits of Layer 2 Segmentation in Network Security
Layer 2 segmentation can significantly reduce the blast radius of security incidents and allows for granular access control. This approach simplifies the enforcement of security policies, allowing for granular access control based on user and device roles and functions. Layer 2 segmentation enhances security posture and supports zero trust policies by minimizing implicit trust and mandating verification for every access attempt. Furthermore, it aids in compliance with regulatory requirements by providing a more controlled and auditable network environment. Layer 2 segmentation provides effective network security, improving the overall effectiveness of security solutions.
Implementing Layer 2 Segmentation Strategies
Implementing Layer 2 segmentation strategies requires careful planning and configuration of network devices. Start by identifying critical assets and defining clear network segment boundaries. This can be based on several factors, including:
- User and device roles
- Application and data sensitivity
- Business functions
Next, configure VLANs on Layer 2 switches to logically separate these segments, enforcing access control policies using MAC address filtering and port security features. Integrate Layer 2 segmentation with other security controls, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to create a layered security approach. Regularly monitor network traffic within each segment to detect and respond to any suspicious activities in real-time. By implementing Layer 2 segmentation strategically, organizations can enhance security, minimize risks, and support the overarching goals of a zero trust network. Ensure that endpoint detection and response solutions are integrated across all segments to further enhance security, with zero trust security. We assure Your Infrastructure is Secure, Safe.
Use Cases of Zero Trust Security
Application and Data Security Use Cases
Zero trust architecture presents compelling use cases for enhancing application and data security, aligning with the core zero trust principles of “never trust, always verify.” Consider a scenario where sensitive customer data is stored within a database. With a traditional security model, once a user gains network access, they might have implicit trust to access this data. However, with a zero trust model, every access request to the database requires authentication and authorization, regardless of the user’s location or device. Zero trust significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, enhancing security and ensuring compliance with new security policies. By implementing zero trust architecture, organizations can enforce granular access control policies, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive data, and only when absolutely necessary. This model can be implemented using endpoint detection and response solutions to enhance security.
Network Security Use Cases in a Zero Trust Model
In the realm of network security, the benefits of zero trust are particularly pronounced, with numerous use cases demonstrating its effectiveness. Consider a situation where a remote user connects to the corporate network via a VPN. With a zero trust model, simply authenticating the user to the VPN is not sufficient. Instead, zero trust mandates that every access attempt to network resources, such as servers and applications, requires additional verification. For instance, before a user can access a specific server, they must undergo multi-factor authentication, and their device must be verified as compliant with the organization’s security policies. Network segmentation further isolates critical resources, limiting the potential for lateral movement in the event of a breach. By enforcing these zero trust policies, organizations enhance network security and minimize the attack surface, safeguarding against potential threats, including those from IoT devices. We assure Your Infrastructure is Secure, Safe. Implementing a zero trust security model enhances security features.
Compliance and Regulatory Use Cases
Compliance and regulatory requirements are increasingly demanding, making zero trust a vital framework for organizations seeking to meet these obligations. Zero trust architecture aids in achieving compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. For example, under GDPR, organizations must demonstrate that they have implemented appropriate security measures to protect personal data. A zero trust approach, with its emphasis on least privilege access and microsegmentation, ensures that data access is strictly controlled and monitored, reducing the risk of data breaches and regulatory penalties. The ability to continuously authenticate and verify users and devices, coupled with comprehensive audit trails, provides the necessary visibility and accountability to demonstrate compliance. By implementing zero trust architecture, organizations enhance their security posture and improve their ability to meet and maintain regulatory compliance. Zero trust helps to implement zero trust policies that validate every access request.
Verification Mechanisms in Zero Trust Security
Verification Techniques for Users and Devices
Multi-factor authentication, device posture assessment, and continuous authentication are paramount for maintaining a robust security posture in zero trust. By implementing these verification techniques, organizations significantly enhance security and minimize the risk of unauthorized access. We assure Your Infrastructure is Secure, Safe. These verification methods assure the enforcement of security policies.
Continuous Monitoring and Assessment
Real-time monitoring of network traffic, threat intelligence feeds, and vulnerability scanning are indispensable components of a robust zero trust security model to validate threats effectively. Threat intelligence feeds provide valuable insights into emerging threats, allowing security teams to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks. Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing help to identify and address security gaps in the network infrastructure. By continuously monitoring and assessing their security posture, organizations can ensure that their defenses remain effective against evolving threats. This proactive approach aligns with the zero trust principles of “never trust, always verify,” enabling organizations to maintain a high level of security and compliance. By implementing continuous monitoring, organizations enhance security and minimize risks.
Integrating Verification with Layer 2 Switches
Integrating verification mechanisms with Layer 2 switches enhances security at the data link layer. For instance, switches can be configured to authenticate users and devices using 802.1X authentication before granting network access. MAC address filtering can be used to restrict access to only authorized devices. VLAN segmentation can further isolate network segments, limiting the potential for lateral movement in the event of a breach. By integrating verification with Layer 2 switches, organizations can create a more comprehensive and resilient security architecture. This enhances security posture and supports zero trust policies by minimizing implicit trust and mandating verification for every access attempt based on authentication methods. We assure Your Infrastructure is Secure, Safe. Integrating with Layer 2 switches will help to implement zero trust.
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture
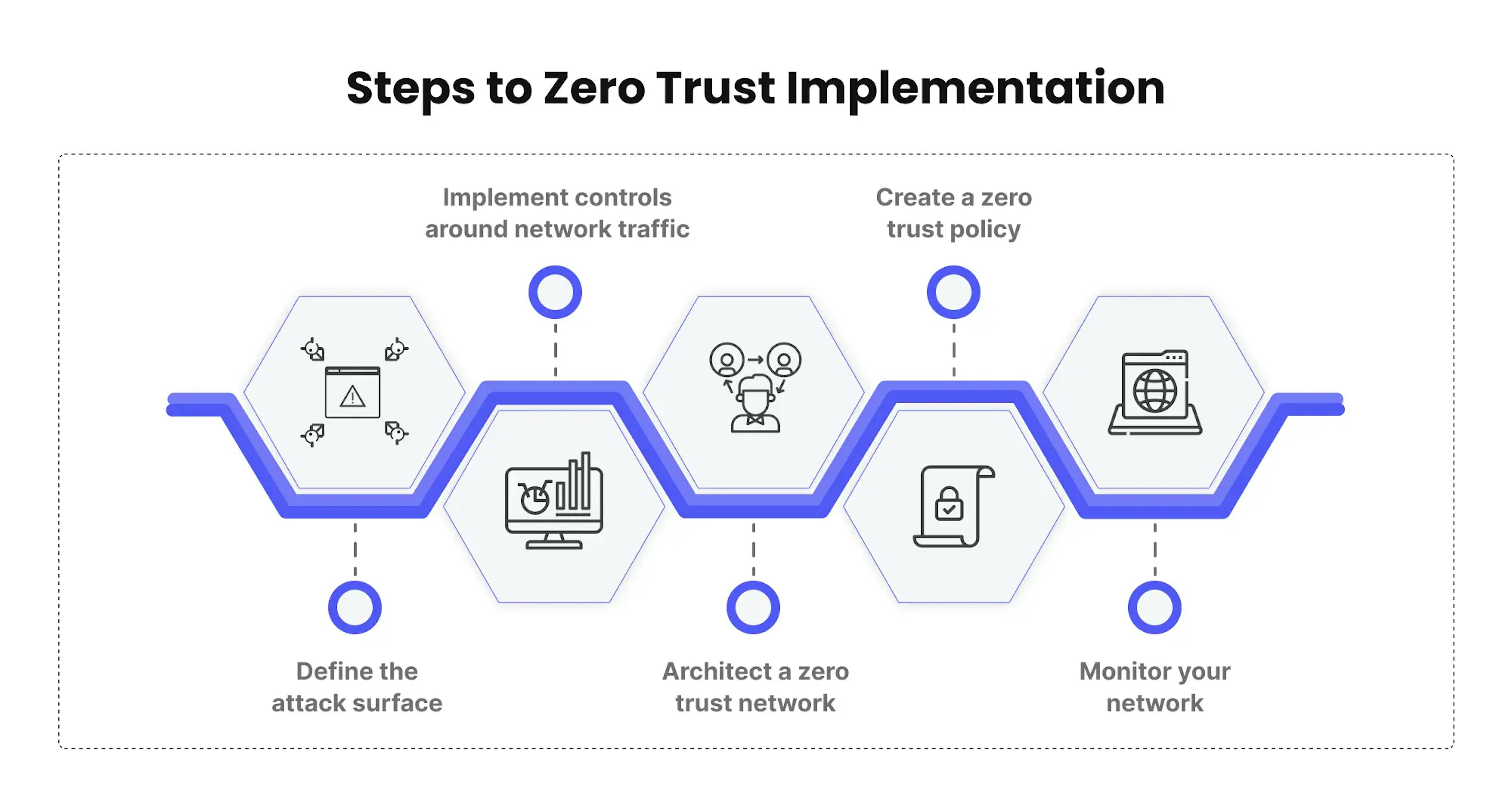
Steps to Implement Zero Trust Architecture
Begin by assessing your current security posture and identifying critical assets and data flows. Define clear network segment boundaries based on user and device roles, application sensitivity, and business functions to enhance cloud security. To strengthen security, consider the following steps:
- Implement multi-factor authentication and device posture assessment as an authentication method to verify the identity and security of users and devices.
- Deploy network segmentation and microsegmentation to isolate critical resources and limit lateral movement.
- Continuously monitor network traffic and user behavior to detect and respond to suspicious activities.
Regularly review and update your security policies to adapt to evolving threats. By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement zero trust architecture and enhance their overall security posture.
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust Security
Implementing zero trust security presents several challenges that organizations must address to ensure a successful transition. Complexity, legacy systems, organizational culture, and user experience are significant hurdles. By addressing these challenges proactively, organizations can overcome obstacles and successfully implement zero trust architecture. We assure Your Infrastructure is Secure, Safe.
Future Trends in Zero Trust Architecture
Automation, AI/ML, cloud-native solutions, and identity-centric security will shape the future of zero trust architecture. AI and machine learning will enhance threat detection and response capabilities, enabling organizations to proactively identify and mitigate emerging threats across multiple platforms. Cloud-native zero trust solutions will become more prevalent, providing scalable and flexible security for cloud environments. Identity-centric security will gain prominence, focusing on verifying and managing user identities as the primary control point. As zero trust continues to evolve, it will become an increasingly integral part of modern security architectures, enabling organizations to effectively protect their assets and data in an increasingly complex threat landscape. The zero trust security model will be enhanced and developed further, with zero trust access. We assure Your Infrastructure is Secure, Safe.
What is the role of layer 2 switches in a zero trust architecture?
Layer 2 switches play a crucial role in a zero trust architecture by facilitating segmentation within the network. They help enforce policies based on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” ensuring that devices are authenticated before being granted access to resources.
How does segmentation contribute to network security in zero trust?
Segmentation is essential in zero trust network security as it limits lateral movement within the network. By dividing the network into smaller, manageable segments, organizations can implement security policies based on the principle of least privilege, thereby reducing the overall attack surface.
What are the benefits of implementing zero trust architecture?
Implementing zero trust architecture provides several benefits, including improved security against internal and external threats, enhanced compliance with regulatory requirements, and increased visibility into network activities. It also allows for better management of identity and access based on user roles.
How do security devices fit into a zero trust model?
Security devices are integral to the zero trust security model as they enforce security policies and monitor traffic for anomalies. These devices include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and layer 2 switches, which collectively help maintain a secure environment and protect critical data.
Can you explain the principle of “never trust, always verify” in zero trust?
The principle of “never trust, always verify” is foundational to zero trust architecture. It implies that no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network perimeter. Continuous verification and monitoring ensure that only authenticated users can access sensitive resources.