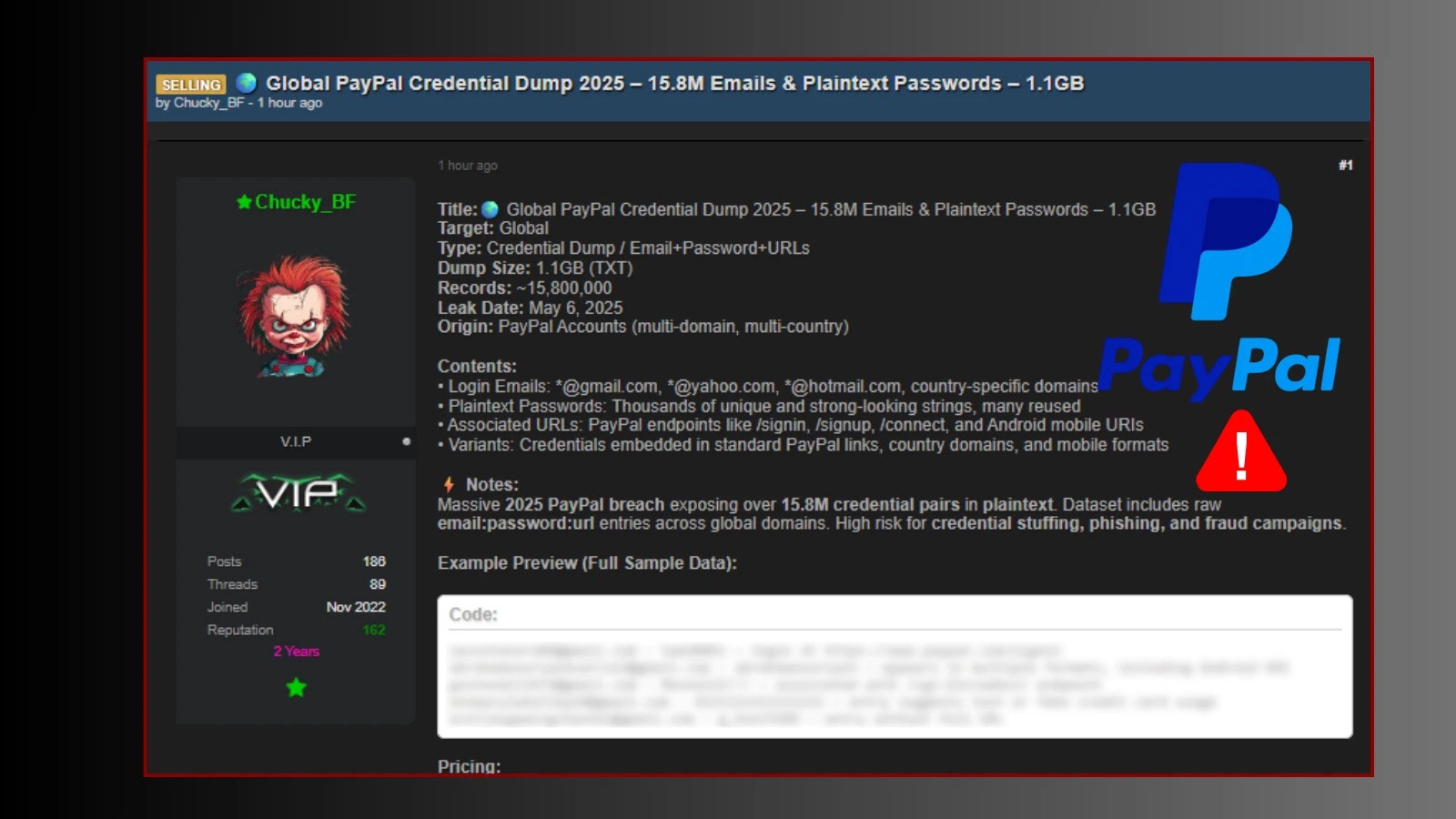
Threat Actor Allegedly Claiming Access to 15.8 Million PayPal Email and Passwords in Plaintext
Urgent Warning: Alleged PayPal Credential Leak – 15.8 Million Plaintext Pairs at Risk
The digital threat landscape continues to evolve at an alarming pace, and a recent development underscores the persistent danger of leaked credentials. A threat actor, identified as “Chucky_BF,” has reportedly advertised a “Global PayPal Credential Dump 2025” on a prominent cybercrime forum, claiming to possess over 15.8 million email and plaintext password combinations. This alleged dataset, weighing approximately 1.16GB, purports to contain sensitive credentials sourced from various PayPal domains. Such a breach, if confirmed, represents a severe security incident with far-reaching implications for individual users and the broader cybersecurity ecosystem.
The Alleged Compromise: What We Know
The advertisement by “Chucky_BF” details a dataset of 15,800,000 unique email and password pairs. The critical aspect of this claim is the assertion that the passwords are in plaintext format. Plaintext passwords are unencrypted and immediately usable by attackers, making them highly valuable for credential stuffing attacks, account takeover (ATO), and phishing campaigns. The sheer volume of records, combined with the plaintext nature, makes this a particularly concerning potential exposure.
While the exact origin of this alleged dump remains unverified, initial speculation points towards potential compromises of third-party services that integrate with PayPal, or perhaps a large-scale phishing operation that successfully harvested credentials. It’s crucial to understand that even if PayPal’s core systems were not directly breached, a leak of this magnitude from associated services or targeted user compromises can still lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
Understanding the Threat: Plaintext Passwords and Credential Stuffing
The alleged existence of 15.8 million plaintext PayPal credentials poses several immediate and long-term threats:
- Account Takeover (ATO): Attackers can directly log into user accounts using the leaked credentials, gaining access to financial information, linked bank accounts, and payment methods.
- Credential Stuffing: Many users reuse passwords across multiple online services. Attackers will leverage these leaked PayPal credentials to attempt logins on other popular platforms (e.g., email providers, social media, e-commerce sites). A successful credential stuffing attack on one platform can compromise numerous other accounts.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: The email addresses within the dump can be used for highly targeted phishing campaigns. Attackers can craft convincing emails, impersonating PayPal or other services, knowing that the recipient is a PayPal user.
- Identity Theft: While not direct personally identifiable information (PII), a compromised PayPal account can be a gateway to other PII, facilitating more extensive identity theft.
- Financial Fraud: Direct access to PayPal accounts enables unauthorized transactions, leading to financial losses for victims.
Remediation Actions and Proactive Security Measures
In light of this alleged threat, immediate and proactive measures are essential for all PayPal users and businesses. Even if you believe your account is secure, assume the worst and take preventative steps.
- Change Your PayPal Password Immediately: Use a strong, unique password that you do not use for any other online service. This password should be long, complex, and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This is the single most effective way to protect your account, even if your password is compromised. PayPal offers 2FA through security keys, authenticator apps, or SMS. Enable it now.
- Monitor Your Account Activity: Regularly review your PayPal transaction history and linked bank accounts/credit cards for any suspicious activity. Set up transaction alerts if available.
- Review Linked Accounts: Audit any services that are directly linked to your PayPal account (e.g., online stores, subscription services) and consider unlinking them if not necessary.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts: Exercise extreme caution with any emails or messages claiming to be from PayPal. Always navigate directly to the official PayPal website (`paypal.com`) to log in, rather than clicking on links in emails.
- Use a Password Manager: A reputable password manager can help you generate and securely store unique, strong passwords for all your online accounts, reducing the risk of credential stuffing.
- Check for Password Reuse: If you use the same password for your PayPal account as you do for other services, change those passwords immediately as well.
Relevant Tools for Detection and Mitigation
While this particular incident focuses on leaked credentials, the broader principles of defending against such threats often involve utilizing various cybersecurity tools. For general security posture improvement and threat detection, consider the following:
| Tool Name | Purpose | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Have I Been Pwned? | Checks if your email address or phone number has been exposed in a data breach. | haveibeenpwned.com |
| Common Password Managers (e.g., LastPass, 1Password, Bitwarden) | Securely generate and store unique, strong passwords; many offer breach monitoring. | bitwarden.com |
| NIST Password Guidelines | Provides best practices for creating and managing secure passwords. | csrc.nist.gov/pubs/sp/800/63b/rev0/final |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Solutions | For organizations: Collects and analyzes security logs to detect suspicious activity and potential breaches. | N/A (Industry solutions vary) |
Conclusion: The Imperative of Vigilance
The alleged PayPal credential dump serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing threats posed by malicious actors. While the validity of the claims by “Chucky_BF” is still under investigation, the potential for 15.8 million plaintext password exposures demands immediate attention. Users must prioritize strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication on all critical accounts. For cybersecurity professionals, this incident highlights the persistent need for robust credential management practices, continuous threat intelligence monitoring, and user education. Maintaining vigilance and adopting proactive security measures are not merely best practices; they are critical components of digital resilience in an increasingly hostile online environment.





