What Is Zero Trust Security and How to Implement It?
What is Zero Trust Security Model and How to Implement it and Implement Zero Trust.
In an era defined by increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, traditional perimeter-based security models are proving inadequate. Organizations are now turning to the zero trust security model as a more robust and effective approach to network security. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the zero trust architecture, exploring its core principles, benefits, and strategies for successful implementation. We will delve into the nuances of adopting zero trust, offering practical insights for security teams seeking to enhance their organization’s security posture. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge to implement zero trust security effectively through the adoption of zero trust access frameworks..
Understanding Zero Trust Security Model
Definition of Zero Trust Security
Zero trust is a security framework built on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that operate on the assumption of implicit trust within the network perimeter, zero trust assumes that no user or device, whether inside or outside the network, should be automatically trusted. Every access request is subjected to rigorous authentication and authorization processes before being granted. The core of zero trust is a shift away from perimeter-based security to a model where every user, device, and application is continuously validated. The zero trust model significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes the potential for lateral movement by malicious actors.
Core Principles of Zero Trust
The core principles of zero trust revolve around several key concepts that dictate how security controls are implemented and managed. These principles include:
- Least privilege, ensuring that users and devices have only the minimum necessary access to perform their tasks.
- Microsegmentation, which divides the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the blast radius of potential security breaches.
- Continuous monitoring and validation, involving constantly assessing the security posture of all entities attempting to access resources.
- Multi-factor authentication, adding an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification.
Understanding these core principles of zero trust is essential for effective zero trust implementation.
Comparison with Traditional Security Models
Traditional security models rely heavily on the concept of a trusted network perimeter, where entities inside the network are granted a certain level of implicit trust. In contrast, the zero trust model operates under the assumption that the network is always hostile, making it a crucial security approach., regardless of location or user status. This fundamental difference leads to vastly different security strategies. Perimeter-based security focuses on protecting the network’s entry points, while zero trust requires authentication and authorization for every access request, regardless of whether it originates from within or outside the network. The benefits of zero trust include enhanced security, reduced risk of lateral movement, and improved compliance with regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Implementing Zero Trust
Enhance Security Posture
One of the primary benefits of zero trust is its ability to enhance security posture. By adopting zero trust principles, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface and minimize the potential for breaches. The zero trust security model requires continuous authentication and authorization for every access request, regardless of the user’s location or device. This means that even if an attacker manages to compromise one part of the network, their lateral movement is severely limited. Implementing zero trust security strengthens overall security posture by ensuring that no user or device is implicitly trusted, forcing every entity to prove its trustworthiness before gaining access to sensitive resources. Furthermore, zero trust implementation allows security teams to gain better visibility into network activity, enabling them to detect and respond to threats more effectively. This proactive approach enhances security and reduces the risk of successful cyberattacks.
Improved Network Access Management
Improved network access management is another key advantage of the zero trust architecture. Traditional security models often rely on perimeter-based security, granting broad access to users and devices within the network. In contrast, zero trust requires granular access control based on the principle of least privilege., ensuring that users and devices have only the minimum necessary access to perform their tasks. This least privilege approach reduces the risk of insider threats and limits the damage that can be caused by compromised accounts. The zero trust model allows organizations to implement network access policies that are tailored to specific users, devices, and applications. By enforcing these policies, security teams can effectively control who has access to what resources and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. This improved network access management enhances security and simplifies compliance with regulatory requirements.
Reduction of Insider Threats
The reduction of insider threats is a significant benefit of zero trust. Insider threats, whether malicious or unintentional, pose a substantial risk to organizations. The zero trust model addresses this risk by eliminating implicit trust and requiring continuous validation of all users and devices. Implementing zero trust principles ensures that even employees with legitimate access to the network are subject to stringent authentication and authorization processes. This makes it more difficult for malicious insiders to exploit their access privileges and reduces the likelihood of unintentional data breaches caused by negligent employees. Moreover, the zero trust security model enhances visibility into user activity, allowing security teams to detect and respond to suspicious behavior more quickly. By reducing the risk of insider threats, zero trust contributes to a stronger overall security posture. Therefore, implementing zero trust policies can help protect sensitive data and prevent costly security incidents.
Zero Trust Architecture Explained
Components of Zero Trust Architecture
The zero trust architecture comprises several crucial components that work together to enforce the core principles of zero trust. These components play distinct roles, such as:
- Identity and access management (IAM) systems, which verify the identities of users and devices.
- Policy engines that evaluate access requests based on predefined security policies.
Furthermore, implementing zero trust also requires robust endpoint security solutions to protect devices from malware and unauthorized access, as well as security information and event management (SIEM) systems that monitor network activity and detect potential security threats. These components facilitate continuous authentication and authorization, ensuring that only trusted entities gain access to sensitive resources. The effectiveness of zero trust implementation heavily relies on the seamless integration and coordination of these various elements. By combining these components, organizations can establish a comprehensive zero trust framework.
Zero Trust Network Access
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a critical component of the broader zero trust security model, focusing specifically on securing network access. ZTNA replaces traditional VPNs with a more secure, context-aware approach to network access. Instead of granting broad network access based on network perimeter, ZTNA provides granular, need-to-know access to specific applications and resources. This limits the attack surface and reduces the risk of lateral movement if a breach occurs. Implementing zero trust network access requires robust authentication mechanisms, continuous monitoring, and adaptive access control policies. ZTNA solutions typically leverage microsegmentation and software-defined perimeters to further isolate resources and prevent unauthorized access. By implementing zero trust network access, organizations can enhance security and simplify network management.
Security Framework for Zero Trust
A robust security framework is essential for successful zero trust implementation. This framework should encompass a well-defined set of security policies, security protocols, and security controls that align with the core principles of zero trust. The framework should also address various aspects of the IT environment, including network security, endpoint security, application security, and data security. Organizations should develop a zero trust maturity model to guide their zero trust implementation efforts. This model helps them assess their current security posture, identify areas for improvement, and track their progress over time. The security framework should also incorporate threat intelligence and vulnerability management to proactively identify and mitigate potential security risks. By establishing a comprehensive security framework, organizations can ensure that their zero trust strategies are effectively implemented.
How to Implement Zero Trust Security
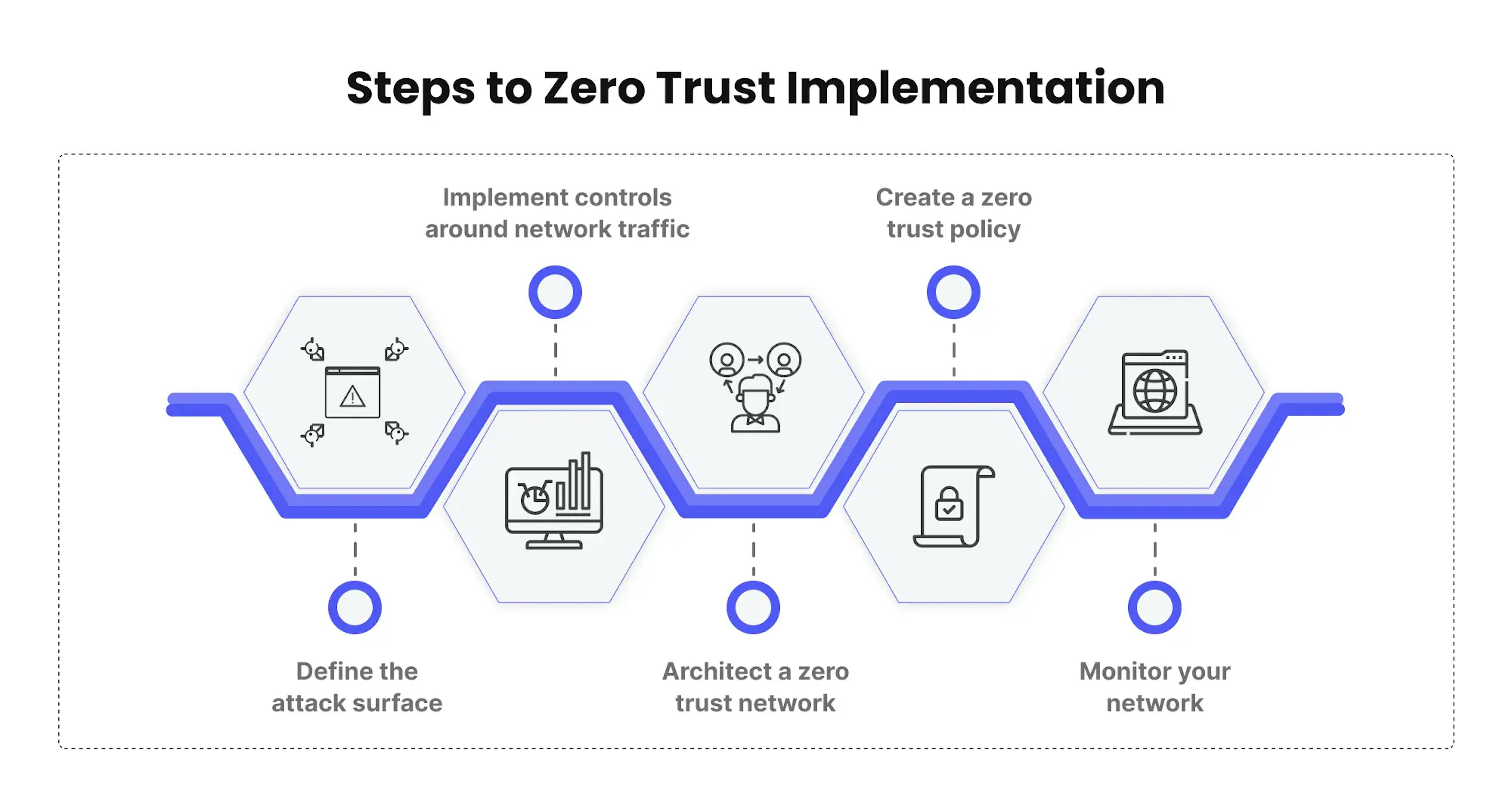
Steps to Implement Zero Trust
Implementing zero trust requires a strategic and multifaceted approach to ensure robust security measures. Several key steps are involved in building a robust zero trust model. These steps include:
- Assessing the current security posture and identifying critical assets.
- Defining clear security policies based on core principles of zero trust, like least privilege and continuous verification.
- Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, including multi-factor authentication, to verify user and device identities.
- Implementing microsegmentation to isolate sensitive resources and limit lateral movement.
- Continuously monitoring and analyzing network traffic to detect and respond to threats is essential in a zero trust security approach.
- Regularly reviewing and updating security policies to maintain the effectiveness of the zero trust security model.
This ensures a robust and adaptive zero trust implementation.
Zero Trust Implementation Strategies
There are several zero trust implementation strategies that organizations can adopt, depending on their specific needs and resources. One common approach is to start with a pilot project, focusing on a specific department or application to test and refine zero trust policies before rolling them out across the entire organization. Another strategy involves prioritizing the protection of the most critical assets first, gradually expanding zero trust controls to other areas of the network. The zero trust architecture is a great security architecture. Zero trust implementation also requires a shift in mindset, from assuming trust to continuously verifying every user and device attempting to access resources. Educating employees about zero trust principles and security best practices is essential for fostering a culture of security. These strategic approaches help organizations effectively implement and manage zero trust in their zero trust solution implementation. environment.
Use Cases for Zero Trust Security
Zero trust is applicable across a wide range of use cases, providing enhanced security in various scenarios. For remote access, zero trust network access (ZTNA) ensures that only authorized user and device can access internal applications, replacing traditional VPNs. In cloud environments, zero trust helps secure sensitive data and workloads by enforcing strict security measures based on the principle of least privilege. access control and continuous monitoring. For IoT devices, zero trust addresses the inherent security risks by requiring strong authentication and authorization for every device connection. In financial services, zero trust protects sensitive customer data and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. In healthcare, it safeguards patient information and prevents unauthorized access to medical records. These diverse use cases demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of zero trust in enhancing security posture.
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
Common Obstacles
Despite its numerous benefits of zero trust, implementing zero trust also presents several challenges. One common obstacle is the complexity of the zero trust architecture, which requires careful planning and integration of various security tools. Legacy systems that are not designed to support zero trust can also pose a significant challenge. Additionally, organizations may struggle with defining and enforcing granular access control policies, ensuring that users and devices have only the least privilege necessary. Resistance to change from employees who are accustomed to traditional security measures can impede the adoption of a zero trust approach. security models can also hinder the implementation of a zero trust approach. zero trust implementation process. These obstacles highlight the need for a strategic and phased approach to adopting zero trust.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges
To overcome the challenges of zero trust implementation, organizations can adopt several strategies. Conducting a thorough assessment of the current IT infrastructure and identifying compatibility issues with existing systems is crucial. Investing in security tools that support the verification of user identities in a zero trust framework. zero trust principles and provide granular access control capabilities is also essential. Providing comprehensive training to employees to educate them about zero trust and its benefits can help address resistance to change. Developing a phased implementation plan that prioritizes the most critical assets and gradually expands zero trust security model to other areas of the network can also ease the transition to a zero trust solution. These solutions enable organizations to effectively address the challenges of implementing zero trust security and reap its benefits
Future of Zero Trust Security
The future of zero trust security is bright, with ongoing advancements in cloud security technology and increasing adoption across various industries. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the zero trust security model will become even more critical for protecting sensitive data and infrastructure. Future trends include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance threat detection and response capabilities. The rise of software-defined perimeters and microsegmentation will further strengthen network security and limit lateral movement. As zero trust maturity models become more refined, organizations will have a clearer path for assessing and improving their security posture. The convergence of zero trust with other emerging security measures that enhance the zero trust work environment. security technologies will drive innovation and enhance overall security effectiveness.
What is Zero Trust Security and How to Implement It?
Zero Trust Security is an approach to security that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It emphasizes the need for strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources in a network, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the perimeter.
What are the Core Principles of Zero Trust?
The core principles of Zero Trust include the assumption that threats could be internal or external, the necessity of verifying every request, and the implementation of least-privilege access. These principles help to enhance security and protect sensitive data.
How Does Zero Trust Work in a Remote Work Environment?
In a remote work environment, Zero Trust Security ensures that all users, regardless of location, are authenticated and authorized before accessing network resources. This is particularly important as remote work increases the risk of unauthorized access.
What are the Benefits of Implementing Zero Trust Security?
Implementing Zero Trust Security helps organizations reduce the risk of data breaches, improve compliance, and enhance overall security posture. It also provides better control over data access and minimizes the potential attack surface.
What are the Pillars of Zero Trust Security?
The pillars of Zero Trust include identity verification, device security, network segmentation, and continuous monitoring. Each pillar reinforces the Zero Trust framework and contributes to a robust security model.
How to Transition Toward a Zero Trust Security Model?
Transitioning toward a Zero Trust Security model involves assessing current security processes, identifying gaps, and gradually implementing Zero Trust principles. Organizations should start with critical assets and expand their Zero Trust framework over time.
What is a Zero Trust Platform?
A Zero Trust Platform is a comprehensive solution that integrates various security technologies to deliver a Zero Trust Security model. It often includes identity and access management, endpoint security, and network access control.
What Use Cases are Common for Zero Trust Implementation?
Common use cases for Zero Trust implementation include protecting sensitive data, securing cloud access, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Organizations in sectors such as finance and healthcare often find Zero Trust particularly beneficial.
How Does a Zero Trust System Enhance Network Security?
A Zero Trust System enhances network security by continuously validating user identities and monitoring access attempts. This proactive approach reduces reliance on perimeter-based security, making it harder for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities.