Zero Trust Architecture: A Zero trust Security Model for Small Business
In today’s digital age, where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated and pervasive, traditional security models that rely on implicit trust are no longer sufficient. For small businesses, which often lack the robust resources of larger enterprises, adopting a more proactive and resilient security posture is critical. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) emerges as a transformative security framework, fundamentally shifting the paradigm from “trust but verify” to “never trust, always verify,” reinforcing the need for security services. This approach mandates rigorous authentication and authorization for every user and device attempting to access network resources, regardless of their location. By implementing zero trust security, small businesses can significantly reduce the risk of breaches and enhance their overall cybersecurity resilience.
Understanding Zero Trust Architecture
What is Zero Trust?
Zero trust is a security model predicated on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security approaches that operate on the assumption that everything inside the network perimeter is safe, zero trust architecture assumes that no user or device should be automatically trusted. Every access request is treated as a potential threat, requiring strict identity verification and continuous monitoring. The concept of zero trust mandates that organizations implement stringent access control policies, ensuring that users and devices only have access to the resources they absolutely need to perform their duties. This approach minimizes the attack surface and limits the potential damage from a security breach, making it an essential component of modern cybersecurity.
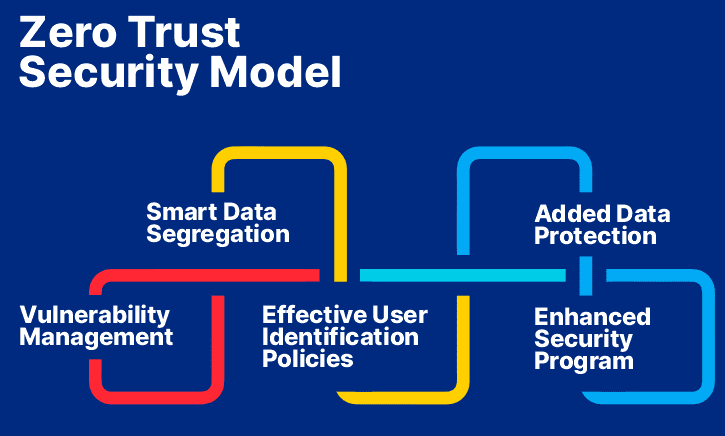
Key Principles of Zero Trust
Zero trust architecture relies on several key principles to achieve its goals. In particular, the approach is based on:
- Identity and access management, demanding strong authentication methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users and devices.
- Least privilege access, ensuring users only access resources needed for their roles, limiting unauthorized access and lateral movement.
Continuous monitoring and validation are also essential for maintaining strong security, assessing user behavior and device integrity to detect and respond to threats. Applying these zero trust principles is vital for any small business aiming to strengthen its cybersecurity.
The Importance of Zero Trust Security for Small Businesses
For small businesses, the importance of zero trust security cannot be overstated. These organizations are often prime targets for cyber threats due to limited resources and expertise in cybersecurity. A single breach can have devastating consequences, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and even closure. Implementing zero trust architecture provides small businesses with a robust security framework that significantly reduces the risk of successful cyberattacks. By adopting a “never trust” approach, small businesses can protect their sensitive data, maintain business continuity, and build trust with their customers. Furthermore, zero trust security can help small and medium-sized businesses comply with increasingly stringent data privacy regulations, enhancing their credibility and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Implementing Zero Trust Security Model
Steps to Implement Zero Trust Architecture
To effectively implement a zero trust architecture, small and medium-sized businesses should adopt a phased approach, starting with a comprehensive assessment of their current security posture. This involves identifying critical assets, mapping data flows, and understanding existing vulnerabilities. Next, organizations need to implement strong security measures; these should include:
- Implementing strong identity and access management (IAM) solutions, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users and devices.
- Implementing least privilege access controls, ensuring that users only have access to the resources they absolutely need.
Continuous monitoring and logging should be established to detect and respond to potential cyber threats in real-time. Applying zero trust principles is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and adaptation.
Best Practices for Implementing Zero Trust
To help small businesses successfully implement zero trust, several best practices can be followed. These practices will strengthen your organization’s security and reduce risk. To begin with, it is important to establish a robust zero trust framework that includes the pillars of zero trust.
- Prioritize the protection of your most critical assets first, focusing on the data and systems that are most vulnerable or essential to your operations.
- Implement strong authentication methods, such as MFA, for all users and devices.
- Regularly review and update access control policies to ensure that users only have the necessary permissions.
- Utilize micro-segmentation to isolate critical systems and data, limiting the impact of a potential breach and supporting a comprehensive security strategy.
- Continuously monitor network traffic and user behavior to detect and respond to anomalies.
- Provide ongoing training to employees on zero trust principles and cybersecurity awareness.
Common Challenges in Applying Zero Trust
Implementing zero trust security is not without its challenges, particularly for small businesses with limited resources. One common challenge is the complexity of integrating zero trust principles into existing infrastructure. Legacy systems may not be compatible with modern authentication methods, requiring significant upgrades or replacements to align with a zero trust framework. Another challenge is the potential for user friction, as strict access control policies and frequent authentication requests can impact productivity. Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, clear communication, and a phased approach to implementing zero trust. Addressing these challenges ensures a smoother transition to a more secure and resilient security model, helping to reduce the risk of cyber threats.
Benefits of Zero Trust for Small Businesses
Enhancing Cybersecurity Posture
For small businesses, adopting a zero trust architecture significantly enhances their cybersecurity posture. Unlike traditional security models that rely on perimeter-based security, zero trust security mandates strict verification for every user and device attempting to access network security. This zero trust approach minimizes the attack surface, reducing the potential impact of a breach and aligning with the pillars of zero trust. By implementing zero trust principles, small and medium-sized businesses can proactively protect their sensitive data and critical assets. This proactive stance builds a robust security framework that defends against evolving cyber threats, providing a more resilient and adaptable security model that shields the organization’s security.
Mitigating Cyber Threats
One of the primary benefits of implementing zero trust is its ability to mitigate cyber threats effectively. By assuming no implicit trust, zero trust architecture forces continuous authentication and authorization, limiting the potential for unauthorized access. In the event of a breach, the zero trust network segmentation contains the damage, preventing lateral movement and minimizing the impact on other systems, which is a key pillar of zero trust security. Applying least privilege access ensures that users only have access to the resources they need, further reducing the risk of insider threats and compromised accounts, thereby enhancing cyber security. This security strategy significantly lowers the likelihood of successful cyber attacks. Using the “never trust” principle as a guide, it ensures that security policies are always active.
Cost-Effectiveness of Zero Trust Strategy
While some may perceive implementing zero trust as a costly endeavor, a well-planned zero trust strategy can be surprisingly cost-effective for small businesses. By reducing the risk of costly data breaches and system downtime, zero trust security offers a significant return on investment. Furthermore, security solutions like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and cloud-based access control can be scaled to meet the specific needs and budget of small and medium-sized businesses. Streamlining security measures and automating threat detection also reduces the burden on IT staff, freeing up resources for other critical tasks. The long-term benefits of enhanced security and reduced risk far outweigh the initial investment in zero trust architecture, making it an excellent security model for small and medium-sized businesses.
Zero Trust Security in Action
Case Studies of Small Businesses Using Zero Trust
Implementing zero trust can seem daunting for small businesses, but real-world examples demonstrate its effectiveness. Consider a small accounting firm that adopted a zero trust architecture after experiencing a phishing attack. By implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access, they significantly reduced the risk of future incidents. Similarly, a local e-commerce store implemented micro-segmentation to protect their customer database, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. These case studies highlight how zero trust principles can be tailored to fit the specific needs and resources of small and medium-sized businesses, enhancing their cybersecurity posture and ensuring business continuity. Our security team is here to guide small and medium-sized businesses in the adoption of zero trust to ensure the organization’s security.
Integrating Zero Trust with Microsoft 365
For many small and medium-sized businesses, Microsoft 365 is a critical tool for collaboration and productivity. Implementing zero trust within this environment can significantly enhance security. This involves leveraging features such as Azure Active Directory for identity and access management, conditional access policies to enforce MFA based on risk factors, and Microsoft Defender for Office 365 to protect against phishing and malware. By integrating zero trust principles with Microsoft 365, small businesses can ensure that only authorized users and devices have access to sensitive data, regardless of their location. This integration strengthens cybersecurity and supports a secure remote work environment. Zero trust security with Microsoft 365 is now a best practice for cyber security policies in modern business.
Monitoring and Adapting Zero Trust Architecture
Zero trust architecture is not a set-it-and-forget-it solution; it requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to maintain customer trust. Small businesses must implement robust monitoring tools to detect anomalies in user behavior, device integrity, and network traffic. This data should be used to continuously refine access control policies and identify potential cyber threats. Regularly assess the effectiveness of your zero trust security measures and adapt your security strategy to address emerging cybersecurity challenges. By proactively monitoring and adapting your zero trust infrastructure, you can maintain a strong security posture and reduce the risk of successful cyber attacks. We assure you infrastructure is secure, safe, by using our zero trust security model.
Future of Cybersecurity with Zero Trust
Emerging Trends in Zero Trust Security
The field of zero trust security is constantly evolving, with several emerging trends shaping its future. One key trend is the increasing adoption of zero trust network access (ZTNA), which provides secure remote access to applications without the need for a traditional VPN, enhancing customer trust. Another trend is the integration of zero trust principles with cloud-native architectures, enabling organizations to build secure and scalable applications in the cloud, which is essential for comprehensive security. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on data-centric zero trust, which focuses on protecting data at rest and in transit, regardless of where it is stored or accessed. These trends point towards a future where zero trust security is more adaptive, automated, and pervasive.
The Role of AI in Zero Trust Models
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in enhancing zero trust models. AI-powered tools can automate threat detection, identify anomalous user behavior, and dynamically adjust access control policies based on real-time risk assessments. For example, AI can analyze login patterns to detect compromised accounts and automatically trigger MFA or block suspicious access attempts. AI can also be used to continuously monitor device posture and identify potential vulnerabilities. By leveraging AI, small businesses can significantly improve the effectiveness and efficiency of their zero trust deployments. The concept of zero trust is constantly changing and AI is one of the biggest factors.
Preparing for Evolving Cyber Threats
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, small businesses must proactively prepare for evolving risks by implementing a zero trust framework. Implementing zero trust security is a critical step in building a resilient cybersecurity posture. Stay informed about the latest threat intelligence and adapt your security strategy accordingly. Regularly conduct security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in your zero trust architecture. Provide ongoing training to employees on zero trust principles and cybersecurity awareness. By staying vigilant and continuously improving your security measures, you can effectively defend against emerging cyber threats and protect your organization’s security. Don’t let security vulnerabilities compromise your organization’s integrity—act now to safeguard your endpoints, with a zero trust approach.
ZTNA vendor comparison table
| Vendor | ZTNA Type | Deployment | Free Version | MFA | Device Posture Check | SSO | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Check Point ZTNA | ZTNA-as-a-Service | Cloud, On-prem, Hybrid | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Enterprises needing unified security with advanced threat prevention |
| Zscaler Private Access | Cloud-native | SaaS | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Large organizations with distributed workforce |
| Palo Alto Prisma Access | ZTNA 2.0 | Cloud, Hybrid | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Enterprises seeking autonomous Zero Trust with SASE integration |
| Cloudflare Zero Trust | Unified Platform | Cloud | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Fast, easy-to-manage Zero Trust with global reach |
| Fortinet FortiClient | ZTNA Agent | Cloud, On-prem | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Organizations using Fortinet ecosystem |
| Twingate | Cloud-native | Cloud | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Teams needing flexible, user-friendly ZTNA alternative to VPNs |
| Appgate SDP | Specialized ZTNA | Cloud, Hybrid | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Secure access across hybrid infrastructures |
| Ivanti Neurons ZTNA | Specialized ZTNA | Cloud | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Enterprises focused on digital employee experience and endpoint security |
| NordLayer ZTNA | Unified Platform | Cloud | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Agile businesses and distributed workforces |
| Google BeyondCorp | Specialized ZTNA | Cloud | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Organizations needing scalable, identity-driven access |
5 Surprising Facts About Zero Trust for Small Businesses
- Zero Trust is not just a security model; it emphasizes the importance of verifying every device and user, making it highly relevant for small businesses facing evolving cyber threats.
- Many small businesses mistakenly believe they are too insignificant to be targeted by cybercriminals, but in reality, they are often seen as easy targets due to their typically weaker security measures.
- Implementing Zero Trust can lead to cost savings in the long run, as it helps prevent costly data breaches and reduces the need for extensive security overhauls.
- Zero Trust can enhance collaboration among remote teams, allowing small businesses to securely share sensitive information without exposing their networks to unnecessary risks.
- Adopting a Zero Trust framework can improve compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA, making it easier for small businesses to meet legal requirements and avoid fines.
-
What is the zero trust security model and why is it important for small businesses?
The zero trust security model is a cybersecurity framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It is crucial for small businesses as it helps mitigate security risks associated with traditional perimeter-based security models, ensuring that all users and devices, regardless of their location, are authenticated and authorized before accessing sensitive data and resources.
How can small businesses implement zero trust architecture effectively?
Small businesses can implement zero trust architecture by first conducting a comprehensive risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities. They should then establish zero trust policies that enforce strict user authentication, device security, and continuous monitoring of network activity. Additionally, integrating security controls and employing best practices can enhance their overall security posture.
What are the benefits of zero trust solutions for small and medium businesses?
The benefits of zero trust solutions for small and medium businesses include improved security against cyber threats, reduced risk of security incidents, and enhanced data protection. By adopting a zero trust strategy, businesses can ensure that sensitive information is shielded from unauthorized access, thereby fostering trust with clients and stakeholders.
What are the key pillars of implementing a zero trust strategy?
The key pillars of implementing a zero trust strategy include identity verification, device security, least privilege access, and continuous monitoring. These components work together to create a robust security architecture that protects against potential breaches and aligns with cybersecurity best practices.
How does zero trust address the limitations of traditional security?
Zero trust addresses the limitations of traditional perimeter-based security by focusing on a model where trust is never assumed, regardless of whether the user is inside or outside the network. This approach ensures a more integrated security framework that is better equipped to handle modern cyber threats.
What are some common security practices within a zero trust model?
Common security practices within a zero trust model include strong user authentication methods, encryption of data in transit and at rest, regular security audits, and implementing multi-factor authentication. These practices help reinforce the security infrastructure and protect businesses from evolving cyber risks.
How can businesses of all sizes benefit from adopting zero trust principles?
Businesses of all sizes can benefit from adopting zero trust principles by enhancing their overall cybersecurity posture. By ensuring that every access request is thoroughly vetted, companies can reduce the likelihood of data breaches and improve their resilience against cyber attacks. This approach is particularly beneficial for small businesses that may lack extensive security resources.
What steps should small businesses take to begin implementing zero trust policies?
To begin implementing zero trust policies, small businesses should start with small steps, such as identifying critical assets, mapping data flows, and assessing user access levels. They should also invest in training employees about security protocols and continuously evaluate their security architecture to adapt to new threats.