Zero Trust Architecture: Implementation Beyond the Buzzword.
Zero Trust Architecture: Implementation Beyond the Buzzword
In today’s rapidly evolving cyber landscape, traditional security models are proving inadequate against sophisticated threats. Enter Zero Trust Architecture, a concept that is moving beyond the buzzword to become a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategies. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we understand the paramount importance of safeguarding your enterprise from potential breaches while ensuring that your infrastructure remains secure and reliable. Embracing Zero Trust requires a shift in mindset—one that assumes threats may exist both outside and inside the network, necessitating a robust framework to protect your assets and maintain your organization’s integrity.
Understanding Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is not merely a fleeting trend but a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity that emphasizes the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This security model challenges the implicit trust often granted under traditional perimeter-based security frameworks, advocating instead for a model where every access request is scrutinized. By implementing zero trust, organizations can fortify their defenses against attackers who exploit the lack of visibility and control inside the network perimeter. This architecture leverages real-time verification, identity and access management, and multi-factor authentication to ensure only legitimate users gain access to critical resources.
Defining Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security is a paradigm shift that focuses on minimizing implicit trust while maximizing security posture through rigorous authentication and access control measures. The concept of zero trust revolves around verifying every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location within the network. By adopting a zero trust model, organizations can effectively mitigate risks associated with lateral movement and potential data breaches. This security model integrates technologies such as segmentation and zero trust network access, ensuring that every interaction within the network is subject to stringent verification processes, thereby enhancing overall cybersecurity resilience.
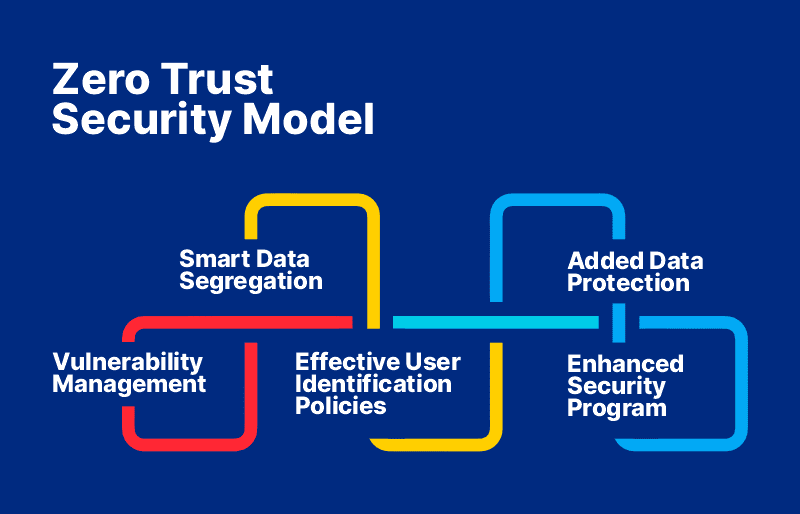
Core Principles of Zero Trust
The core principles of Zero Trust Architecture are designed to provide a robust framework for cybersecurity. At its heart is the tenet of least privilege, which ensures that users have only the minimum access necessary to perform their functions. This is coupled with continuous verification and identity management, where multi-factor authentication (MFA) plays a crucial role. The architecture also emphasizes segmentation to limit the impact of potential breaches and enhance visibility inside the network. By embedding these zero trust principles into security policies, organizations can move beyond traditional models and embrace a comprehensive zero trust strategy.
Zero Trust vs Traditional Security Models
Traditional security models have long relied on a strong perimeter to keep threats at bay, assuming that threats primarily originate outside the network. However, this approach often falls short in addressing modern cyber threats, which exploit the implicit trust granted within the network. Zero Trust Architecture addresses these vulnerabilities by treating every access request as potentially malicious, regardless of its origin. Unlike traditional models, zero trust requires continuous monitoring and real-time authentication, providing a dynamic and adaptive security posture. Through this proactive approach, security professionals can anticipate and mitigate risks more effectively, safeguarding your organization’s infrastructure against evolving threats and security incidents.
The Importance of Moving Beyond the Buzzword
Why Zero Trust is More than Just a Trend
At Team win Global Technological, we emphasize that zero trust architecture transcends mere buzzword status to become an essential component of modern security practices. This architecture is not simply a reactionary measure to evolving cyber threats but a proactive strategy designed to fortify organizational defenses. By implementing the zero trust model, companies are positioning themselves ahead of potential breaches, ensuring robust protection of sensitive data. This approach represents a shift from traditional network security measures, which often relied on perimeter-based defenses. Zero trust redefines security by continuously verifying every access request, ensuring that only authenticated users engage with critical resources. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, adopting zero trust principles is no longer optional but imperative for maintaining a resilient security posture.
Common Misconceptions about Zero Trust
Despite its widespread adoption, misconceptions about zero trust architecture persist, potentially hindering effective implementation and understanding of the security controls involved. One frequent misunderstanding is that zero trust is solely about technology, when in reality, it encompasses a broader security strategy that integrates technology, policies, and user behavior management. Another fallacy is the belief that zero trust is limited to external threats, whereas it also addresses insider risks by minimizing implicit trust within the network. Some may perceive zero trust implementation as overly complex or costly, yet the long-term benefits, including reduced lateral movement and enhanced visibility, outweigh initial challenges. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we guide organizations through these misconceptions, ensuring a seamless transition to a zero trust environment that secures both internal and external boundaries.
Real-world Applications of Zero Trust
Zero trust architecture is not merely theoretical; its real-world applications are transforming cybersecurity landscapes across various industries. By implementing zero trust, companies are effectively safeguarding endpoints and ensuring that sensitive information remains secure, regardless of user location. In practice, this involves leveraging multi-factor authentication, segmentation, and continuous identity verification to control access. Organizations that have embraced zero trust report significant reductions in data breaches and an improved security posture against the evolving threat landscape. For instance, financial institutions are employing zero trust to protect critical customer data, while healthcare providers use it to secure patient records. As security professionals, we at Teamwin Global Technologica are committed to helping clients harness the full potential of zero trust principles, providing solutions that are both innovative and reliable.
Implementation of Zero Trust Architecture
Key Steps in the Zero Trust Journey
Embarking on the journey to implement zero trust architecture requires a strategic approach that aligns with the overarching goals of your cybersecurity framework. The initial step involves a comprehensive assessment of existing security measures, identifying areas where implicit trust has been historically granted. Organizations must then integrate zero trust principles by redefining access control policies and authorization to ensure every access request is subject to verification. A crucial component is the deployment of identity and access management systems, which streamline authentication processes and enforce the principle of least privilege. By adopting these foundational steps, enterprises can transition smoothly towards a robust zero trust security model, fortifying their defenses against potential breaches.
Strategies for Successful Implementation
Successful implementation of zero trust architecture hinges on a carefully crafted strategy that encompasses technology, policy, user behavior, and robust security controls. Organizations should prioritize real-time monitoring and continuous verification to anticipate and mitigate threats proactively within the current threat landscape. This involves integrating segmentation and zero trust network access to limit lateral movement within the network. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) serves as a cornerstone in this strategy, enhancing the security posture by ensuring only authenticated users gain access to critical resources. Embracing zero trust requires collaboration between security teams and stakeholders to redefine security architecture in a manner that aligns with business objectives, ensuring both protection and operational efficiency.
Challenges and Solutions in Adoption
Adopting zero trust architecture presents unique challenges that organizations must address to ensure a successful transition within their network security framework. One significant challenge is overcoming the inertia of traditional security models, which often rely on perimeter-based defenses. To move beyond these limitations, companies should focus on enhancing visibility inside the network and reducing implicit trust. Implementing zero trust can appear daunting, but solutions such as phased deployment and leveraging existing technologies can alleviate complexities. By prioritizing user education and fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can surmount barriers to adoption, ultimately enhancing their cybersecurity resilience and safeguarding against sophisticated attackers.
Zero Trust Network Access and Authentication
Understanding Zero Trust Network Access
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a pivotal component of the broader zero trust architecture, emphasizing the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models, ZTNA ensures that every access request is scrutinized, regardless of the user’s location inside the network. By implementing ZTNA, organizations can effectively mitigate risks associated with lateral movement and potential breaches. This approach involves integrating technologies like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and segmentation to ensure that only verified users can access critical resources. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we empower clients to embrace zero trust principles, providing solutions that fortify their defenses and enhance their security posture.
Role of Authentication in Zero Trust Security
Authentication plays a crucial role in realizing the zero trust security model, acting as a gatekeeper that verifies identities before granting access. By adopting robust identity and access management practices, organizations can ensure that implicit trust is minimized, and every access request is subject to verification. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a cornerstone of this strategy, enhancing security by requiring additional verification steps beyond traditional password-based methods. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we recognize the paramount importance of safeguarding your enterprise and ensure that only authenticated users engage with your network, thus reducing the risk of breaches and maintaining a resilient security posture.
Integrating Multi-Factor Authentication
Integrating Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Integrating security controls into your security architecture is essential for effective zero trust implementation. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of verification, significantly enhancing security by ensuring that only legitimate users can access sensitive resources. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, implementing MFA becomes imperative in maintaining a robust defense against security incidents. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we guide organizations through the seamless integration of MFA into their security strategies, ensuring that your infrastructure is secure and resilient. By adopting MFA, you can anticipate and mitigate cyber risks, safeguarding your enterprise from potential breaches and reinforcing your commitment to security.
Building a Zero Trust Security Model
Pillars of Zero Trust Security
The pillars of zero trust security form the foundation of a robust architecture designed to protect against evolving cyber threats. Central to this model is the concept of least privilege, ensuring users have only the access necessary to perform their tasks, thus minimizing the risk of lateral movement. Continuous verification and real-time monitoring are essential to maintaining visibility inside the network, detecting and responding to potential threats swiftly. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we help organizations build a zero trust environment by integrating these core principles into their security strategies, empowering clients to fortify their defenses and achieve peace of mind through proactive measures.
Creating a Zero Trust Environment
Creating a zero trust environment involves redefining security measures to align with modern security challenges and reduce the attack surface. This process requires an overhaul of traditional perimeter-based defenses, shifting towards a model where every access request undergoes rigorous scrutiny. By implementing zero trust policies that prioritize granular segmentation and continuous verification, organizations can effectively mitigate risks and enhance their security posture. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we assure our clients that transitioning to a zero trust environment is not only feasible but essential for enhancing their network security. We work closely with your security teams to integrate zero trust principles seamlessly, ensuring your infrastructure remains secure and resilient against potential breaches.
Aligning Security Strategies with Zero Trust Principles
Aligning your security strategies with zero trust principles is crucial for maintaining a robust defense against cyber threats. This alignment involves moving beyond traditional network security models and adopting a proactive approach that emphasizes continuous verification, least privilege access, and robust security controls. At Teamwin Global Technologica, we encourage organizations to embrace a zero trust strategy that integrates cutting-edge technologies such as multi-factor authentication and identity management. By doing so, you can anticipate and mitigate cyber risks, fortifying your defenses and safeguarding your enterprise. Our commitment is to provide you with reliable solutions that align with your business objectives, ensuring both protection and operational efficiency.
5 Surprising Facts About Zero Trust Architecture Beyond the Buzzword
- Zero Trust isn’t just a technology but a comprehensive strategy that requires a cultural shift within organizations.
- Over 70% of organizations adopting Zero Trust report increased security effectiveness and reduced risks.
- Zero Trust can significantly improve remote work security, making it crucial in today’s hybrid work environments.
- Implementing Zero Trust can lead to faster incident response times, as it relies on continuous monitoring and verification.
- Zero Trust principles can be applied beyond IT security, influencing areas like data governance and compliance practices.
What are the implementation strategies for embracing Zero Trust?
Implementation strategies for embracing Zero Trust include identifying critical assets, evaluating current security protocols, and integrating identity providers for better authentication. Organizations should also consider adopting zero trust network access solutions to enforce strict access controls and reduce potential vulnerabilities in their cybersecurity framework.
How can organizations ensure security without compromising user experience in a Zero Trust Architecture?
Organizations can ensure security without compromising user experience by implementing seamless authentication methods, such as single sign-on (SSO) and adaptive authentication. These techniques allow for a streamlined user experience while still adhering to the strict access controls central to a Zero Trust Architecture.
What role do identity providers play in a Zero Trust Environment?
Identity providers are crucial in a Zero Trust Environment as they facilitate the authentication and authorization processes. By ensuring that only verified users have access to sensitive resources, identity providers help enforce the strict access controls that are a hallmark of the Zero Trust Security model.
What is the threat landscape in relation to Zero Trust Security?
The threat landscape in relation to Zero Trust Security is ever-evolving, with cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated. By adopting a Zero Trust approach, organizations can better protect themselves from these emerging threats by minimizing trust and ensuring that every access request is scrutinized, thus reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
What are the pillars of Zero Trust in a modern security strategy?
The pillars of Zero Trust in a modern security strategy include identity verification, device security, network segmentation, and data protection. These pillars work together to create a comprehensive security posture that effectively mitigates risks and enhances the overall integrity of an organization’s cybersecurity effort