DHCP Snooping: Preventing Rogue DHCP Servers
Rogue DHCP Server Protection: DHCP Snooping Preventing on Networks
In the realm of network security, safeguarding against unauthorized access and malicious activities is paramount. DHCP snooping emerges as a critical layer 2 security feature on Cisco networks. It is designed to mitigate the risks associated with rogue DHCP servers and DHCP spoofing, ensuring that only authorized DHCP servers assign IP addresses within the network. This article delves into the intricacies of DHCP snooping, exploring its functionality, configuration, and importance in maintaining network integrity.
Understanding DHCP Snooping
What is DHCP Snooping?
DHCP snooping is a security feature implemented on network switches, particularly Cisco switches, that acts as a security guard for DHCP traffic. Its primary goal is to prevent rogue DHCP servers from operating on the network. A rogue DHCP server is an unauthorized DHCP server that may be introduced by an attacker. DHCP snooping works by filtering DHCP messages, allowing only authorized DHCP servers to respond to DHCP requests from DHCP clients. This prevents unauthorized DHCP servers from assigning IP addresses, gateway information, and DNS server settings, which could lead to a man-in-the-middle attack or other malicious activities.
How DHCP Snooping Works
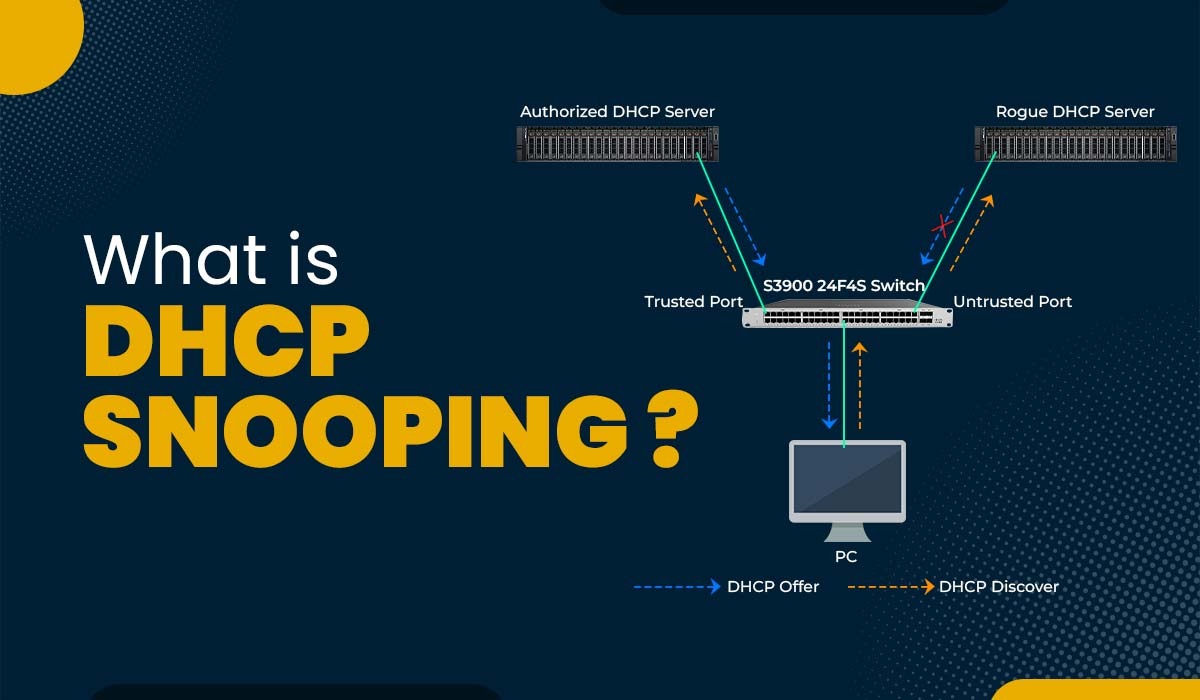
DHCP snooping works by categorizing switch ports into trusted ports and untrusted ports. Trusted ports are connected to authorized DHCP servers, DHCP relay agents, or other network devices that are permitted to send DHCP responses. Untrusted ports, on the other hand, are typically connected to end-user devices or network segments where rogue DHCP servers might be present. When a DHCP offer or other DHCP responses are received on an untrusted port, DHCP snooping intercepts and drops the DHCP packets, preventing them from reaching the DHCP client. This ensures that only legitimate DHCP server responses are processed, safeguarding the network from IP address conflicts and malicious configurations.
Importance of DHCP Snooping in Network Security
The importance of DHCP snooping in network security cannot be overstated. Without DHCP snooping, a network is vulnerable to various attacks, including DHCP spoofing and DHCP starvation attacks. DHCP spoofing involves an attacker setting up an unauthorized DHCP server to distribute incorrect IP address information, potentially redirecting traffic or capturing sensitive data. DHCP starvation attacks, on the other hand, flood the legitimate DHCP server with DHCP requests, exhausting the available IP address pool and causing denial of service for legitimate users. DHCP snooping helps to prevent rogue DHCP servers, ensuring that only authorized DHCP servers assign IP addresses, thus maintaining network stability and security. By implementing DHCP snooping, network administrators can effectively block DHCP attacks and protect their networks from malicious activities.
Common Attacks on DHCP
DHCP Spoofing
DHCP spoofing is a common server attack where an attacker deploys an unauthorized DHCP server on the network to distribute incorrect IP addresses. This malicious DHCP server can assign IP addresses, default gateways, and DNS server settings that redirect network traffic through the attacker’s machine, enabling a man-in-the-middle attack. DHCP snooping helps mitigate DHCP spoofing by ensuring that only legitimate DHCP servers can assign IP addresses, effectively preventing rogue DHCP servers from hijacking network configurations.
DHCP Starvation Attack
A DHCP starvation attack involves an attacker flooding the legitimate DHCP server with a deluge of DHCP requests, rapidly depleting the available IP address pool. Once the DHCP pool is exhausted, legitimate DHCP clients are unable to obtain IP addresses, leading to a denial of service. DHCP snooping can prevent DHCP starvation attacks by limiting the rate of DHCP requests from untrusted ports, thus preventing rogue DHCP clients from monopolizing the IP address resources. By controlling DHCP traffic, DHCP snooping helps maintain network availability and prevents unauthorized devices from disrupting network services.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Man-in-the-middle attacks occur when an attacker intercepts network traffic between a client and a server, allowing the attacker to eavesdrop on or manipulate the data being transmitted. Rogue DHCP servers can facilitate man-in-the-middle attacks by assigning the attacker’s machine as the default gateway or DNS server. DHCP snooping helps to prevent rogue DHCP servers from distributing malicious network configurations. By ensuring only authorized DHCP servers assign IP addresses, DHCP snooping minimizes the risk of traffic redirection and protects sensitive data from falling into the wrong hands, thus enhancing overall network security.
Configuring DHCP Snooping on Cisco Switches
Enabling DHCP Snooping
To enable DHCP snooping on a Cisco switch, use the global configuration command ip dhcp snooping. This command activates the DHCP snooping feature on the switch, allowing it to begin filtering DHCP messages based on the trust status of the ports. Enabling DHCP snooping is the first step in securing the network against rogue DHCP servers. Once enabled, the switch begins building the DHCP binding table, which tracks the association between IP addresses, MAC addresses, and VLANs. By using the ip dhcp snooping command, you ensure your network is protected by DHCP snooping.
Configuring DHCP Snooping on VLANs
DHCP snooping can be configured on a per-VLAN basis to provide more granular control over DHCP traffic. To configure DHCP snooping on a specific VLAN, use the command ip,dhcp snooping vlan<vlan-id>. This command restricts DHCP snooping to the specified VLAN, allowing you to selectively enable DHCP snooping on different parts of the network. By configuring DHCP snooping on VLANs, you can tailor the security policy to match the network segmentation, providing better protection against unauthorized DHCP servers. By enabling this on the right VLANs, you make sure dhcp traffic is safe.
Setting Up Trust and Untrust Ports
Configuring trust and untrust ports is a crucial step in the DHCP snooping configuration process. Trusted ports are connected to legitimate DHCP servers or DHCP relay agents, while untrusted ports are connected to end-user devices or network segments where rogue DHCP servers might be present. To configure a port as trusted, use the interface configuration command ip dhcp snooping trust. This command tells the switch to forward all DHCP messages received on that port without filtering. Ports are untrusted by default. By correctly configuring trust and untrust ports, you ensure that only authorized DHCP servers can respond to DHCP requests, preventing rogue DHCP servers from assigning IP addresses.
Preventing Rogue DHCP Servers
Identifying Rogue DHCP Servers
Identifying a rogue DHCP server on the network requires vigilance and the use of network monitoring tools. Network administrators can use packet capture software to analyze DHCP traffic and identify unauthorized DHCP servers issuing IP addresses. Examining the DHCP offer messages can reveal discrepancies in the provided gateway or DNS server settings. Regularly monitoring the network for unexpected DHCP servers is crucial for maintaining network security and preventing man-in-the-middle attack scenarios.
Using DHCP Option 82
DHCP option 82, also known as the DHCP relay agent information option, enhances DHCP snooping by providing additional information about the DHCP client’s location. DHCP option 82 inserts information into the DHCP request, such as the switch port and VLAN from which the DHCP request originated. This information can be used to enforce more granular security policies and prevent rogue DHCP servers from assigning IP addresses. Configuring DHCP option 82 is one way of configuring DHCP snooping to secure a network.
Dynamic ARP Inspection for Additional Security
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) complements DHCP snooping by preventing ARP spoofing attacks, which can be used to bypass DHCP snooping. DAI validates ARP packets against the DHCP binding table to ensure that only legitimate IP address-to-MAC address bindings are allowed. By combining DAI with DHCP snooping, network administrators can create a more robust security posture, effectively blocking unauthorized access and preventing rogue DHCP servers from compromising the network. This can prevent rogue DHCP servers in a network.
Monitoring and Managing DHCP Security
Understanding the DHCP Binding Table
The DHCP binding table is a crucial component of DHCP snooping, as it stores the mappings between IP addresses, MAC addresses, VLANs, and associated switch ports. This table is dynamically built as DHCP clients receive IP addresses from authorized DHCP servers. Regularly reviewing the DHCP binding table can help identify unauthorized or suspicious entries, indicating the presence of rogue DHCP servers or DHCP spoofing attempts. Understanding the DHCP binding table is essential for effective network security management.
Blocking Unauthorized DHCP Offers
DHCP snooping effectively blocks DHCP offers from unauthorized DHCP servers by inspecting all DHCP messages traversing the network switches. When a DHCP offer is received on an untrusted port, DHCP snooping drops the DHCP packets, preventing the rogue server from assigning IP addresses. Configuring trusted ports ensures that only legitimate DHCP server responses are processed, thus maintaining network integrity. By blocking unauthorized DHCP offers, DHCP snooping prevents rogue DHCP servers from disrupting network services and compromising network security.
Regular Security Audits for DHCP Configuration
Regular security audits of the DHCP snooping configuration are essential for ensuring its effectiveness and identifying potential vulnerabilities. These audits should include reviewing the trusted and untrusted port settings, verifying the DHCP snooping configuration on each VLAN, and examining the DHCP binding table for anomalies. Additionally, ensure that any routers in your network are not acting as a DHCP server. Regularly updating the DHCP snooping configuration based on the latest security best practices helps maintain a robust defense against rogue DHCP attacks and enhances overall network security.
IP DHCP snooping: What is DHCP snooping and how does it prevent rogue DHCP servers?
DHCP snooping is a layer 2 security feature that monitors DHCP server messages and filters untrusted DHCP traffic to prevent fake DHCP servers from handing out IP addresses to clients. By building a binding table of legitimate ip assignments (MAC, IP, VLAN, lease time and port), dhcp snooping helps prevent attacks like rogue devices offering incorrect network configuration or rogue ip assignments that can lead to mitm attacks. Implementing dhcp snooping means marking trusted ports (where legitimate dhcp server or router/gateway reside) and untrusted ports (access ports) so only trusted dhcp server messages are accepted.
IP: How do I verify DHCP snooping status with show IP DHCP snooping?
Use the command show ip dhcp snooping to display current dhcp snooping configuration, the VLANs being snooped, the size of the binding database, and any offline or active entries. This output helps you understand how dhcp snooping is behaving in your network environment and confirms which ports are trusted for legitimate dhcp server messages and which are untrusted.
VLAN: How does VLAN configuration affect dhcp snooping and client IP assignment?
DHCP snooping works per VLAN: you enable ip dhcp snooping for specific VLANs so the switch tracks dhcp discover message traffic and server replies only within those VLANs. The binding table stores ip addresses to clients per VLAN, ensuring that DHCP offers and replies are limited to the correct network segment and preventing fake dhcp servers from servicing devices in other VLANs.
Router: Do I need to configure the router or gateway when implementing dhcp snooping?
Yes. The gateway or router often hosts legitimate dhcp server functionality or forwards DHCP requests. You must ensure the router/gateway interface connected to the switch is marked as trusted so legitimate dhcp server messages are allowed. Also coordinate any relay or helper-address settings on the router so dhcp discover and offer messages flow correctly and aren’t blocked by snooping rules.
Untrusted: What are untrusted ports and why are they important for preventing server attack?
Untrusted ports are switch ports where client devices or potential rogue devices connect; by default these ports are configured as untrusted. DHCP snooping blocks any DHCP server messages received on untrusted ports, preventing fake dhcp servers from responding to dhcp discover messages. This reduces the risk of attacks like MITM attacks and other network attacks that rely on rogue DHCP behavior.
Legitimate DHCP server: How do I designate a legitimate dhcp server so it isn’t blocked?
Designate the switch port connected to your legitimate dhcp server or to the router offering DHCP as a trusted port in the dhcp snooping configuration. This allows DHCP server messages (offers, acknowledgements) to pass. You should also verify bindings with show ip dhcp snooping and ensure any DHCP relay paths are trusted so the network infrastructure recognizes the legitimate dhcp server and honors ip addresses to clients properly.
DHCP snooping configuration: What other protections work with dhcp snooping, such as ip source guard?
DHCP snooping pairs well with features like ip source guard and Dynamic ARP Inspection. ip source guard uses the dhcp snooping binding table to filter traffic from devices that try to use an IP not assigned to their MAC, blocking spoofed or rogue ip assignments. Dynamic host configuration protocol protections combined with dhcp snooping help prevent attacks like fake dhcp servers and other network attacks that target devices on the network.
Implementing DHCP snooping: What common pitfalls should I avoid when implementing dhcp snooping?
Common pitfalls include forgetting to mark the router or gateway interface as trusted, enabling snooping on the wrong VLANs, not accounting for DHCP relays (dhcp discover messages forwarded by helper-address), and failing to size the binding database. Also watch for legitimate services that might behave like rogue devices and ensure show ip dhcp snooping reveals expected bindings. Proper planning of trusted dhcp ports and testing reduces the chance of inadvertently blocking legitimate dhcp server messages.