How to Perform a Penetration Test
How to Perform a Penetration Test: Process, Types, and Key Cyber Security Tools
In today’s complex digital landscape, ensuring robust cyber security is paramount. A penetration test, often called a pen test, is a crucial security assessment method. It helps organizations identify security vulnerabilities before malicious attackers can exploit them. This article will delve into the penetration testing process, the various types of penetration testing, and the key cyber security tools used by security professionals.
Understanding Penetration Testing
What is a Penetration Test?
A penetration test, or pen test, is a simulated cyber attack performed on a target system to evaluate its security posture. The goal of a pen test is to The team will identify and exploit security vulnerabilities that could be present in web applications, networks, or other systems, as part of the purpose of penetration testing.. A penetration tester, also known as a pen tester or ethical hacker, uses various testing tools and techniques to simulate real-world attacks, seeking to gain access to sensitive data or disrupt normal operations. The insights gained from the pen test are then documented in a penetration test report, which provides actionable recommendations to improve security measures.
Importance of Cyber Security in Penetration Testing
Cyber security is fundamental to the penetration testing process. The primary aim of a pen test is to strengthen an organization’s security posture by uncovering security flaws and weaknesses. A penetration test can help in identifying vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches, financial losses, or reputational damage. By simulating cyber attacks, penetration testing services enable organizations to understand how attackers might exploit vulnerabilities in their web application security, network security, and other critical systems. Proactive security testing through penetration tests ensures that security controls are effective and that the organization’s information security is maintained, underscoring the purpose of penetration testing.
Key Terminology in the Pen Testing Process
Understanding the key terminology is crucial in the penetration testing process. Several key terms related to the purpose of penetration testing are worth defining:
- A vulnerability A security vulnerability refers to a weakness in a system that an attacker can exploit, highlighting the purpose of penetration testing.
- An exploit is a technique or tool used to take advantage of a vulnerability to gain access to a system or data.
Reconnaissance involves gathering information about the target system before launching an attack. Social engineering is a type of attack that relies on manipulating individuals to divulge sensitive data. Types of penetration testing include black box, white box, and grey box tests, each offering different levels of information about the target system to the testing team.
Types of Penetration Testing
Black Box Penetration Testing
Black box penetration testing is a type of penetration test where the penetration testing team has no prior knowledge of the target system. This type of pen test simulates an external attacker attempting to gain access to a network or web application with limited information. The penetration tester must perform reconnaissance to gather information about the target system, identify security vulnerabilities, and then attempt to exploit them. This method effectively assesses how well an organization’s security measures stand up against unknown threats, making it a valuable security assessment technique.
White Box Penetration Testing
In contrast to black box testing, white box penetration testing provides the penetration testing team with complete knowledge of the target system’s infrastructure, code, and architecture. With this information, the penetration tester can conduct a thorough analysis to identify security vulnerabilities that might be difficult to detect otherwise. White box testing allows for a more in-depth assessment of the application security and network security, helping the security team pinpoint specific weaknesses and develop targeted security controls. This type of pen test is particularly useful for identifying internal vulnerabilities and ensuring robust security measures.
Internal Penetration Testing
Internal penetration testing assesses security vulnerabilities from within the organization’s network. This type of penetration test simulates an insider threat, such as a disgruntled employee or a compromised user account, to identify potential security flaws. By conducting internal penetration, the penetration tester can evaluate the effectiveness of internal security controls and policies. Addressing vulnerabilities through a successful penetration test can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and help maintain robust information security, and supports employees’ personal and professional growth through a robust internal network infrastructure.
Network Penetration Test
A network penetration test focuses specifically on identifying security vulnerabilities within an organization’s network infrastructure. The penetration testing process includes scanning network devices, servers, and other systems to detect weaknesses that an attacker could exploit, ensuring the test is complete. A network penetration test can help in identifying misconfigurations, outdated software, and other security flaws that could lead to a breach. By simulating cyber attacks on the network, security professionals can help organizations improve their network security and prevent unauthorized access, a critical purpose of penetration testing.
Web Application Penetration Testing
Web application penetration testing involves assessing the security posture of web applications to identify vulnerabilities. These types of pen test covers a range of security flaws, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other common web application security issues. The penetration testing team uses specialized testing tools and techniques to simulate real-world attacks and attempt to exploit vulnerabilities. Through web application penetration testing, organizations can ensure that their web applications are secure and that sensitive data is protected from cyber threats.
Social Engineering in Pen Tests
Social engineering is a type of pen test that relies on manipulating individuals to divulge sensitive information or perform actions that compromise security. In a social engineering attack, an attacker might use phishing emails, phone calls, or other tactics to trick employees into revealing passwords or granting access to systems. Social engineering can be a highly effective method for gaining access to an organization’s network or data. Therefore, a penetration test may incorporate social engineering to evaluate an organization’s susceptibility to such attacks.
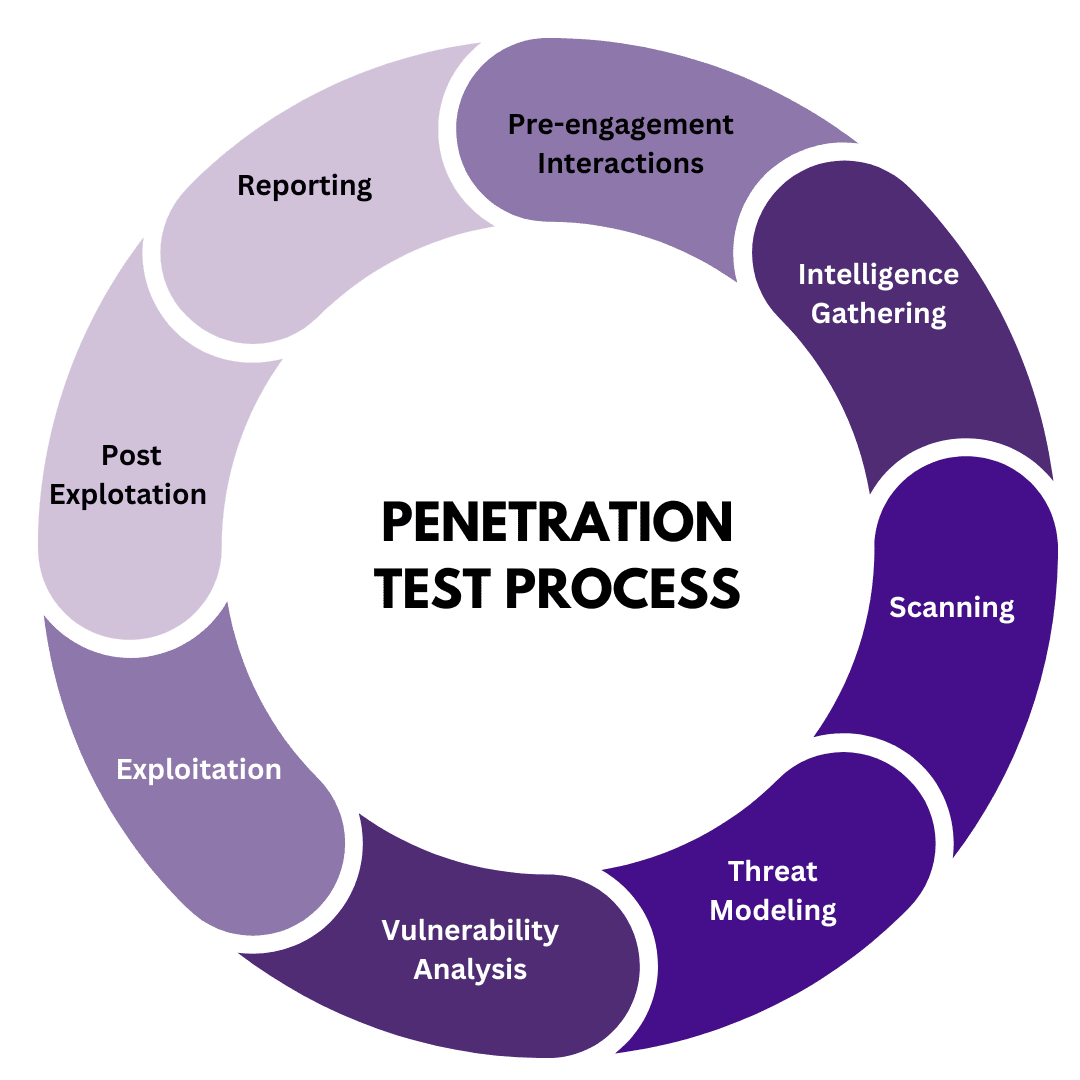
The Penetration Testing Process
Planning and Scope Definition
The initial stage of the penetration testing process is critical. It involves defining the scope and objectives of the penetration test. This includes identifying the target system, determining the types of penetration testing to be performed, and establishing clear boundaries for the pen test. The planning phase ensures that the penetration test aligns with the organization’s security goals and that the penetration testing team understands the specific assets and vulnerabilities to be assessed. Proper planning is essential for a successful penetration test.
Information Gathering
Once the scope is defined, the penetration testing team proceeds with information gathering, also known as reconnaissance. This involves collecting as much information as possible about the target system. This information can be gathered through various means, including open-source intelligence, network scanning, and social engineering. The goal is to identify potential security vulnerabilities and gain a better understanding of the target system’s security posture. Effective reconnaissance is vital for the penetration tester to simulate real-world cyber attacks.
Vulnerability Assessment
Following information gathering, the penetration testing team conducts a vulnerability assessment to ensure the test is complete. This involves analyzing the collected information to identify potential security vulnerabilities in the target system. The penetration tester utilizes various testing tools and techniques to scan for vulnerabilities in web application security, network security, and other critical systems. The vulnerability assessment helps prioritize which vulnerabilities to exploit during the next phase of the penetration test. Expert Network Security Assessment includes analysis and identification of security vulnerabilities.
Exploitation Phase
In the exploitation phase, the penetration tester attempts to exploit the identified security vulnerabilities to gain access to the target system. This phase involves using various exploits and testing tools to simulate real-world cyber attacks. If the penetration test is successful, the penetration testing team can gain access to sensitive data or disrupt normal operations. The exploitation phase demonstrates the potential impact of the identified vulnerabilities and highlights the importance of implementing effective security controls.
Reporting and Remediation
The final stage of the penetration testing process is reporting and remediation, confirming that the test is complete. After completing the penetration test, the penetration testing team prepares a comprehensive penetration test report that details the identified security vulnerabilities, the methods used to exploit them, and the potential impact on the organization. The penetration test report also provides actionable recommendations for remediation to improve the organization’s security posture once the test is complete. Addressing these security flaws helps to bolster information security and defend against future attacks.
Key Tools for Penetration Testing
Popular Penetration Testing Tools
The market offers a plethora of penetration testing tools to aid the penetration tester in their simulated cyber attacks. These penetration testing tools range from vulnerability scanners to exploit frameworks, each designed to identify and exploit specific security vulnerabilities. Some popular examples include:
- Metasploit
- Nmap
- Wireshark
- Burp Suite
The penetration testing team leverages these tools to perform reconnaissance, conduct vulnerability assessments, and gain access to target systems, ensuring a comprehensive security assessment. The choice of testing tools depends on the type of penetration test and the target system’s complexity.
Testing Tools for Network Penetration
Network penetration tests require specialized testing tools to assess network security effectively. To illustrate, consider the following examples:
- Nmap is essential for network scanning, helping the penetration tester discover open ports, services, and operating systems running on the target system.
- Wireshark is used for network packet analysis, allowing the penetration testing team to capture and analyze network traffic to identify security vulnerabilities.
These penetration testing tools enable the penetration testing team to simulate network attacks and identify weaknesses in network security controls, ultimately enhancing the organization’s network security posture. This type of pen test ensures robust security measures are in place.
Web Application Testing Tools
Web application security demands specialized tools designed to identify web application security vulnerabilities. Burp Suite is a popular choice among security professionals for web application pen tests, offering features like proxying, scanning, and intrusion testing. OWASP ZAP is another widely used open-source web application security testing tool. These penetration testing tools assist the penetration testing team in identifying security flaws such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other common web application security issues. By using these tools, the penetration testing team can enhance web application security, which serves the purpose of penetration testing.
Benefits of Conducting Penetration Tests
Identifying Vulnerabilities
One of the foremost benefits of conducting a penetration test is the identification of security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious attackers. A penetration test’s thorough security assessment process helps uncover weaknesses in web application security, network security, and other critical systems. By identifying these security flaws, organizations can proactively address them, preventing potential data breaches and financial losses, which is a key purpose of penetration testing. Expert Network Security Assessment includes analysis and identification of security vulnerabilities and helps in prioritizing remediation efforts to enhance overall security posture.
Enhancing Cyber Security Posture
Regular penetration testing significantly enhances an organization’s cyber security posture. By simulating cyber attacks, a penetration test provides valuable insights into how an attacker might exploit security flaws in the system. This allows the security team to strengthen security controls, patch vulnerabilities, and improve incident response capabilities. Penetration testing services also help organizations understand their attack surface and prioritize security investments effectively, leading to a more resilient and robust information security framework and ensuring that the target system remains secure against potential threats and evolving attack vectors.
Meeting Compliance Requirements
Many industries and regulatory bodies require organizations to conduct regular penetration testing to ensure compliance with security standards and regulations. Penetration tests provide evidence that an organization is taking proactive steps to protect sensitive data and maintain a strong security posture. Meeting these compliance requirements not only helps organizations avoid penalties but also demonstrates a commitment to information security and builds trust with customers and stakeholders. Cloud Security & Regulatory Assurance services are dedicated to securing cloud-based operations and ensuring adherence to relevant regulatory requirements.
5 Surprising Facts About Penetration Testing
- Penetration testing is as much about people and processes as it is about technology. Many successful engagements reveal that weak policies, misconfigurations, or human error are the real entry points — technical vulnerabilities often only matter when organizational practices allow them to be exploited.
- Legal and contractual boundaries matter more than technical skill. A technically skilled tester can cause major disruption or legal exposure if they operate outside an agreed scope. Clear authorization, rules of engagement, and communication channels are often the most critical elements of a safe engagement.
- Surprising results frequently come from low-tech methods. Simple techniques like analyzing public information, misconfigured cloud storage, or expired certificates repeatedly expose sensitive data — often more so than complex exploits.
- Regular testing improves security posture more than one-off high-effort tests. Continuous assessments, bug bounty programs, and red-team/blue-team exercises tend to yield cumulative improvement, uncovering drift and regressions that a single annual test can miss.
- Penetration tests can reveal business risks beyond technical breaches. Findings often point to operational, reputational, and compliance risks (for example, exposure of customer data, interruption of critical services, or regulatory gaps) that require cross-functional remediation, not just code fixes.
What is a type of pen test and how does it fit into testing methodologies?
A type of pen test refers to the specific focus or approach used during an engagement, such as network, web application, mobile, wireless, or physical security assessments. These tests follow established testing methodologies—like OWASP for web apps, PTES, or NIST guidance—to ensure consistent phases of penetration testing, repeatable processes, and clear reporting. Understanding the type of testing helps define the scope of a penetration test and align the work with the organization’s current security and security strategy.
Who is a pen tester and what qualifications should a penetration tester have?
A pen tester (penetration tester) is a security professional who simulates cyber attacks to find security weaknesses. Effective penetration practitioners typically have experience in testing methodologies, familiarity with pen testing tools, knowledge of information security fundamentals, and certifications such as OSCP, CEH, or CREST. A qualified tester also understands the scope of the test, legal constraints, and can advise on remediation to improve existing security and reduce the risk of security breaches.
What penetration testing services are available and how do I choose a testing provider?
Penetration testing services range from automated vulnerability scans and web app assessments to targeted red team engagements and physical security tests. When choosing a testing provider, consider the provider’s expertise in specific test performed, their use of pen testing tools, whether they support automated testing and manual exploitation, and their ability to map results to your security strategy. Verify experience with relevant compliance frameworks such as Payment Card Industry Data Security (PCI DSS) if card industry data security is in scope, as this testing can also impact compliance.
What are the benefits of penetration testing for my organization?
Benefits of penetration testing include discovering security weaknesses before attackers do, validating existing security controls, improving incident response, and supporting compliance requirements. Regular testing helps find security gaps in networks, applications, and physical security, supports a proactive security strategy, and demonstrates to stakeholders that penetration testing helps reduce the likelihood of security breaches and protects data security and privacy.
How do exploit techniques and pen testing tools factor into a penetration test?
Exploit techniques are the methods a penetration tester uses to validate a vulnerability by attempting to gain unauthorized access or escalate privileges. Pen testing tools—both automated testing solutions and manual toolkits—help identify vulnerabilities, craft exploits, and document findings. A mix of automated testing and manual exploitation is often necessary to confirm real-world risk and avoid false positives, and to ensure the test begins with accurate reconnaissance and proceeds through the defined phases of penetration testing.
What are the phases of penetration testing and when does the test begin and end?
Typical phases of penetration testing include planning and scoping, information gathering, threat modeling and vulnerability analysis, exploitation, post-exploitation and persistence, and reporting with remediation recommendations. The test begins once the scope of the test and rules of engagement are agreed, and it is complete when deliverables include a prioritized list of findings, evidence, and guidance to improve current security. Follow-up retesting may be scheduled to confirm fixes.
How do you define the scope of a penetration test to align with my security strategy?
The scope of a penetration test should define assets to be tested, test performed (external, internal, web app, mobile, wireless, physical), depth of exploitation permitted, and success criteria, ensuring the purpose of penetration testing is met. Aligning the scope with your security strategy and regulatory needs ensures testing targets the most critical systems, protects sensitive data security, and balances risk with operational impact. Clear scoping also guides selection of testing methodologies and the testing provider.
Can penetration testing be automated and what are the limits of automated testing?
Automated testing uses scanners and tools to quickly identify common vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, which is useful for baseline assessments and regular checks, ensuring the testing can also be efficient. However, automated testing cannot replicate creative adversary behavior, complex exploit chains, or nuanced business logic flaws. Effective penetration testing combines automated testing with manual analysis and exploitation to find deep security weaknesses and simulate realistic cyber attacks.
How does penetration testing help with compliance and payment card industry data security?
Penetration testing helps demonstrate compliance by identifying weaknesses that could lead to security breaches and by verifying controls required by standards such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Tests performed against cardholder systems should be scoped appropriately, use accepted testing methodologies, and be conducted by qualified testers to ensure findings are actionable and to support remediation that protects card industry data security and customer privacy.